How Ionic Bonds Form?
advertisement

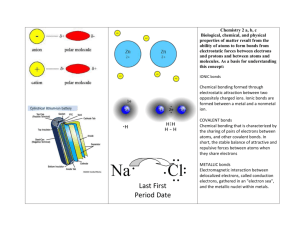
Ionic Bonds Essential Question: How do ionic bonds form? What is an Ion • An ion is any atom or combination of atoms that has a charge, negative or positive. • An ion is formed when electrons are add or taken away from an atom. • They are never formed by protons being added or removed, NEVER. • Opposite charges of atoms attract each other. Why do Ions form? • Ions form because atoms want to have a complete octet. • An Octet is 8 electrons in the outer energy level or shell. • How can we make complete shells? How Ionic Bonds Form? • An ionic bond is the force of attraction that holds together positive and negative ions. • It forms when atoms of a metallic element give up electrons to atoms of a nonmetallic element. Ions • When an atom loses a negative electron, the overall charge becomes positive • It’s called a cation • When an atom gains an electron, the overall charge becomes negative • It’s called an anion Table Salt • Sodium and Chlorine have equal and opposite charges. • They “attract” and cling together in a strong ionic bond. • Ionic bonds form between metal and nonmetal atoms Why Ionic Bonds Form • Ionic bonds form only between metals and nonmetals. That’s because metals “want” to give up electrons, and nonmetals “want” to gain electrons. • Look at the Lewis Dots that you drew on your Periodic Table & think about the Octet Rule • Alkali Metals (#1) bond with Halogens (#17) • Predict which might bond with Alkaline Earth Metals • Alkaline Earth Metals (#2) bond with the Oxygen Family (#16) Energy and Ionic Bonds • Energy holds the electrons in orbit around the nucleus • Energy is needed to remove valence electrons from one atom and attach them to another • These ionic bonds are very strong and difficult to break – for example, try burning salt • These compounds have high melting and boiling points and are good electrical conductors. • Because water has polar bonds, ionic compounds do dissolve in water. Ionic Bonds form Crystals • Many compounds form molecules, but ionic compounds form crystals instead. • A crystal consists of many alternating positive and negative ions bonded together in a matrix. Ionic Crystals • In this demo, we will cause a minor chemical reaction of several metals and nonmetals: • We’ll use table salt, which contains Sodium and Chlorine • “Bluing” which contains Ferric hexacyanoferrate which has Iron, Nitrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen • Water = Oxygen and Hydrogen Ionic Crystals Demo • In a glass or plastic bowl, put some pieces of charcoal, porous brick, tile, cement or sponge. Day 1: Over the base material, 10 ml of water, 10 g salt and 10 ml Mrs. Stewart's Bluing. Day 2: Add two more tablespoons of salt. Day 3: Pour into the bottom of the bowl (not directly on the base material) two tablespoons each of salt, water, and Mrs. Stewart's Bluing, and then add a few, vegetable coloring each piece. Observe over the next few days… • Next week, we’ll discuss covalent bonds and create a polymer. • You will be asked to compare and contrast the result of these two activities.