Phylum Cnidaria Hydras, jellyfish, sea anemones & corals Radially symmetrical Acoelomate

Phylum Cnidaria
Cnidarians Include Hydras, jellyfish, sea anemones & corals
Radially symmetrical
Acoelomate
Two basic forms:
– Polyp : Cylindrical form which attach bases to substratum
– Medusa : Flattened, mouth down version of the polyp. Moves freely
Forms of Cnidarians
Body Plan
Basic Body Plan:
Has an outer epidermis
Has an inner gastrodermis which forms a gastrovascular cavity
Has a middle "jelly filled" layer called mesoglea
Cnidocytes
Cnidarians are predators which have tentacles possessing batteries of special cells called Cnidocytes
Cnidocytes contain special stining capsules called nematocysts .
When triggered, these cells shoot out a discharge thread which can entangle and/or poison it's intended prey
Reproduction
– Reproduction can occur sexually by fertilization of egg and sperm forming larvae.
– Reproduction can also occur asexually through budding
3 Major classes
– Class Hydrozoa : Hydras
– Class Scyphozoa : Jellyfish
– Class Anthozoa : Anemones and corals
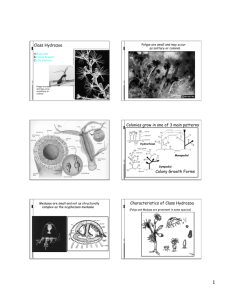
Class Hydrozoa: The Hydras
Polyp phase is dominant
Generally microscopic
Generally freshwater
Class Scyphozoa: The Jellies
Generally refered tro as jellies
Medusa stage is dominant
Come in a variety of forms
Aggressive predators, and can be dangerous to humans
Jelly
Portugese
Man-o-war
Class Anthozoa: Anemones & Corals
Appear like plants but are animals.
Polyp form is dominant.
Corals build calcium shells to protect themselves
– Have symbiotic relationship with algae.
Can build extensive masses which can form land masses.
Anemone
Coral Polyps
Coral Reefs
Clownfish living in
An anemone