Brain Day 1
advertisement

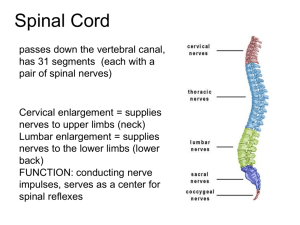
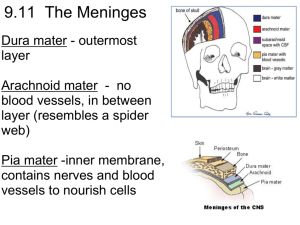
The Brain Greater than the sum of its parts Sensory receptors • Specialized to respond to changes in the environment (stimuli) types of sensory neurons • Mechanoreceptors: touch, pressure, vibration, stretch and itch • Thermoreceptors: temperature changes • Photoreceptors: light energy • Chemoreceptors: chemicals in solution, smell, taste, blood chemistry • Nocioceptors: damaging stimuli that result in pain Spinal nerves • Nerve pairs that arrive from the spinal cord Cranial nerves • Nerve pairs that arise from brain All feed into here… Like a mushroom Four Major Divisions • • • • Cerebrum Cerebellum Diencephalon Brain Stem • P449 of text – overview of each area’s function Gross Anatomy • Elevated ridge: gyrus (plural = gyri) • Groove/furrow: sulcus (sulci) • Deeper grooves = fissures • Landmarks – same in all people Longitudinal fissure Lateralization = specialization of each hemisphere Sheep Brain Dissection • External Anatomy today: (each person) – Draw a top view, side view, and underneath view – Label: transverse fissure, longitudinal fissure – Label: brain stem, cerebrum, cerebellum – Label: Spinal cord, medulla oblongata, pons – Label: example of a gyrus, example of a sulcus Corpus Callosum • Axons connecting the hemispheres • Pathway for communication Brain Stem = highway The cerebrum • 80% of the brain’s mass • Divided into section based on the major landmarks – sulci and fissures Named for the parts of the skull they sit under gray and white matter • Gray Matter – Top outermost portion of the cerebrum = cerebral cortex – Cell bodies and interneurons • White matter – Bulk of cerebrum – Myelinated axons • Dissection continued… What does the brain do? Electrical and magnetic detection • • • • Electroencephalogram (EEG) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) Positron emission Tomography (PET) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) • Uses electrodes to measure electrical activity (impulses) Electroencephalogram (EEG) EEG Recording from multiple places Using a needle electrode: record directly from surface of brain Patient is still awake and talking Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) • NOVA Now segment • Using a magnet to alter the electrical messages of the brain Positron emission Tomography (PET) • Measures blood flow • Inject radioactive material • Detect the decay • • Same amount of env. radiation that you’d be exposed to in 3 years’ time Short lifespan, cleared quickly by body MRI • Use a magnetic field to excite electrons in your body = produce radio waves • radio waves are measured and analyzed by a computer fMRI • Looking at oxygen levels • More oxygen = more activity • A strong magnetic field is created by passing an electric current through the wire loops. While this is happening, other coils in the magnet send and receive radio waves. This triggers protons in the body to align themselves. Once aligned, radio waves are absorbed by the protons, which stimulate spinning. Energy is released after "exciting" the molecules, which in turn emits energy signals that are picked up by the coil. This information is then sent to a computer which processes all the signals and generates it into an image. The final product is a 3-D image representation of the area being examined. • Sensory information communicated to brain (via spine)* • Brain = interneurons • Generates a motor response – delivery • * spinal reflex = bypasses brain involvement