Cycle 2
advertisement

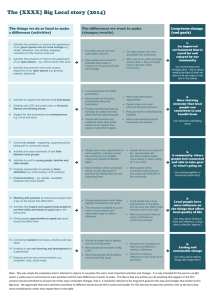
August 2015 Throughput rates for 3-year degree 2008 student cohort in public HEIs (excluding UNISA) 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Graduated Dropped out 2010 30% 5% 2011 2012 non-accumulative 18% 8% 3% 1% 2013* 2010 3% 3% 30% 35% (VitalStats Public Higher Education 2013, CHE) 2011 2012 accumulative 48% 56% 37% 39% 2013* 59% 41% National Planning Commission 2012 “Higher education is the major driver of the information/knowledge system, linking it with economic development. However, higher education is much more than a simple instrument of economic development. Education is important for good citizenship and enriching and diversifying life... Massive investments in the higher education system have not produced better outcomes in the level of academic performance or graduation rates. While enrolment and attainment gaps have narrowed across different race groups, the quality of education for the vast majority has remained poor at all levels. The higher education therefore tends to be a low-participation, high-attrition system.” Focus of the Quality Enhancement Project The enhancement of student learning with a view to producing an increased number of graduates with attributes that are personally, professionally and socially valuable. 1. enhanced student learning, leading to an 2. increased number of graduates that have 3. improved graduate attributes STUDENT SUCCESS Both institutionally-based and nationally coordinated activities Institutional enhancement HE system enhancement Less of this…. http://www.wisconsinsilo.com/ More of this… http://exotic.vn/abbvie-team-building-2014/ Staff from the Indian Space Research Organization celebrate at the ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network in Bangalore after their Mars Orbiter spacecraft successfully entered Mars orbit on September 24, 2014. Credit: Manjunath Kiran/AFP/Getty Images http://www.purdue.edu/uns/html4ever/000212.Rubelocal.2000. html http://cars.aol.co.uk/2013/03/26/video-how-to-build-a-formula-1-car/ Process Select focus areas Institutional submissions Analysis Individual Institutional feedback Feedback Symposia, working groups Collaboration Analysis Feedback Institutional reports Projects of other bodies Research projects Institutional capacity development Focus areas for Phase 1 1. Enhancing academic as teachers 2. Enhancing student support and development 3. Enhancing the learning environment 4. Enhancing course and programme enrolment management Responses from Private Providers 48 for profit 21 non-profit 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Programme offerings Single focus-one programme Narrow focusseveral related programmes Multiple focus-a number of different programmes 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Number of students [<500 500-2000 2001-5000 >5000 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Mode of delivery Contact Distance Contact & Distance Focus area 2 Once a university admits a student it has a moral obligation to do everything within its power to create an environment within which the student has a good chance of succeeding. “Access without support is not opportunity” [Vincent Tinto] Developing institutional mechanisms for student support Focus area 2 Curriculum development Assessment Counselling Support Monitoring Teaching Career guidance and curriculum advising Provided before enrolment? 56 YES Face-to-face, telephonic, email (18) Screening tests during application (10) Provided after enrolment? 54 YES Part of learning programme (15) Discussions with dedicated individuals (16) Exposure to industry (8) Advising students on curriculum planning? 58 YES Dedicated people to offer advice (15) Counselling Provided to registered students when needed? 22 YES Educational, academic, psycho-social, spiritual, lifestyle, health, finances Done by lecturers, academic development coordinators, academic managers or counsellors Specialised or professional counselling provided by psychologists, psychiatrists, student support coordinators and other external providers (10) Students first go to staff or appointed counsellors before being referred to a specialist (10) Appraising students’ life and academic skills Is there a mechanism? 