Individuals & Families
Diverse Perspectives
Family Studies 11/12
Ms. Larson
PGSS
Becoming A Couple
Marriage
For most Canadian couples,
getting married is the
beginning of a relationship
that will last a lifetime.
How do you choose the one
person with whom you
would like to share your
life?
What can you do to ensure
that your relationship will
last?
Theories of Attraction & Mate
Selection
• The eternal question in romantic relationships
is:
“How do I know if this is the right
person for me?”
Romantic Movies
Decisions
•
•
•
•
•
Whether or not to marry
Whom one should marry?
Whom one wants to marry?
What one’s marriage will be like?
What other form of relationship might suit one’s
needs better?
• Will it be possible to form a satisfying relationship
that will last a lifetime without having to give up
who you are and who you want to be?
Marriage
• Binding and enduring
– Not the case for many people
– Some sociologists estimate that only 10%
of contemporary marriages end up to be
truly monogamous (1 man for 1 woman for
life)
• Polygamy – marriage between 1 man and 2
or more women
• Polyandry – marriage between 1 woman
and 2 or more men
– Not affordable for most people
Marriage
• Same-sex marriages
– Recently legalized in Canada and in other
countries
• Serial monogamy
– Marriage to several spouses – one after the other
– a natural result of divorce
• Arranged marriages
– Immigrants from other cultures where this is the
norm
Marriage
• Increase in cohabitation and divorce rates
makes one wonder if marriages are meeting
individuals’ needs ………… but
• Newly-weds in most societies expect that their
own marriage will last for life – why?
Theories of Attraction & Mate
Selection
• Canada
– Lasting couple relationships are based on
romantic love and sexual attraction between two
people
– Marriage has its roots in the biological drive to
reproduce basic social and economic unit in
human societies
– Is romantic love a recent social development or
does love have a basis in human biology? (Wilson,
2001)
Theories of Attraction & Mate
Selection
• Historically romantic love is considered a
hindrance to marital stability (Kelman, 1999)
– 87% of all cultures the relationships between men
and women exhibit romantic love (Nadeau, 1997)
– In A History of the Wife, Marilyn Yalom of Stanford
University suggests that a man and a woman who
lived and worked together, shared a bed, and
raised children together would probably grow to
love each other regardless of how their marriage
came about (2001)
Theories of Attraction & Mate
Selection
• In Canada – Free-choice mate selection
– Attraction
– Fall in love
– Decide to marry
• How successful is this model?
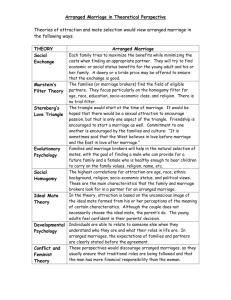
Evolutionary Psychology and Attraction
• Individuals are attracted to those who appear
to provide the best chance for producing and
raising children.
• Helen Fisher (1992) identified 4 adaptive
behaviours for sexual attraction
– Women preferred to mate with men who had the
resources to be good providers for themselves and
their children because women were unable to
both care for infants and gather enough food
Evolutionary Psychology and Attraction
• Men preferred to mate with women who could bear
healthy babies, who could feed their children, and who
had the intelligence and temperament to raise them
well.
• Prehistoric men formed lasting relationships because
women could refuse sex until they got what they
wanted or needed in evolutionary terms.
• Children raised without a father were poorer and could
not compete well in prehistoric society because they
had less food and did not learn the necessary skills
Evolutionary Psychology and Attraction
• Men and women who made successful
choices would have more children to inherit
• Individual preferences for an attractive mate
and competition with others for a mate
Modern Sexual Attraction Research
– Men attracted to
women who are
physically appealing,
younger, and healthy
• Shiny hair
• Clear skin
• Full lips and a shapely
hourglass figure are
markers of estrogen
which suggest fertility
and the ability to give
birth without
difficulty
• Common
characteristics of
female beauty in all
cultures
Modern Sexual Attraction Research
• Women are attracted
to:
– Older mate with
financial resources
good providers
• Men and women are
attracted to:
–
–
–
–
–
Intelligence
Kindness
Understanding
Dependableness
healthy
Social Homogamy
• Explains how individuals are attracted to people
from similar social and cultural backgrounds so
that they share social, cultural, and economic
values and lifestyle expectations
– Unconscious factors
– May explain the attraction of two individuals of
different races or ethnic backgrounds but who were
born and socialized within the same socio-economic
environment
• People marry people who are like themselves and
like their family
Social Homogamy
• Education is a major factor
– More likely to marry someone with the same level of
educational attainment
Culture
- first-generation immigrants generally have similar
ideas to other Canadians about what is attractive,
they also look for someone who shares their cultural
values
- Guided by values of family reputation and parental approval
- Second-generation immigrants more likely to marry
someone of a different culture but still value parental
approval
Ideal Mate Theory
• Attraction is based on an individual’s unconscious
image of the ideal mate formed from his or her
perceptions of the meaning of certain factors (physical,
cultural, or socio-economic characteristics) based on
how they see themselves or others
• “love at first sight” concept is supported
• Perceptions of an ideal mate are formed from pleasant
experiences with other individuals in childhood –
family, people in the community, media
• Identify characteristics that will be “deal breakers” for a
successful marriage