Standard 2 - Jenks Public Schools
advertisement

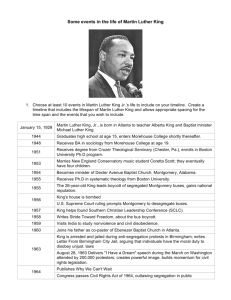
Civil Rights CS #1.1 & CS # 5.5 by: Becky Rampey Post Civil War Amendments • 13th Free – Ends Slavery • 14th – Establishes who is a Citizen Citizens • 15th – Who gets to Vote (No Women) Can Vote Reconstruction Policies • Three Plans –Lincoln’s 10% Plan –Johnson – President’s Plan –Congress – Radical Reconstruction • Resulted in the South being rebuilt and controlled by the US Army until Northern citizens were tired of funding this program – left white southerners upset and eager to regain control of their lives. Reconstruction Policies Con’t • Sharecropping – New Form of Slavery • Black Codes – Restrict Freedman’s Rights • KKK – Secret Society - goal to ensure White Supremacy • Plessy v. Ferguson – Separate but Equal = OK • Jim Crow – Laws to keep AA’s from voting and taking advantage of other freedoms they were entitled to following their emancipation. Civil Rights During Progressivism • Booker T Washington – “Pull yourself up by your bootstraps” – believed in training blacks so they could prove themselves worthy of equality. • WEB DuBois – Equality Now – Opposite of BTW but in reality they both wanted the same thing. • Marcus Garvey – • Poll Taxes – Taxes meant to keep Blacks from Voting. • Literacy Tests – Test that blacks would be forced to take before they could vote. (generally very Hard). Civil Rights Movement • Executive Order – 9981 – Truman desegregated the US military. • NAACP – founded in 1909 – Use the legal system to fight against discrimination. – Slowly begin making small wins. – Thurgood Marshall – Lawyer for the NAACP – fights many of the most significant cases during the movement. – Supreme Court Cases – in both of these cases students seeking higher education in Oklahoma sued to the Supreme Court and were able to force changes in Universities “Separate but Equal” policies. • Ada Lois Sipuel • George McLaurin • Brown v Board of Education – Ends “separate but equal” in schools – opens the way to end all segregation. • Montgomery Bus Boycott - Black citizens from Montgomery refused to ride the buses for more than one year after Rosa Parks was arrested for refusing to give up her seat. – First major act – MLK is involved in. – Forced Montgomery to desegregate the buses. • Sit-Ins – Students and other young people would sit down in a restaurant and refuse to leave until they had been served. – Clara Luper – OKC teacher who led a successful sit-in at Katz drug store who immediately changed all their stores/ lunch counters. • Little Rock Nine – 9 black students go to Central HS in Little Rock, under the protection of the United States military after the white students, teachers, and governor or Arkansas all tried to keep them out. – Sets precedent for desegregating other southern schools. • Freedom Rides – Intention – Desegregation of interstate busing in the South. Summer of 1961 – Met with opposition in Alabama – Beatings and Fire bombs – resulted in numerous injuries. Especially to the white supporters. • Birmingham Church Bombing - 16th Street Baptist Church – bombed on September 15, 1963. Killed three young black girls. • March on Washington – August 28, 1963 – 250,000 people to campaign for equality. – Martin Luther King – Gives the “I Have a Dream” speech. (Setting before the nation the goals of the movement). • Selma Montgomery March – Marchers attempt to march from Selma to Montgomery to protest for equality. Met with opposition twice – 3rd March – resulted in 25,000 marchers from all over showing up in Montgomery. Legislation • 24th Amendment – Makes the POLL TAX illegal. • Civil Rights Act of 1964 – No discrimination of any kind based on race, color, religion, or national origin. • Voting Rights Act of 1965 – Make it easier for Black southerners to vote – No more literacy test or other methods used to prevent them from voting. MLK / Malcolm X • Martin Luther King (MLK) – believed in Civil Disobedience and Non-Violent Resistance to unfair/unjust laws in an effort to change them. – Ghandi / Jesus Christ influential in his decisions. – Organized and participated in many important protest and activities fighting for equality for all. • Malcolm X – More Militant than MLK – Seeks separation of the races- leads to a break in the movement. – Malcolm X would later change his views but he’s early leadership had developed a new group within the Civil Rights movement – who were not afraid to use violence for what they wanted. • Assassination of MLK – April 4, 1968 – James Earl Ray – MLK was 39 years old. Organizations • SCLC – Southern Christian Leadership Conference – Group of southern ministers who worked together to organize the movement. • CORE – Congress of Racial Equality – Organized Voting Registration Drives and the Freedom Rides • SNCC – Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee – Early involvement with MLK and SCLC – Later under leadership of Stokley Carmichael became Violent – change name to the Student National Coordinating Committee.