Net Ionic Equations
advertisement

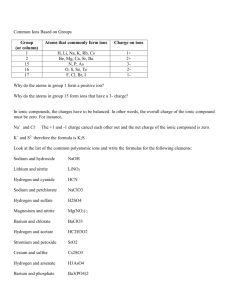
Net Ionic Equations Context • Some things are soluble, some are not • Ionic compounds dissociate into ions • Precipitates can be formed if a combination of ions results in an insoluble compound • How do we show this? Ions in Solution In aqueous solutions, ionic compounds dissociate into their ions. E.g. Sr(NO3)2(aq) → Sr2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Some combinations of ions result in a precipitate. It is these ions ONLY that are actually reacting Total ionic equations show all dissociated ions of soluble ionic compounds. Spectator ions are ions that remain in solution (do not form a precipitate) and therefore are not involved in a chemical reaction. Net ionic equations show only ions involved in a chemical reaction (I.e. spectator ions are NOT included) An Example The reaction between aqueous sodium chloride & silver nitrate. Chemical Equation: NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) Total Ionic Equation: Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + AgCl(s) Net ionic Equation: Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl(s) Another Example The reaction between potassium carbonate & barium nitrate. Chemical Equation: K2CO3 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) ? K2CO3 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) 2 KNO3 (aq) + BaCO3 (s) Total Ionic Equation: 2 K+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) 2 K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + BaCO3(s) Net ionic Equation: Ba2+ + CO32- BaCO3(s) • By predicting if a product will make a precipitate, you can calculate how much is produced • Precipitation reactions can also be used to test for the presence of certain ions in an unknown solution • This is called qualitative analysis Qualitative Analysis 1. Solution Colour – The identity of a metal ion can be inferred by the colour of the aqueous solution it forms Ion Solution Colour Cu2+ blue Co2+ pink Ni2+ green MnO4 purple Alkali Metals colourless 2. Flame Test – The identity of a metal (atom or ion) can be inferred by the colour of the flame containing the metal Metal Flame Colour Li+ red Na+ yellow K+ violet Cu2+ Blue-green Sr2+ red http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1EXr_L7Ojqg 3. Sequential Analysis – Unknown aqueous ions can be identified by testing the solubility, by adding ions known to form low solubility products – More than one test can be done in sequence to identify more than one ion Sequential Analysis aqueous solution possibly containing: Ag+, Pb2+, Sr2+ (only possibilities) + NaC2H3O2 (aq) ppt contains: Ag+ filter does not contain Ag+ ppt test filtrate contains: Pb2+ filter no ppt no ppt ppt + NaCl(aq) no ppt does not contain: Pb2+ ppt test no ppt filtrate ppt contains: Sr2+ + Na2CO3(aq) no ppt does not contain: Sr2+ Practice • worksheet