Plate Margins & Characteristics
advertisement

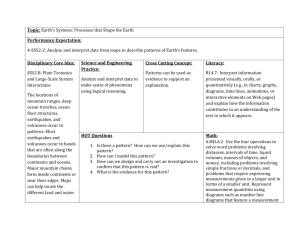
Constructive Margins: Oceanic Ridges Plates are moving apart (Divergent) Slow rate: 15mm per year, produces a wide ridge axis and inward facing faulting scarps (MID-ATLANTIC RIDGE) Intermediate rate: 90mm per year, produces a smoother outline ridge (GALAPAGOS RIDGE) Rapid rate: +90mm per year, produces a smooth crest with no ridge (EAST PACIFIC RISE) Can form volcanoes such as Surtsey, Iceland Volcanoes are of low viscosity, no build-up of pressure so frequent gentle eruptions Transform faults can occur at right angles to the margin (potential for earthquakes) Rift valleys can form – African Rift Valley Destructive margins: Oceanic/Continental Denser oceanic plate is forced underneath the continental plate (subduction) Down warping of the plate causes an ocean trench to develop South American and Nazca plate (subducting) forming the Peru-Chile trench Sediments accumulate on the continental shelf which are deformed and made into fold mountains e.g. Andes Benioff zone may produce shallow focus earthquakes as the plate melts As the plate melts the magma becomes less dense than the surrounding asthenosphere and so rises causing plumes of magma and volcanoes Lava is of viscous nature and forms explosive composite volcanoes If eruptions take place offshore, island arcs can be formed Oceanic/oceanic Convergence: One plate is forced underneath the other Earthquakes can occur in the benioff zone Melting of the pate creates plumes which form volcanoes in an island arc Deep ocean trenches are formed due to down pulling of the plate –PACIFIC AND PHILIPPINE PLATE FORMING GUAM ISLANDS Continental/continental Convergence: As the pates have much lower density than the underlying layers, little subduction occurs The geosyncline is forced to fold forming synclines and antisynclines TETHYS SEA WHEN THE INDIAN AND EURASIAN PLATES FORMED THE HIMALAYAS Little volcanic activity due to little subduction Movement of plates can cause shallow focus earthquakes – Nepal 2015 Material is forced downwards to form deep mountain roots Conservative Margins: Plate s can move in the same or different directions Two crustal plates slide past each other No creation or destruction of crust No subduction or volcanic activity Earthquakes likely SAN ANDREAS FAULT WITH THE NORTH AMERICAN AND PACIFIC PLATE