9/14/2015
advertisement

ITS 328
CHAPTER 3: STORING DATA IN MEMORY
1
Storing Data in Memory
After today you will be able to:
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Explain how a DataTable stores data
Add new data rows to a table
Examine, update, and remove existing values in a table row
Explain how ADO.NET differentiates between pending and final data values
Integrate data verification code into your DataTable object
2
Today’s Exercise
Chapter 3 CSharp Project
◦ Open Chapter 3 CSharp.sln in files folder
Add DataRow programmatically (p.41)
Fill Form Display Fields (p.43)
Edit a DataRow (p.43)
Validating Content (p.54)
3
Creating a Table (Chapter 2)
Create a Table
◦ DataTable someTable = new DataTable("Customer");
Add a Column
◦ someTable.Columns.Add("ExpireDate", typeof(DateTime));
Add Column with Constraints
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
DataColumn newColumn;
// Use to specify properties
newColumn = someTable.Columns.Add("FullName", typeof(string));
newColumn.MaxLength = 30;
newColumn.AllowDBNull = false;
newColumn.Unique = true;
4
Adding Constraints to Columns (Chapter
2)
DataColumn newColumn;// Use to specify properties
newColumn = someTable.Columns.Add("FullName", typeof(string));
newColumn.MaxLength = 30;
newColumn.AllowDBNull = false;
newColumn.Unique = true;
newColumn.Caption = "Student Name";
5
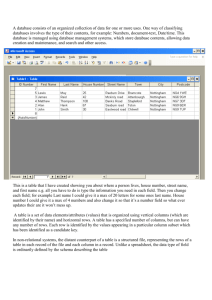
Adding Data
Create a new row object
◦ DataRow oneRow = someTable.NewRow();
Store the actual data values in the row object
◦ oneRow.Item[2] = "Joe Schmoe";
◦ oneRow["FullName"] = "Joe Schmoe";
Add the row object to the table
◦ someTable.Rows.Add(oneRow); // Adds to end of table
◦ someTable.Rows.InsertAt(oneRow,0);
// Inserts at beginning of table
Add data directly, without row object
◦ someTable.Rows.Add(new Object[] {1L, DateTime.Parse("12/31/2016"), "Joe Schmoe"});
6
Exercise Part 1 – Adding Rows (P. 41)
Open Chapter 3 CSharp project
◦ Contains two Windows.Forms classes: AccountManager and AccountDetail
Open AccountManager.cs (F7 from AccountManager Design window)
Locate the Load Form event handler AccountManager_Load
Review Creation of Table
◦
◦
◦
◦
oneColumn for adding constraints to columns
ColumnChanging event handlers for specifying business rules
Primary Key
Optional Columns
7
Exercise Part 1 – Adding Rows (P. 41)
Below "// ----- Build some sample data rows." comment, add:
◦ CustomerAccounts.Rows.Add(new Object[] {1L, "Blue Yonder Airlines", true, 500m,
DateTime.Parse("1/1/2007")});
◦ CustomerAccounts.Rows.Add(new Object[] {2L, "Fourth Coffee", true, 350m,
DateTime.Parse("7/25/2009")});
◦ CustomerAccounts.Rows.Add(new Object[] {3L, "Wingtip Toys", false});
◦ Yourself active with a $100 annual fee starting tomorrow.
