Sec_ 22
advertisement

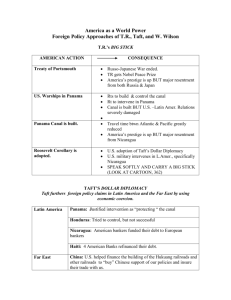
LATIN AMERICAN POLICIES Sec. 22-4 Pages 656-661 • Define: isthmus – anarchy – dollar diplomacy Roosevelt corollary ( Big Stick policy)“ watchful waiting” • Identify: Teddy Roosevelt - Dr. William Gorgas Dr. Walter Reed – Sec. of State, John Hay P. Bunau-Varilla - William TaftFrancisco Madero - Porifrio Diaz – Victoriano Huerta – Venusitano Carranza Woodrow Wilson – John Pershing – Pancho Villa PANAMA • Isthmus– Narrow strip of land connecting two larger bodies of land with water on either side. • Caribbean Sea & Pacific Ocean-50 miles wide • 1879 – French company will lease from Colombian gov’t the rights to build a canal through Panama • Ferdinand De Lesseps (built Suez Canal -Egypt)- project fails – ran out of money • Workers died of malaria & yellow fever US BUILDS CANAL • 1901 – US buys lease from French for $40 million • Pres. Roosevelt wants canal for naval power • 1903- Sec. of State John Hay negotiates treaty with Colombia - 99 year lease on 6 miles – $10 million - Annual rent of $250,000 • Colombia refuses - wants more money • 1903- USS Nashville gunboat helps Panamanians rebel – gain independence US BUILDS PANAMA CANAL • Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty – US gets 10 miles strip for building canal • Panama is paid $10 million – annual rent $250,000 • 10 years to complete • Col. William Gorgas (army doctor) eliminates yellow fever – clear swamps – destroy mosquito breeding places SUMMARIZE • Vocab term- narrow strip of land connecting two larger bodies of land • What country first began building a canal through Panama? • What country controlled Panama? • How did the US get the right to build the canal? • What disease was hindering construction? PANAMA CANAL PANAMA CANAL MAP US BUILDS PANAMA CANAL • Lock system allowed ships to be raised or lowered to ocean levels • 1914 –Canal opened to any country in world – canal will be neutral – US will protect • Saved 7000+ miles from voyage around South America POLICING WESTERN HEMISPHERE • Roosevelt’s foreign policy slogan “Speak softly and carry a big stick”. • Big Stick policy – US would responds to foreign crises by using military action • Keep world from anarchy – disorder and lawlessness – society without government or law 1904-1905 European nations threatened Venezuela – Dominican Republic when debts were owed. POLICING WESTERN HEMISPHERE • Germany wanted to send troops to Dom. Republic • US intervenes – collected fees and repaid debts • Roosevelt Corollary – addition to the Monroe Doctrine – US has right to intervene in affairs of Latin American nations whenever these nations seem unstable SUMMARY • What was Roosevelt’s slogan? • What vocab term means disorder and lawlessness – overthrow a government? • What country wanted to send in troops to the Dominican Republic to collect debts? • What addition to the Monroe Doctrine allowed the US to intervene in affairs of Latin American nations when it seemed unstable? TAFT’S FOREIGN POLICY • Dollar Diplomacy – Encourage bankers to lend money to troubled countries to bring stability • US would profit and gain power – no need to use military power. • US helped Latin American countries gain railroads, roads, harbors, mines, banana and coffee plantations MEXICO • Poor country controlled by small group of rich landowners (wealthy, Catholic Church, military) • US investors spend billions of dollars into Mexican oil wells, railroads, mines and ranches • 1880-1911 – Mexico ruled by Porfirio Diaz – encouraged American, British, German investments. As politicians, foreign investors, and landowners grew richer, the common people remained poor. MEXICO • 1911 – Diaz overthrown by Francisco Madero in a coup (act of seizing power – overthrow a government illegally or by force) • Americans feared Madero would seize US property • 1913 – Gen. Victoriano Huerta killed Pres. Madero – seized power. Pres. Wilson annoyed by act of violence – refused to recognize Huerta’s gov.t SUMMARY • Taft’s foreign policy that encouraged bankers to give money to stabilize a nation. • Name 2 of the 3 groups that ruled Mexico in the 1800s. • What vocab term means to overthrow a gov’t? • Whose gov’t rule in Mexico did Wilson refuse to recognize because of violence? WILSON’S FOREIGN POLICY • Watchful waiting – wait for opportunity to act against a government in which he disapproves • Civil war breaks out in Mexico – Pres. Wilson authorizes sale of arms to help Huerta’s rival, Venustiano Carranza • April 1914 – American sailors arrested in port of Tampico, Mexico. Pres. Wilson sends marines to intervene – closed off supplies of guns & supplies coming from Germany for Huerta. • Over 100 Mexicans and 19 Americans died in invasion MEXICO WILSON & MEXICO • European press condemned US • Wilson allows ABC Powers (Argentina, Brazil, Chile) to mediate dispute – Huerta flees and Carranza takes power in Mexico • 1916- Mex. rebels, Pancho Villa and Emiliano Zapata kill 18 American mining engineers in Mexico – crossed border and killed 17 Americans in Columbus, New Mex. • Both returned and hid in Mexico Gen. Pershing • Pres. Wilson sends Gen. John “Blackjack” Pershing with 15,000 troops to capture Villa. • Mexicans angry with US invasion – Carranza demands troops leave – Wilson refused • Wilson will withdraw troops by Jan. 1917 to send to Europe when US joins fighting in WWI • Mexico will adopt constitution that gives gov’t control of oil and mineral resources - placed strict regulations on foreign investors. SUMMARY • Name of Wilson’s foreign policy that said to wait for an opportunity to act against a disapproving gov’t. • Name the Mexican rebel the US tried to capture. • Who was sent to capture him? • Why did the US pull out US troops in 1917?