Unit One – Chemistry of Life
advertisement

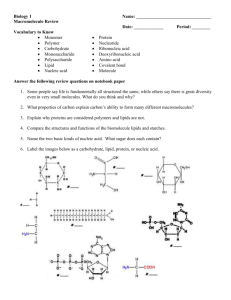
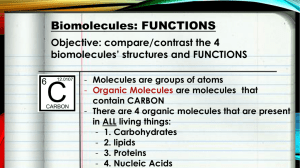
Unit One – Chemistry of Life Honors Biology Student Learning Targets Always know vocabulary!!! Note: This unit we have the following vocab words that are not included in your textbook: Homeostasis (HONORS ONLY) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Dehydration Synthesis reaction Hydrolysis reaction ____ 1.1 Identify the 4 primary elements essential for life that make up macromolecules and the importance of elements. ____ 1.2 Describe the structure of an atom. 1.2.A Know the subatomic particles, their charge, and where they are located within the atom. 1.2.B Explain what happens when at atom gains or loses electrons, how this determines the charge of an ion, and what this might have to do with bonding. ____ 1.3 Describe the structure of a water molecule and how it relates to the unique properties of water. 1.3.A Explain how the structure of water leads to a polar molecule. 1.3.B Explain how the polarity of a water molecule leads to hydrogen bonding between molecules. 1.3.C Explain how polarity leads to cohesion and adhesion. 1.3.D Explain how polarity leads to high specific heat. 1.3.E Explain how polarity affects the density of water. 1.3.F Explain the difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic and how this relates to the structure of water. 1.3.G (HONORS ONLY) Explain how the polarity affects the ability of water to dissolve different substances. ____ 1.4 Explain the importance of pH. 1.4.A Explain how pH indicates if a solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. 1.4.B (HONORS ONLY) Define buffer, and explain why buffers are important for maintaining homeostasis in the human body. ____ 1.5 Describe why carbon atoms form the basis of organic molecules and the formation and how their ability to bond is important in the formation of organic monomers and polymers. ____ 1.6 Describe and name the reactions used to synthesize and break apart polymers and monomers. ____ 1.7 Explain the basic structure and importance of carbohydrates. 1.7.A Describe the basic structure of carbohydrates. 1.7.B List the monomer and polymer of a carbohydrate. 1.7.C List the three main types of carbohydrates (starch, cellulose, glycogen). 1.7.D Describe the basic function of the three types of carbohydrates. 1.7.E Explain why starch and cellulose have different functions in a plant. ____ 1.8 Explain the basic structure and importance of lipids 1.8.A Describe the common property and categorizes all lipids together 1.8.B List the three main types of lipids (fats, phospholipids, steroids) 1.8.C Describe the common functions of the different types of lipids 1.8.D Describe the interaction of lipids with water ____ 1.9 Explain the basic structure and importance of nucleic acids 1.9.A List the monomer and polymer of a nucleic acid 1.9.B List the two main types of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) 1.9.C Describe the basic function of nucleic acids ____ 1.10 Explain the basic structure and importance of proteins 1.10.A Describe the basic structure of a protein 1.10.B List the monomer and polymer of a protein 1.10.C Describe the basic function of an amino acid, and what part of the structure makes each amino acid unique 1.10.D Describe some basic functions of proteins ____ 1.11 Explain what happens in a chemical reaction. 1.11.A Identify the products and reactants of a chemical reaction. 1.11.B Explain how chemical reactions are essential for allowing non-living elements to make living organisms. 1.11.C Explain how bonding is involved in chemical reactions. ____ 1.12 Describe the importance of enzymes in chemical reactions 1.12.A Explain the role of enzymes in chemical reactions, including the role they play in lowering activation energy 1.12.B Describe what it means for any protein to denature and what factors might cause denaturation and explain how this can affect protein function. Scientific Skills Learning Targets These are skills that are used repeatedly through all units and do not correspond to any one particular unit. ____ SS.1 Identify the following parts of a scientific article and explain the purpose of each section (abstract, introduction, methods and materials, results, calculations, conclusion, references) ____ SS.2 Examine data from a scientific article to learn more about biological concepts