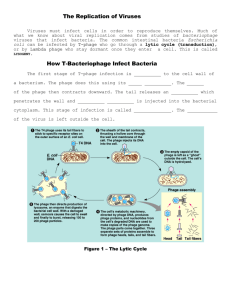
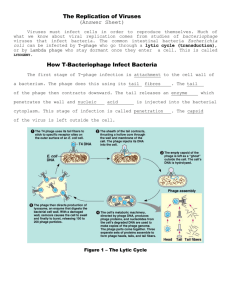
Evolution Review Questions
advertisement

1. Locate Core 40 Study Guide • Today’s Goal: Indy 100 Speed Trials Bring a digital picture of yourself on Thursday. 1. Locate your Core 40 Study Guide. Today’s Goal: • Reinforce Genetics. Core 40 Test Practice Second Third Inning Visitor Home 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 First Total Home Outs Batter Up! Second Third Inning Visitor Home 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 First Total Home Outs In the event of an environmental change, which of the following increases the likelyhood that a species will survive? A. Genetic diversity B. Asexual reproduction C. Rapid growth rate D. Dominant traits According to the table below, which species are most closely related? A.A and B B. B and D C. C and D D. A and C Species A and B % difference in DNA A and C 1.2 B and D 2.4 C and D 1.8 A and D 2.4 1.4 Look carefully at the pictures of bird beaks above. Choose the response that matches each beak with the most likely diet. A. 1:nectar, 2:nuts & seeds, 3:aquatic organisms, 4: meat B. 1:nectar, 2:meat, 3:nuts and seeds, 4: aquatic organisms C. 1:aquatic organisms, 2:nuts & seeds, 3:nectar, 4:meat D. 1:aquatic organisms, 2:nuts & seeds, 3:meat, 4:nectar Two subpopulations of a species of bird became isolated through geographic change a long time ago. A scientist wonders if the 2 populations are still the same species. Which question must the scientist answer to determine if the populations are still the same species? A. Do they look identical in every aspect? B. Do they have the same behavioral patterns? C. Will they raise each other’s offspring? D. Can they mate to produce fertile offspring? Which of these ideas was part of Darwin’s Origin of Species in which he presented a mechanism for evolution? A. Human beings evolved from monkeys. B. The genetic code found in DNA is the same for almost all organisms. C. Only biologically inherited characteristics can be passed on to offspring. D. Characteristics that an individual acquires during its lifetime can be passed on to offspring. • Explain three (3) of the main components of Darwin’s theory of evolution. Include a description of the evidence used by Darwin. • Explain three (3) of the main contributions of Gregor Mendel. Briefly describe how Mendel developed his evidence. 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 human Thr Leu Ser Glu Leu His Cys Asp Lys Leu His Val Asp Pro Glu Asn Phe Arg Leu gorilla Thr Leu Ser Glu Leu His Cys Asp Lys Leu His Val Asp Pro Glu Asn Phe Lys Leu chimp Thr Leu Ser Glu Leu His Cys Asp Lys Leu His Val Asp Pro Glu Asn Phe Arg Leu monkey Gln Leu Ser Glu Leu His Cys Asp Lys Leu His Val Asp Pro Glu Asn Phe Lys Leu Scientists often compare the amino acid sequence found in the protein hemoglobin to infer the evolutionary relationships between organisms. Based on the data above, which organisms are most closely related? A. gorilla and monkey B. chimp and gorilla C. monkey and human D. chimp and human A population of snakes lives on a large island that becomes two separate islands when the sea level rises. What would you expect to happen after a very long period of time? A. Competition will increase. B. Speciation will occur. C. Interbreeding will continue. D. Natural selection will stop. The best measure of evolutionary relationship between two species can be estimated from their…. A. length of time on Earth. B. amount of cooperation. C. genetic similarities. D. behavioral similarities. Complex, multicellular organisms were able to evolve primarily because….. A. the atmosphere changed. B. water began to condense. C. cells with nuclei developed. D. of availability of resources. According to natural selection, which is the best explanation of the evolution of the giraffe’s neck? A. Giraffes evolved long necks so they could eat the leaves of tall trees. B. The necks of giraffes gradually got longer as they reached for the leaves of tall trees. C. Giraffes were designed to have long necks so they could reach the leaves of tall trees. D. Giraffes evolved long necks because those with longer necks were more likely to pass the gene to offspring. How did the identification of genes help explain the theory of evolution by natural selection? A. Genes are segments of DNA on chromosomes. B. Organisms that are “best fit” are more likely to survive. C. Species change over time in response to their environment. D. Inherited traits are passed to offspring through genes. Identify two (2) sources of scientific evidence of evolution. Describe two (2) of the main components of Darwin’s theory of natural selection. Compare and contrast evolution and ecology. Describe Lamarck’s hypothesis for how organisms change over time. Then describe one piece of biological evidence that refutes his theory. Describe two of the adaptations birds have evolved that allow most of them to fly. Describe two of the adaptations birds have evolved that allow most of them to fly. Island chain made famous by Darwin’s work. 24 What is an example of divergent evolution? 