Notice foreach adding Items to the AllAccounts ListBox component
8
Exercise Part 2 – Modifying Rows (P. 43)
Examine ActAdd_Click() and ActEdit_Click() button event handlers
◦ Each Invokes AccountDetail().EditAccount(ref editRecord, table)
Open AccountDetail.cs [Design]
◦ Load event handler fills the fields from DataRow from AccountManager
◦ Properties and Events including AccountDetail Load event handler
◦ Identify Components: AccountID, AccountName, AnnualFee, StartDate
Arguments
◦ eventRecord and CustomerAccounts are arguments from AccountManager
◦ whichAccount and baseTable are parameters in AccountDetail
◦ AccountEntry and AccountTable are instance names
9
Exercise Part 2 – Fill Form Code (P. 43)
In AccountDetail_Load() add:
if (AccountEntry != null) {
AccountID.Text = string.Format("{0:0}", AccountEntry["ID"]);
ActiveAccount.Checked = (bool)AccountEntry["Active"];
if (DBNull.Value.Equals(AccountEntry["FullName"]) == false)
AccountName.Text = (string)AccountEntry["FullName"];
if (DBNull.Value.Equals(AccountEntry["AnnualFee"]) == false)
AnnualFee.Text = string.Format("{0:0.00}", (decimal)AccountEntry["AnnualFee"]);
if (DBNull.Value.Equals(AccountEntry["StartDate"]) == false)
StartDate.Text = string.Format("{0:d}", (DateTime)AccountEntry["StartDate"]);
}
Search Google for "c# string.format"
10
Exercise Part 2 – Click OK Code (P. 43)
Below workArea.BeginEdit(); add:
workArea["Active"] = ActiveAccount.Checked;
if (AccountName.Text.Trim().Length == 0) workArea["FullName"] = DBNull.Value;
else workArea["FullName"] = AccountName.Text.Trim();
if (AnnualFee.Text.Trim().Length == 0) workArea["AnnualFee"] = DBNull.Value;
else workArea["AnnualFee"] = decimal.Parse(AnnualFee.Text);
if (StartDate.Text.Trim().Length == 0) workArea["StartDate"] = DBNull.Value;
else workArea["StartDate"] = DateTime.Parse(StartDate.Text);
11
Deleting Rows
Use Remove() or RemoveAt() methods to remove DataRow objects.
Remove() accepts row instance as argument:
◦ DataRow oneRow = someTable.Rows[0];
◦ someTable.Rows.Remove(oneRow);
RemoveAt() accepts index position as argument
◦ someTable.Rows.RemoveAt(0);
Clear() removes all the rows
◦ someTable.Rows.Clear();
12
Batch Processing
Allows a batch of changes before committing to any of them
Preferable when changes occurring across multiple rows must be collectively valid
After updates are complete
◦ someTable.AcceptChanges();
◦ someTable.RejectChanges();
// Commit all row changes
// Reject changes since last commit
Use DataRow.BeginEdit() to postpone data checks and exceptions until DataRow.EndEdit();
13
Exception-Based Errors
Assigning data of the wrong data type to a column value.
Supplying string data to a column that exceeds the maximum length defined in the column’s
DataColumn.MaxLength property.
Attempting to store a NULL value in a primary key column.
Adding a duplicate value in a column that has its Unique property set.
Operation that violates one of the table’s custom (e.g., relational) constraints.
14
Validation-Based Errors
DataTable Column and Row Change Event Handlers
◦ ColumnChanging, RowChanging, RowDeleting, TableNewRow
◦ ColumnChanged, RowChanged, RowDeleted, TableClearing, TableCleared
Example Check Age column for valid range:
private void Applicant_ColumnChanging(Object sender, System.Data.DataColumnChangeEventArgs e) {
// ----- Check the Age column for a valid range.
if (e.Column.ColumnName == "Age") {
if ((int)e.ProposedValue < 18 || (int)e.ProposedValue > 29)
e.Row.SetColumnError(e.Column,"Applicant's age falls outside the allowed range.");
}
}
15
Exercise Part 3 – Validate Content (P. 54)
Follow the directions on Page 54 checking Annual Fee and Start Date. In the
CustomerAccounts_ColumnChanging event handler, add:
if (e.Column.ColumnName == "AnnualFee") {
// ----- Annual fee may not be negative.
if (DBNull.Value.Equals(e.ProposedValue) == false) {
if ((decimal)e.ProposedValue < 0m)
e.Row.SetColumnError(e.Column, "Annual fee may not be negative.");
}
} else if (e.Column.ColumnName == "StartDate") {
// ----- Start date must be on or before today.
if (DBNull.Value.Equals(e.ProposedValue) == false) {
if (((DateTime)e.ProposedValue).Date > DateTime.Today)
e.Row.SetColumnError(e.Column, "Start date must occur on or before today.");
}
}
16
Exercise Part 3 – Validate Content (P. 54)
In the CustomerAccounts_RowChanging event handler, add the following:
if (e.Row.HasVersion(DataRowVersion.Proposed) == true) {
if (((bool)e.Row["Active", DataRowVersion.Proposed] == true) &&
(DBNull.Value.Equals(e.Row["StartDate", DataRowVersion.Proposed]) == true))
e.Row.RowError = "Active accounts must have a valid start date.";
}
Run the program to confirm it works.
Make sure the instructor confirms your program works before you leave
17