49 YES Using formative and summative assessment (17) Assessment reports and workshops (9) Entrance assessments (7) Mentoring and “skills passports” (17) Feedback from WIL or clinical placements Development of life and academic skills Voluntary activities provided? For whom? 45 YES All students may participate (23) Integrated into curriculum so all participate (7) Target groups, e.g. underperforming students, SRCs What activities are provided? Community engagement (28) Extra classes, workshops, mentoring and tutoring, academic literacy development activities (28) WIL linked to community engagement Development of life and academic skills Compulsory activities provided? For whom? 53 YES All students (16) At-risk students, in certain years or programmes, SRC members (22) What activities are provided? Work-integrated learning and/or experiential learning (24) Skills development programmes (15) Bridging courses, mentoring programmes, subject-specific tutorials, cultural activities Mechanism for identifying students at risk of failing 68 YES Performance in assessments and exams, class participation, submission of work Responsible individuals, e.g., academic managers, programme managers, QA facilitators, academic advisers, academic staff Support to at-risk students 40 30 20 10 0 Voluntary Support Compulsory Support No Formal Support One-on-one guidance, advising and counselling (39) Mentoring, tutoring, extra classes (43) Involving parents, guardians, sponsors (14) Activities to develop academic skills (6) Other good practices • Low lecturer-student ratio so more engaged with students and their needs (26) • Mentoring and tutor systems and academic skills development (14) • Student leadership development activities • Academic literacy programmes (9) • Industry placement, clinical practice, simulations • Support for students with disabilities (8) • Welfare support (food, emotional support, pastoral care) Main challenges • Lack of resources for academic development, including enough staff • Inadequate infrastructure, including wheelchair ramps, internet access, equipment • Funding • Time for staff and students to participate in academic development • Students not accessing support • Distance learning– lack of infrastructure, difficulty in organising student support activities Discussion For Focus Area 2: Enhancing student support and development and on the basis of what you have heard, 1. What good practices could your institution implement (if not there already) or improve upon (if there already)? 2. What challenges does your institution face and how could they be addressed? Dimensions of students’ lives that affect their success Subject matter Academic literacies Physical health Study skills STUDENT Life Skills Material needs Vocation Wellbeing Academic support and development helping students successfully execute the tasks required to succeed in their academic programme. Non-academic support and development helping students successfully navigate the challenges associated with being a university student and with life in general. Institution-wide activities Orientation programmes First-year experience Identification of student needs (through surveys) Life skills Study skills Teaching and Learning Division Academic literacies Careers Disability support Student Services Division Counselling Writing Mentoring Tutoring Advising Monitoring Faculty (or Department) Challenges Timing, timetabling and voluntary nature of support Tutors and tutor training Non-credit bearing courses Technology challenges Structural, financial and staffing constraints Communication and use of available services Discussion For Focus Area 2: Enhancing student support and development, 1. What additional good practices that you have heard about today could your institution implement (if not there already) or improve upon (if there already)? 2. What challenges would need to be overcome and how for these new practices to be implemented? Focus area 3 Providing institutional resources Learning environment Curriculum development Assessment Counselling Support Monitoring Teaching Enhancing the learning environment Teaching spaces Labs Multipurpose spaces Individual learning spaces Collaborative learning spaces Library Technical spaces ICT resources Teaching spaces for promoting learning Effective Gymnasium (1) Outdoor learning facilities (2) Common areas (2) Simulation rooms (4) Student workspaces (6) Library (9) Learning studios (8) Computer labs (16) Work Integrated Centre /… Lecture room / auditorium (17) Online spaces (22) 0 5 10 15 20 25 • Good, appropriate IT infrastructure (33) • Well-maintained, comfortable, well-resourced spaces for contact sessions (34) • Suitable, adequate teaching equipment (28) • Good spaces for practicals, simulations, WIL (11) Teaching spaces that are not effective Limited building infrastructure and maintenance (27) Insufficient equipment (11) 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Building / IT Infrastructure Equipment (8) infrastructure (9) (14) Library (2) Individual student learning spaces Spaces in library (40) Computer labs for individual use (13) Common areas Resource and/or study centre (8) Teaching rooms when not in use (7) Effective features IT infrastructure (27), well-resourced buildings (16) Studios well-equipped (10) Features that hamper student success Limited space (14), IT