Masers and the Process of High
advertisement

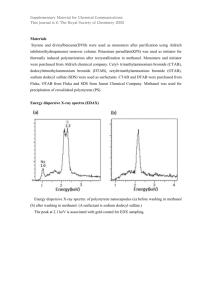
107/108 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Simon Ellingsen University of Tasmania Methanol masers – what and where • Methanol masers are empirically divided into two groups: – Class I masers are associated with outflows and low velocity shocks, they are collisionally pumped. Strong transitions at 36, 44, 95, 229 GHz. – Class II masers are exclusively associated with the environment close to very young high-mass stars, they are radiatively pumped. Strong transitions at 6, 12, 107 GHz. • You frequently find class I and II methanol masers associated with the same object, but not coincident. • Often multiple class II (or class I) methanol transitions are observed to be coincident spatially and in velocity. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA + = 6.7 GHz methanol masers + = OH masers + = water masers Green contours = 95 GHz methanol Black contours = 3cm continuum. Blue = 3.6 μm Green = 4.5 μm Red = 8.0 μm Great Barriers in High-Mass Star Formation 13-17 September 2010 Methanol masers - Science • What can you do with multiple coincident maser transitions? – Determine the physical conditions at very high resolution, by modeling the observed ratio of the different transitions. – Utilize the presence/absence of different transitions as an evolutionary clock. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Methanol Maser pumping models Cragg et al. (2005) Great Barriers in High-Mass Star Formation 13-17 September 2010 EGOs Methanol masers - Science water OH • What can you do with multiple coincident class II methanol 6.7 GHz maser transitions? 12.2 GHz II – Determine the physical conditionsUCH at very high resolution, by modeling the observed ratio of class I methanol the different transitions. 0 1 2 3 4 4 Relative lifetime (x 10 years) 5 – Utilize the presence/absence of different transitions as an evolutionary clock. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Methanol masers in A+ rotational subspecies : Class I Class II Figure courtesy of Maxim Voronkov. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Low-hanging fruit • The 107 GHz (31-40 A+) methanol masers are direct analogues of the 6.7 GHz (51-60 A+). • Approximately 25 107 GHz masers have been detected in previous single-dish searches (e.g. Caswell et al. 2000). • These look like ideal targets for cycle 0 science : – Intense – Compact – Low frequency Caswell et al. (2000) 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Class I masers • There are a number of relatively strong and common class I transitions in band 3 (84 GHz and 95 GHz). • Also the 229 GHz transition falls within band 6. • These are more spatially distributed and may be better targets for later cycles. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA Conclusions • ALMA observations of 107 GHz methanol will allow us to – Constrain the physical conditions in the masing regions. – Constrain evolutionary maser-based clocks. - “close the loop” on the class II methanol masers. 107 GHz methanol masers with ALMA