25 What is adaptation or natural selection? 26 What is evolution? 27 Phrase used for natural selection. 28 Example of biochemical evidence among common ancestors (just need one). 29 What are other evidences of evolution? 30 What is the ultimate source of variation in a population so that evolution can occur? 31 What is a vestigial structure? 32 What are homologous structures? 33 What are analogous structures? 34 What is an example of homologous structures? 35 Bacteria and Viruses Virus Structure Label the structures and match them to their function (What they do) A. DNA or RNA 1. Helps the virus attach B. Protein Coat or Capsid 2. Instructions a virus carries C. Tail SHeath 3. Protective covering Bacteria Structure Label the structures A. DNA B. Nucleus C. Cell Wall D. Flagellum E. Pili Lytic vs. Lysogenic Cycle Match these letters to the correct steps and cycles A. Lytic Cycle B. Lysogenic Cycle C. Bacteriophage attaches and inserts DNA D. Host cell produces more bacteriophage E. Bacteriophage DNA joins host cell DNA F. Bacteriophage escape by bursting host cell Classifying Bacteria Label the shapes A. Coccus B. Spirilla C. Bacillus Review Questions 1) Unlike Chemoautotrophs, Photoautotrophs get their energy… a) Directly from the sun c) Directly from food molecules b) directly from inorganic molecules d) directly from other organisms 2) The term that is not closely related to the others is a) Eubacteria b) bacteria c) Prokaryote d) Eukaryote Review Questions 3) Certain viruses called _______ viruses cause cancer in animals a) Bacteriophage b) oncogenic c) AIDS c) Prophage 4) Bacteria help the environment by a) Carrying out photosynthesis b) Recycling nutrients c) Nitrogen fixation d) All of the above Review Questions 5) Bacteriophage infect a) Other viruses c) any available host c) bacteria only d) cells undergoing the lytic cycle Answers… Virus Structure B A C Label the structures and match them to their function (What they do) A. DNA or RNA 1. Helps the virus attach B. Protein Coat or Capsid 2. Instructions a virus carries C. Tail SHeath 3. Protective covering Bacteria Structure E C Label the structures A. DNA B. Nucleus C. Cell Wall D. Flagellum E. Pili D A Bacteria don’t have a nucleus and flagella are longer than pili Lytic vs. Lysogenic Cycle Match these letters to the correct steps and cycles C A. Lytic Cycle B. Lysogenic Cycle C. Bacteriophage attaches and inserts DNA A B F D. Host cell produces more bacteriophage E. Bacteriophage DNA joins host cell DNA F. Bacteriophage escape by bursting host cell D E Classifying Bacteria Label the shapes A B C A. Coccus B. Spirilla C. Bacillus Review Questions 1) Unlike Chemoautotrophs, Photoautotrophs get their energy… a) Directly from the sun b) directly from inorganic molecules c) Directly from food molecules d) directly from other organisms Photo means light. Photoautorophs make their own energy from light. How do chemoautotrophs get energy? 2) The term that is not closely related to the others is a) Eubacteria b) bacteria c) Prokaryote d) Eukaryote A, B, and C are all bacteria. A Eukaryote has a true (eu) Nucleus (karyote). Bacteria don’t have a nucleus Review Questions 3) Certain viruses called _______ viruses cause cancer in animals a) Bacteriophage b) oncogenic c) AIDS c) Prophage To cause (gen) cancer (onco)=> onco-genic 4) Bacteria help the environment by a) Carrying out photosynthesis b) Recycling nutrients c) Nitrogen fixation d) All of the above Look back at your notes and homework, these are listed Review Questions 5) Bacteriophage infect a) Other viruses c) any available host c) bacteria only d) cells undergoing the lytic cycle Things to study (Look at your notes and homework) Structures of bacteria and viruses The difference between Lytic and Lysogenic cycle How to classify bacteria – What makes them different from others How do viruses get us sick How are bacteria useful