Chapter 39 – Plant Response to Signals – Guided Reading
advertisement

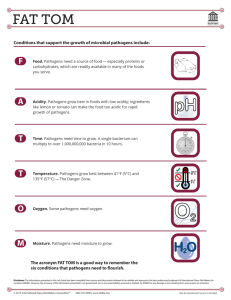
Chapter 39 – Plant Response to Signals – Guided Reading 1. Why do different flowers open at different times of the day? 2. What are etiolation and de-etiolation? 3. What role does phytochrome play in de-etiolation? What part of the signal transduction pathway is this an example of? 4. How are extremely weak signals amplified during transduction? 5. What are the two main mechanisms by which a signaling pathway can enhance a response? 6. What is a hormone? 7. What is another name for a plant hormone? 8. What are the six main types of hormones in plants? 9. What are the main functions of an auxin? 10. What are expansins? How are they activated? What do they do? 11. What is cytokinin? What are its major roles? 12. What are gibberellins and what do they do? 13. What are brassinosteroids and what role do they serve in plants? 14. What is ABA? What is its role? 15. How does ethylene affect plant growth and development? 16. What is photomorphogenesis? 17. What is an action spectrum? What does Figure 39.16 tell us about wavelength of light and coleoptile curvature? 18. What types of responses do blue-light receptors initiate in plants? 19. For what processes do phytochromes act as photoreceptors in plants? 20. Label the diagram: 21. What are circadian rhythms? 22. What is photoperiodism? 23. Describe the short-day, long-day, and day-neutral plant cycles. 24. What is critical night length? 25. What is vernalization? 26. What is a florigen? 27. What is a tropism? 28. Describe the three main tropisms. 29. What are statoliths? What do they apparently do? 30. How do some plants respond to the following environmental stresses: a. Drought b. Flooding c. Salt stress d. Heat stress e. Cold stress 31. Label the diagram and describe how plants defend against some herbivores. 32. What are virulent and avirulent pathogens? How do plants defend against some pathogens?