Phylum Cnidaria
advertisement

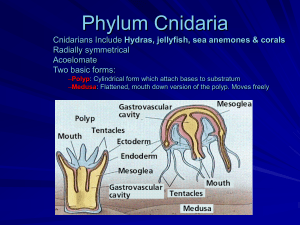
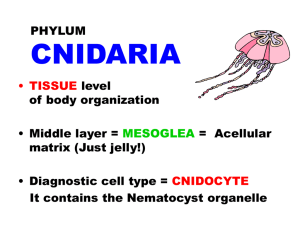
Phylum Cnidaria= Greek for “nettle” Next evolutionary jump Radial symmetry Tissue organization No organs The “stingers” 10,000 species, mostly marine Ex: jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, sea pansies, sea fans, gorgonians Radial Symmetry & anatomy Radial symmetry = similar parts of body are arranged and repeated around a central axis. Ex: if animal cut like a pizza, all slices would be similar NO head, front, back Instead Oral Surface & Aboral Surface Oral Surface Central mouth surrounded by tentacles Brings in food particles Mouth opens into a gut (only 1 opening) Used for ingestion and waste expelling Gut cavity = “stomach” Aboral Surface-other end Cnidarian Body Plan Polyp Medusa Anchored to bottom Free-floating Mouth upwards Mouth downwards Some life history includes both, others are either polyp or medusa Phylum Cnidaria Nematocysts stinging structures for prey capture Contained in cnidocytes, specialized cells. Found on tentacles Harpoon filled capsules Fire when touched Nematocysts Firing Feeding and Digestion Cnidarians are carnivores Can eat large prey Extracellular digestion Begins break down of food outside of gut cells Intracellular digestion Break down of food and uptake of nutrients is completed inside cells of the gastrodermis Phylum Cnidaria: 4 classes 1) Hydrozoa 2) Scyphozoans 3) Cubozoa 4) Anthozoans Class Hydrozoa Garveia annulata Tubularia marina Class Hydrozoa Hydractina milleri Aglaophenia latirostris Class Hydrozoa Velella velella Hydrozoa: Feathery or bushy colonies of tiny polyps attached to pilings, shells, seaweeds, and other surfaces Polyps may be specialized for feeding, defense, or reproduction Hyrodozoan life cycle Obelia dichotoma polyp and medusa Class Scyphozoa Haliclystus auricula Aurelia aurita Class Scyphozoa Chrysaora melanaster Scyphozoa Larger jellyfish Large medusa dominates life cycle Bell reach diameter of 2 m (6.6 ft) Bell diameter-deep water species is 3 m (10 ft) Swim with rhythmic contractions of bell but easily carried by currents Some species stings range from a rash to fatalities Cubomedusae once classified as scyphozoa now own class Cubozoa. Ex: Sea wasp= Box-jellyfish Class Anthozoa Most Cnidarian species are Anthozoan Ex: Corals, anemones, sea fans, sea pansies Only polyp stage Corals ---calcium carbonate skeletons forming coral reefs Class Anthozoa Anthopleura xanthogrammica Metridium senile Class Anthozoa Anthopleura elegantissima Class Anthozoa Tealia lofotensis Epiactis prolifera Symbiotic Relationship Clownfish eat undigested anemone prey which could rot and cause disease Anemones eat fecal waste of fish Clownfish not affected by nematocysts toxins Anemones provide safe shelter for fish Corals, Anthozoa Hard calcium carbonate skeleton Cold and warm waters In warm waters, form coral reefs Symbiotic zooxanthelle (single celled, photosynthetic algae) Class Anthozoa, corals Phylum Cnidaria: 4 classes 1) Hydrozoa 2) Scyphozoans 3) Cubozoa 4) Anthozoans Phylum Ctenophore The comb jellies Less than 100 species Radial symmetry 8 rows of ciliary combs, that beat in waves