Organ systems
advertisement

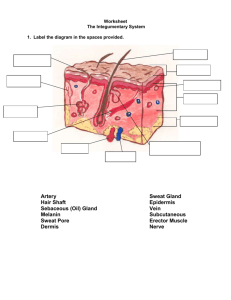
Human Body Systems Homeostasis – Maintain a stable internal environment. Examples: temperature, breathing and blood pressure Four types of tissues Tissue is made up of a group of similar cells that work together. Epithelial - covers and protects underlying tissue. Ex. skin Nervous – sends electrical signals throughout the body. Found in the brain, nerves and sense organs. Muscle – cells that contract and relax to produce movement. Connective – joins, supports, protects, insulates, nourishes and cushions organs. Cell Organization Tissues are made up of a group of cells that work together. Organs are formed by two or more tissues working together. Organ systems are formed by two or more organs working together. Organ Systems 1. Skeletal System A framework that supports and protects body parts. 2. Muscular System Allows for movement of body parts. Organ Systems 3. Circulatory System Transports materials throughout the body in the blood. 4. Respiratory System Exchanges gases in the lungs. Organ Systems 5. Digestive System Breaks down food into nutrients for the body. 6. Excretory System Removes wastes from the body. Organ Systems 7. Nervous System Controls activities using electrical signals. 8. Endocrine System Regulates body functions using chemical signals. Skeletal Muscular Digestive Respiratory Nervous Sensory Endocrine Circulatory Urinary April 21st 1. Write down homework: • Page 9-5 in packet • Study flashcards for 8 body systems. • Quiz Thursday! 2. Get out your homework to be checked. 3. Think about what you know about the skeletal and muscular systems. Digestive Respiratory Circulatory Excretory Skeletal Muscular Nervous System System System System System System System Integumentary System What does the Integumentary system do? Protects Helps you from the outside world maintain a healthy internal environment. What makes up the Integumentary System? Skin Hair Nails Integumentary System What are the four important things that skin does? – keeps moisture in and keeps foreign particles out Protects Allows you to feel surroundings with nerves Controls body temperature by producing sweat in sweat glands. Removes wastes in sweat. Integumentary System What determines your skin color? The amount of melanin, a chemical, in your skin What are the two main layers of skin? Epidermis Dermis What does the epidermis do? Thin layer, on top Made up of epithelial tissue Many layers, thin, mostly dead cells Keratin makes skin tough Integumentary System What does the dermis do? Thick layer, deeper down, underneath epidermis Connective tissue and collagen that provide strength and flexibility Nerves, blood vessels, sweat and oil glands, muscle fibers & hair follicles are found here. How does hair grow? New cells cells grow at the hair follicle and push out old dead Integumentary System What does hair do? Protects from UV light and foreign particles Controls body temperature What do nails do? Protects tips of fingers and toes to allow for feeling (sense of touch).