Weak Acid/Base ICE Tables
advertisement

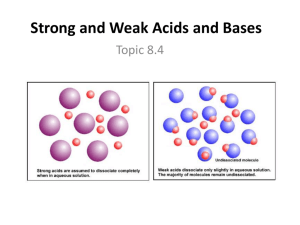
Weak Acids/ICE Boxes Objective: Today I will be able to: Determine the concentrations of reactants and products intitially and during equilibrium for a reaction by using an ICE table Calculate the concentrations of weak acids and bases at equilbrium Evaluation/Assessment: Informal assessment: monitoring student questions as they complete the practice problems Formal assessment: analyzing responses to the practice and exit ticket Common Core Connection Build strong content knowledge Reason abstractly and quantitatively Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them Lesson Sequence • • • • Evaluate: Warm – Up Explain: ICE Tables Elaborate: ICE Table Practice Evaluate: Exit Ticket Warm - Up • Complete #2 on your Equilibrium Practice (ICE Boxes) worksheet Objective • Today I will be able to: Determine the concentrations of reactants and products intitially and during equilibrium for a reaction by using an ICE table Calculate the concentrations of weak acids and bases at equilbrium Homework • Finish Practice Problems from Class Agenda • • • • • • Warm – Up Intro to ICE Boxes Notes Ice Box Practice Weak Acid Notes Weak Acid Practice Problems Exit Ticket ICE Boxes Take out your homework for last night. Let’s review #3 & #4 Weak Acids/Bases and ICE Boxes Remember this next slide? … Strong Acids/Bases vs. Weak Acids/Bases • STRONG: – Ionize almost 100% in water (react to completion) • WEAK: – Do not ionize completely, achieve an equilibrium Q: How can I tell the difference between strong and weak acids? Two different ways: 1. Study the list of strong acids and bases 1. Look at the arrow in an acid/base balanced equation – If arrow is one direction it is STRONG – If arrow is two directions it is WEAK Examples • Strong Acid Example – HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + NO3-(aq) • Weak Acid Example – CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) • Strong Base Example: – NaOH(aq) + H2O(l) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) • Weak Base Example: – NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) Instead of using Keq we use a different constant for weak acids and bases Ionization Constant of a Weak Acid • Ka = acid ionization constant – Ka varies at different temperatures • Generic example of a weak acid reaction: Weak Acid Specific Example • CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) – [H3O ][CH3COO ] Ka [CH3COOH] • Weak acids have a Ka < 1 – Leads to small [H3O+] • pH of weak acids is calculated by solving the expression for [H3O+] at equilibrium and then taking the –log[H3O+] Ionization Constant of a Weak Base • Kb = base ionization constant • Weak bases = Kb < 1 – Leads to a small [OH-] • To find pOH take -log[OH-] Weak Acid/Base Worked Examples 1) Weak Acid Example HA(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + A-(aq) Q: Initially, you have 1.00 M HA. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of HA, H3O+, A-, and calculate the pH. Ka = 1.80 x 10-5 – Hint: Use an ICE table! Weak Acid Example Cont. HA H3O+ A- I 1.00 0 0 C -x +x +x E 1.00 – x +x +x Weak Acid Example Cont. • Write Ka expression: Ka = 1.80 x 10-5 = [H3O+][A-] = x2 [HA] 1.00-x • Assume x is small because Ka is very small, therefore x can be ignored (5% Rule) Ka = 1.80 x 10-5 = x2 1.00 Weak Acid Example Cont. Ka = 1.80 x 10-5 = x2 1.00 • x = [H3O+] = [A-] = 4.20 x 10-3 M • pH = - log [H3O+] = 2.37 2) Weak Base Example NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) • Initially, you have a concentration of 0.010 M NH3. Find the concentrations at equilibrium. Calculate the pH. Kb = 1.80 x 10-5 – Hint: Use an ICE table! Weak Base Example Cont. NH3 NH4+ OH- I 0.010 0 0 C -x +x +x E 0.010 – x +x +x Weak Base Example Cont. • Write Kb expression: Kb = 1.80 x 10-5 = [NH4][OH-] = x2 [NH3] 0.010-x • Assume x is small because Kb is very small, therefore x can be ignored Kb = 1.80 x 10-5 = x2 0.010 Weak Base Example Cont. Kb = 1.80 x 10-5 = x2 0.010 • x = [NH4+] = [OH-] = 4.20 x 10-4 M • pOH = - log [OH-] = 3.37 • pH + pOH = 14 • Therefore, 14 - 3.37 = 10.6 = pH Weak Acid/Base Practice Complete the practice at your desk. Whatever you do not finish will become your homework. Exit Ticket • Which problems on the weak acid/base practice were the most challenging? • One thing I am confused about is ___________________________.




![Acids and Bases Homework 3O+]? 1000x lower in [H ]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008705019_1-bcba3d05374bbb16a4904187ff3180b5-300x300.png)