1st Semester Final Review
advertisement

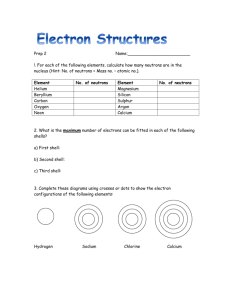
Use these slides to quiz your knowledge of 1st Semester Stuff!! The first slide is the “quiz” the slide that follows you will find the answers Sig Figs How many sig figs? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.751 g 0.157 kg 28.0 mL 2500 m 0.0067 g Sig Figs How many sig figs? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.751 g 0.157 kg 28.0 mL 2500 m 0.0067 g 4 3 3 2 2 **Click for a tutorial video on Sig Figs To Review Sig Fig Rules see “Problem-Solving Strategy” p. 51 in Red Book Periodic Table Stuff Atomic number = position on table (what does the number tell you?) Atomic mass – what makes up this mass Isotopes – What are they? Periodic Table Stuff Atomic number = position on table (what does the number tell you?) The number of protons in the nucleus Also, ID’s the element on the periodic table Atomic mass – what makes up this mass Number of protons + number of neutrons Isotopes – What are they? Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons Element, Compound & Mixtures? Indicate which of the following is an element, compound, heterogeneous mixture or solution: 1. Ocean water 2. Calcium 3. Vitamin C 4. Dry ice (solid CO2) 5. Copper 6. Grain alcohol 7. After-shave lotion Element, Compound & Mixtures? Indicate which of the following is an element, compound, heterogeneous mixture or solution: 1. Ocean water heterogeneous mixture 2. Calcium element 3. Vitamin C compound 4. Dry ice (solid CO2) compound 5. Copper element 6. Grain alcohol solution or compound 7. After-shave lotion solution Physical & Chemical Properties Classify each as a chemical or physical property: 1. Reacts with water 2. Is red 3. Conducts electricity 4. Resists corrosion 5. Boils at 88oC 6. Is 1.5 m long Physical & Chemical Properties Classify each as a chemical or physical property: 1. Reacts with water chemical 2. Is red physical 3. Conducts electricity physical 4. Resists corrosion chemical 5. Boils at 88oC physical 6. Is 1.5 m long physical Solute, Solvent & Precipitate Salt water: What is the solute? What is the solvent? What is a precipitate? Solute, Solvent & Precipitate Salt water: What is the solute? What is the solvent? Salt = solute Water = solvent What is a precipitate? A solid produced during a chemical reaction Naming – Writing Formulas Write the formulas for the following: 1. Lithium fluoride 2. Calcium oxide 3. Barium hydroxide 4. Sodium sulfate 5. Potassium perchlorate 6. Magnesium sulfite 7. Calcium hypophosphite 8. Hydrochloric acid 9. Nitric acid 10. Manganese (III) chloride Naming – Writing Formulas Write the formulas for the following: 1. Lithium fluoride LiF 2. Calcium oxide CaO 3. Barium hydroxide Ba(OH)2 4. Sodium sulfate Na2SO4 5. Potassium perchlorate KClO4 6. Magnesium sulfite MgSO3 7. Calcium hypophosphite Ca3(PO2)2 8. Hydrochloric acid HCl (aq) 9. Nitric acid HNO3 (aq) 10. Manganese (III) chloride MnCl3 Naming – Writing Names Name the following compounds: 1. Fe2(SO4)3 2. KNO2 3. KClO3 4. CuCl 5. PbI2 6. NiBr2 7. Hg(IO3)2 8. NO2 9. H3PO4 (aq) 10. H2SO4 (aq) Naming – Writing Names Name the following compounds: 1. Fe2(SO4)3 Iron (III) Sulfate 2. KNO2 Potassium Nitrite 3. KClO3 Potassium chlorate 4. CuCl Copper (I) chloride 5. PbI2 Lead (II) iodide 6. NiBr2 Nickel (II) bromide 7. Hg(IO3)2 Mercury (II) iodate 8. NO2 Nitrogen dioxide 9. H3PO4 (aq) Phosphoric acid 10. H2SO4 (aq) Sulfuric acid Balancing Equations Balance the following: Mg + O2 MgO 2. Al + Pb(NO3)2 Al(NO3)3 + Pb 3. Chlorine + magnesium iodide magnesium chloride + iodine 4. Zinc + sulfuric acid zinc sulfate + hydrogen 1. Balancing Equations Balance the following: Mg + O2 MgO 2Mg + O2 2MgO Al + Pb(NO3)2 Al(NO3)3 + Pb 2Al + 3Pb(NO3)2 2Al(NO3)3 +3 Pb Chlorine + magnesium iodide magnesium chloride + iodine Cl2 + MgI2 MgCl2 + I2 Zinc + sulfuric acid zinc sulfate + hydrogen Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 Calculate the Formula Mass Calculate the formula mass or molecular mass: 1. H2SO4 2. Fe(CH3COO)3 Calculate the mass in grams **The only difference between