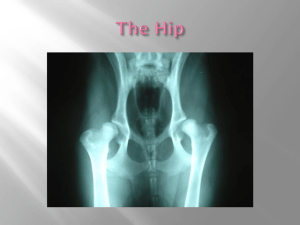
Hip and pelvis
advertisement

Hip and pelvis Iliopsoas / Gluteus Medius / Gluteus Minimus / Gluteus Maximus / Piriformis / Pectineus / Sartorius / Rectus Femoris / Tensor Fasciae Latae / Biceps Femoris / Semitendinosus / Semimembranosus / Adductor Brevis / Adductor Longus / Adductor Magnus / Gracilis Iliopsoas Iliopsoas is sometimes classified as two muscles, Iliacus and Psoas major. Origin Inner surface of the Ilium Base of the sacrum Sides of the bodies of T12-L5 Insertion Lesser trochanter of the femur Actions Flexion of the hip Lateral rotation of the hip Flexes torso when the legs are fixed (e.g. laying to sitting) Innervation Femoral nerve and branches of the lumbar plexus Daily uses Climbing a step Gluteus Medius Gluteus Medius is an important muscle in controlling the level of the hips. Weaknesses in gluteus medius often result in a trendelenburg sign, an abnormal gait cycle where the hip of the swinging leg drops down, rather than raises up. This results in increased degrees of knee flexion in order to clear the ground. Origin Outer surface of the ilium, just below the crest Insertion Greater trochanter of the femur Actions Hip abduction Posterior fibres externally rotate the hip Anterior fibres internally rotate the hip Innervation Superior gluteal nerve Daily uses Stepping sideways out of the bath Gluteus Minimus Origin Outer surface of the ilium, below the origin of Gluteus medius Insertion Greater trochanter of the femur Actions Hip abduction Internal rotation of the hip Innervation Superior gluteal nerve Daily uses Getting out of a car Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Maximus is the largest and most superficial of the three gluteal muscles. Origin Posterior crest of the ilium Posterior surface of the sacrum Insertion Gluteal tuberosity of the femur Iliotibial band (ITB) Actions Hip extension External rotation of the hip Innervation Inferior gluteal nerve Daily uses Extension phase of walking upstairs Piriformis The Piriformis muscle is an important muscle. The sciatic nerve passes underneath this muscle on its route down to the posterior thigh. In some individuals the nerve can actually pass right through the muscle. This can lead to sciatica symptoms due to a condition known as piriformis syndrome. Origin Anterior surface of the lateral sacrum Insertion Greater trochanter of the femur Actions External rotation of the hip Hip abduction Innervation Branch of the sacral plexus Daily uses Taking the first leg out of the car Pectineus Pectineus is positioned between the Iliopsoas and Adductor Longus muscles. Origin Upper front of the pubic bone Insertion Upper medial shaft of the femur, inferior to the lesser trochanter Actions Hip adduction Hip flexion Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Kicking a football Sartorius Muscle The Sartorius is a two joint muscle and so is weak when the knee is flexed and the hip is flexed at the same time. It works better during single movements. Origin Area between the ASIS (Anterior Superior Iliac Spine) and AIIS (Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine) Insertion Anterior part of the medial condyle of the tibia Actions Flexion of the hip Flexion of the knee External rotation of the hip as it flexes the hip and knee Abducts the hip Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Sitting in a cross-legged position Rectus Femoris The Rectus Femoris muscle is part of the Quadriceps muscle group. It is the only muscle of the group which crosses the hip joint and is a powerful knee extensor when the hip is extended, but is weak when the hip is flexed. Origin Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS) Insertion Top of the patella and the patella tendon to the tibial tuberosity Actions Flexion of the hip Extension of the knee Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Kicking a football Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle The Tensor Fasciae Latae is a small muscle which attaches inferiorly to the long thick strip of fascia, known at the iliotibial band (ITB) Origin Anterior Iliac crest and ilium Insertion Lateral condyle of the tibia via the Iliotibial band Actions Flexion of the hip Hip abduction Innervation Superior gluteal nerve Daily uses Keeping one foot in front of the other when walking Biceps Femoris Biceps Femoris is one of the three muscles which form the hamstring group. The muscle is often described as having a long head (the attachment from the ischium) and a short head (attached to the femur). Origin Tuberosity of the ischium Lower1/2 of the linea aspera of the femur Lateral supracondylar ridge Insertion Lateral condyle of the tibia Head of the femur Actions Hip extension Knee flexion Lateral rotation of the hip when the knee is flexed Innervation Tibial part of the sciatic nerve Daily uses Bending the knee to step over something Semitendinosus When running the hamstrings act eccentrically to slow down the knee extension motion. Hamstring strains are common in individuals with chronically tight hamstrings or who do not warm-up thoroughly. Origin Ischial tuberosity Insertion Upper medial surface of the tibia Actions Hip extension Knee flexion Internal rotation of the hip when the knee is flexed Innervation Tibial part of the sciatic nerve Daily uses Bending the knee to step over something Semimembranosus Semimembranosus is the most medial (inside) of the three hamstring muscles and along with the semitendinosus muscle provides dynamic stability to the knee joint. Origin Ischial tuberosity Insertion Posterior part of the medial condyle of the tibia Actions Hip extension Knee flexion Internal rotation of the hip when the knee is flexed Innervation Tibial part of the sciatic nerve Daily uses Bending the knee to step over something Adductor Brevis Adductor Brevis is the smallest and shortest of the five adductor muscles with the others being Adductor longus, Adductor magnus, Gracilis and Pectineus. Origin (where it starts from) The pubic bone Insertion (where it inserts into) Upper part of the femur or thigh bone. Actions (what does it do?) Hip adduction Hip flexion Which nerve makes it move? Obturator nerve Everyday uses Bringing your second leg into the car Adductor Longus Adductor Longus is the middle of the three short adductor muscles (adductor brevis and pectineus are the other two). The adductor magnus and gracilis are the two long adductor muscles which go from the pubic bone to the knee. Origin (where it starts from) Superior pubic ramus, just below the crest Insertion (where it inserts into) Middle third of the linea aspera of the femur Actions Hip adduction Hip flexion Which nerve makes it move? Obturator nerve Everyday uses Bringing your second leg into the car Adductor Magnus Adductor Magnus is the largest of the adductor muscles and with the gracilis muscle forms the long adductor group. Origin (where it starts from) Adductor head: Inferior ramus of pubis and ischial ramus Hamstring head: Ischial tuberosity Insertion (where it inserts into) Adductor head: Gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera and proximal supracondylar line Hamstring head: Adductor tubercle of the femur Actions Adductor head: Adducts and flexes hip Hamstring head: Extends hip Which nerve makes it move? Adductor head: Obturator nerve Hamstring head: Sciatic nerve Everyday uses Bringing your second leg into the car Gracilis Gracilis is another muscle which works in conjunction with the groin muscles, or adductors. Origin Lower pubic body, near the pubic symphesis Insertion Upper medial surface of the tibia (pes anserine insertion) Actions Adducts hip Flexes knee Internally rotates the hip when the knee is flexed Innervation Obturator nerve Daily uses Sitting with the knees pressed together