infrastructure (15), limited access to and resources in library (10), high noise levels (9) Collaborative learning spaces Teaching spaces when not in use (31) IT “spaces” (LMS, internet access) Common areas (e.g. cafeteria) (13) Effective features Flexible furniture arrangements, internet access (33) Availability of resources (29) Features that hamper student success Limited spaces available (13) High noise levels (12) Limited IT infrastructure (7) Spaces used for socialising, not studying (7) Learning management systems (LMS) 40 have, 29 do not have 40 30 20 10 0 Access on campus None or Almost None About 1/2 About 3/4 All or almost all 20 15 10 5 0 Access at home None or Almost None About 1/4 About 1/2 About 3/4 All or almost all Fraction of courses/ modules that use the LMS 20 15 10 5 0 None or Almost None About 1/4 About 1/2 About All or 3/4 almost all Uses of technology E-learning (classroom, tutorials, discussion forums such as wikis) (59) General use of IT equipment by students and lecturers (email, printing, cameras) (42) Access to on-line journals in the library (25) Internet access in computer labs, library and some classrooms (27) LMS (16) Power point presentations in lectures (16) Communication of information to students (14) Simulation labs and practical lab with high technology software and other necessary applications (11) Administrative purposes (7) Online Work sharing (1) Challenges in using technology Internet access and reliability (39) Finances to support the costs (25) Students’ lack of computer literacy (19) Library facilities Good aspects Provide research facilities, e.g. databases (51) Good infrastructure (39) Good accessibility (in time and space) (42) Staff for support (26) IT infrastructure (22) Needs improvement Student learning spaces (39) Resources (25) Access (in time and space) (16) IT infrastructure and access (12) Equipment (13) Discussion For Focus Area 3: Enhancing the learning environment and on the basis of what you have just heard, 1. What good practices could your institution implement (if not there already) or improve upon (if there already)? 2. What challenges does your institution face and how could they be addressed? Spaces • Conflict between large lecture room and spaces that enable interactive teaching and learning • Student numbers often exceed carrying capacity • Some state of the art specialised teaching spaces that link with industry, professions or community • General shortage of student learning spaces • Some innovative uses of spaces for learning • Crowding can be caused by inefficiencies “Built pedagogy” – the architectural embodiment of our educational philosophy Decisions about physical space needs and configurations need to be pedagogically driven Technology-enabled learning LMS provide opportunities for more interaction among students and each other and with lecturer, expanded learning opportunities Some institutions have apps to enable students to access LMS and student portal More wi-fi enables students to use own devices, but bandwidth is an issue Cost of data and internet access off-campus a problem for many students Designing on-line learning materials takes knowledge skill. Need learning designers to work with subject specialists. Also need increased IT infrastructure There is a shortage of skilled ICT technicians and support staff; students can help https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2015/03/20/austin-communitycolleges-promising-experiment-personalized-remedialmathematics#.VQwIPxCe7q0.mailto https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xHxq936GQoQ Libraries • Libraries playing more and more important role • Physical spaces for learning and accessing information, using computers, own devices, books moved into storage • Increasing access needed by students; students can be employed to help. • Librarians help with knowledge management for institution and training for staff and students • Librarians’ role getting more complex and demanding, so sometimes hard to find right people Discussion For Focus Area 3: Enhancing the learning environment 1. What additional good practices that you have heard about today could your institution implement (if not there already) or improve upon (if there already)? 2. What challenges would need to be overcome and how for these new practices to be implemented? Promising practice Shown to be successful in a specific context Decontextualise Identify core elements Recontextualise Adapt for a new context Implement and evaluate Good practice Expected outcomes of the QEP • Benchmarks and codes of good practice for quality undergraduate provision • Policy recommendations • Tools and resources for improving student success • Research • Communities of practice Raise the bar for what can be expected of institutions in promoting student success in future