calculating formula mass and mass in grams is the units. The procedure is the same. Calculate the Formula Mass Calculate the formula mass or molecular mass: 1. H2SO4 1. (2 x 1.01) + 32.1 + (4 x 16) = 98.12 g Fe(CH3COO)3 55.8 + (6 x 12.0) + (9 x 1.01) + (6 x 16.0) = 232.89 Calculate the mass in grams **The only difference between calculating formula mass and mass in grams is the units. The procedure is the same. Percent Composition calculate the percentage of nitrogen in ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, an important source of nitrogen in fertilizers. Calculate the percent compositions of the following: Fe2O3 Ag2O Percent Composition Answer calculate the percentage of nitrogen in ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, an important source of nitrogen in fertilizers. Percent Composition Answer Fe2O3 Empirical & Molecular Formula Determine the empirical formula for sodium sulfite. Sodium sulfite contains 36.5% sodium, 25.4% sulfur, and 38.1% oxygen. An organic compound is found to contain 92.25% carbon and 7.75 % hydrogen. If the molecular mass is 78.0 grams, what is the molecular formula? (not on test) A hydrated compound has an analysis of 18.29 % Ca, 32.37% Cl, and 49.34% H2O. What is its formula? Empirical & Molecular Formula Determine the empirical formula for sodium sulfite. Sodium sulfite contains 36.5% sodium, 25.4% sulfur, and 38.1% oxygen. Empirical & Molecular Formula A hydrated compound has an analysis of 18.29 % Ca, 32.37% Cl, and 49.34% H2O. What is its formula? Electron Configuration Write the electron configurations of the following elements: 1. Sulfur 2. Calcium 3. Bromine Use the noble-gas notation, write the electron configuration of the following: 1. Fluorine 2. Cobalt 3. Phosphorus Electron Configuration Write the electron configurations of the following elements: 1. Sulfur 2. Calcium 3. Bromine Electron Configuration Use the noble-gas notation, write the electron configuration of the following: 1. Fluorine 2. Cobalt 3. Phosphorus Electron Dot Structures How do you know how many valance electrons elements have? Write the electron dot structures for the following elements: 1. Nitrogen 2. Aluminum 3. Neon 4. Lead Electron Dot Structures How do you know how many valance electrons elements have? Look for the highest energy level, then total up the number of electrons in the s & p sublevels. Electron Dot Structures Write the electron dot structures for the following elements: 1. Nitrogen 2. Aluminum 3. Neon 4. Lead Development of the Modern Periodic Table Which Scientist characterized the “Law of Octaves”? Which Region contains the : Halogens Alkaline Earths Noble Gasses Alkali Metals Development of the Modern Periodic Table Which Scientist characterized the “Law of Octaves”? Which Region contains the : Halogens - C Alkaline Earths - B Noble Gasses - D Alkali Metals - A Development of the Modern Periodic Table Which region is referred to as the p-block d-block s-block f-block Development of the Modern Periodic Table Which region is referred to as the p-block D d-block C s-block A f-block B Classification of the Elements Which element has an electron configuration that ends in the 5th energy level? Which element is most metallic? Classification of the Elements Which element has an electron configuration that ends in the 5th energy level? C Which element is most metallic? A Classification of the Elements What is the most important characteristic in determining an element’s chemical properties? Classification of the Elements What is the most important characteristic in determining an element’s chemical properties? The number of valence electrons Periodic Trends Which diagram correctly depicts the trend in Electronegativity First ionization energy Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Periodic Trends Which diagram correctly depicts the trend in Electronegativity B First ionization energy B Atomic Radius C Ionic Radius C Periodic Trends In each pair which one is larger? Na, Rb Br, BrS, Mg K, K+ Periodic Trends In each pair which one is larger? Na, Rb Br, BrS, Mg K, K+ Rb BrMg K