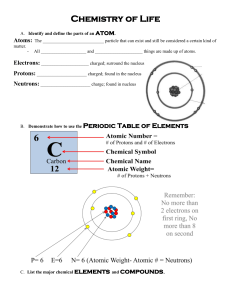
Basic Chemistry Part 2 Presentation

Basic Chemistry
Mixtures
A mixture is two or more substances blended together ( not bonded ).
Each substance in a mixture keeps all of its chemical and physical properties.
Mixtures
Mixtures, unlike compounds, can be separated into their individual substances by physical means.
Example: salt and water can be separated by evaporation .
Mixtures
A solution is a mixture of two or more substances, one dissolved in another.
Two parts of a solution are the solute and the solvent .
Mixtures
Solute – substance being dissolved
Examples: sugar , salt
Solvent – substance doing the dissolving
Example: water
Mixtures
A solution becomes saturated when the solvent holds all the solute that it can. It can no longer dissolve solute.
Mixtures
Suspensions are a mixture of particles scattered throughout another. The particles do not dissolve. Examples: clouds , dust , fog , smoke , mud , blood
Compounds
Compounds are two or more elements chemically joined by bonds .
They are represented by chemical formulas .
Compounds
Properties of compounds are usually different than the atoms.
Example: Hydrogen( gas ) +
Oxygen( gas ) = Water ( liquid )
Example: Iron + Oxygen = Rust
Compounds
Compounds can be separated into their elements only if the chemical bonds are broken . This can be done by chemical means
(chemical reaction )
Compounds
A molecule is the smallest part of a compound—like water—that has all the properties of the compound.
Compounds vs. Elements
1. C Two or more elements combined
2. E Made up of one type of atom
3. E Cannot be chemically broken down
4. C Table Salt (NaCl)
5. E Sodium (Na)
6. C Glucose
7. C Water (H
2
O)
8. B Smallest unit of a substance
9. E Smallest unit of matter
10. B Units of matter
11. E Hydrogen (H)
12. C Can be broken down chemically
Formation of Chemical Bonds
A covalent bond is a bond formed when atoms share electrons to form a compound .
Strong physical bond
Covalent Bond hydrogen oxygen
8
8
H
2
O Molecule
2 covalent bonds hydrogen
Formation of Chemical Bonds
An ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
It is a weak electrical attraction, not a physical bond.
Example: table salt ( NaCl )
Ionic Bond
Ionic Bond
Instead of being neutral, atoms of sodium and chlorine making up salt become charged .
Ions are charged atoms that have gained or lost one or more electrons .
Chemical Reactions
A chemical reaction is the process of breaking down existing chemical bonds of compound and forming new bonds.
Chemical Reactions
Elements combine in ways that cause their atoms to be stable .
The energy required to start a chemical reaction is activation energy and the most common form of this energy is heat .
Chemical Reactions
A reaction that gives off more energy than it uses up is an exothermic reaction.
A reaction that gives off less energy than it uses up is an endothermic reaction.
Chemical Reactions
Living things need a constant supply of energy from food because all cells use more energy than they produce.
Chemical Reactions
Example reactions:
Photosynthesis
Water + Carbon Dioxide Glucose (Sugar) + Oxygen
H
2
O + CO
2
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Chemical Reactions
Example reactions:
Respiration ( Breathing )
Oxygen + food (glucose) water + carbon dioxide
6O
2
+ C
6
H
12
O
6
H
2
O + CO
2
Chemical Reactions
Example reactions:
Rusting , Burning , Digestion , etc…
Reactants are on the left .
Products are on the right .