Life Cycles and Reproduction Housekeeping! - Emery
advertisement

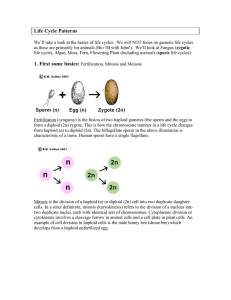
Life Cycles and Reproduction Housekeeping! Binary Fission – a from of asexual reproduction that produces identical daughter cells • Bacteria undergoing Binary Fission • Another view of bacteria reproducing • An explanation with Ameoba Conjugation – a form of sexual reproduction • Bacteria conjugating & paramecium conjugating (results in an exchange of genetic material) With Eukaryotes and especially multicelluar organisms things get more complicated • Sexual reproduction involves specific sex cells (egg and sperm cells) called gametes • Gametes are haploid (n) – contain only 1 set of chromosomes • When an egg & sperm cell fuse they form a zygote, which becomes diploid • Diploid cells (2n) contain 2 sets of chromosomes – one set inherited from each parent cell How are haploid and diploid cells formed • Diploid cells created through mitosis • (e.g. Body or somatic cells) • Haploid cells created through meiosis • (e.g. Egg & sperm) Mitosis Meiosis Sexual Life Cycles • There are 3 different types of sexual life cycles – Gametic – Zygotic – Sporic • All cycles alternate between meiosis, which makes sperm and eggs, and fertilization, which merges sperm and egg to create a zygote. Sporic life cycle Sporic life cycle • Ex. of an alteration of generations = a life cycle in which diploid individuals (sporophytes) produce spores that create haploid individuals called gametophyes • Haploid individuals reproduce sexually, producing sporophytes • Spore = a haploid reproductive structure, usually a single cell, capable of growing into a new cell • E.g. Brown algae, all vascular plants Zygotic Life Cycle Zygotic Life Cycle • Zygotes is the only diploid cell ever • Meiosis occurs in the zygote to produce spores • Spores germinate to produce vegetative phases that are haploid • Organisms with this type of lifecycle are algae and fungi • E.g. Life cycle of a basidiomycete (i.e. Mushrooms) Gametic Life Cycle Asexual Life Cycle