NRSG 422

NRSG 422
High Risk Labor & Delivery
Simulation Clinical
Dawn Tassemeyer
Spring 2014
Plan for today
Review
Short Break
Split into 2 groups
Switch, quick BR break
Lunch
Simulations
NCLEX review, wrap up
Have fun!
Outcomes/Expectations
Comfort in Clinical Setting
Prioritization/critical thinking
Learn from own mistakes, and mistakes & experiences of peers
Trust yourself, but don’t be afraid to ask questions
Be the kind of nurse you want caring for you or a loved one
#1 Goal of Labor/Delivery
Nursing…
Healthy Mom & Healthy Baby
Safe nursing care
Prepare for possible complications before they happen
Example of hospital wide safety initiative
TeamSTEPPS
Team structure
Leadership
Situation Monitoring
Mutual Support
Communication
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EXpVKz4
NDj8
Concept: Perfusion
As it relates to the OB Setting
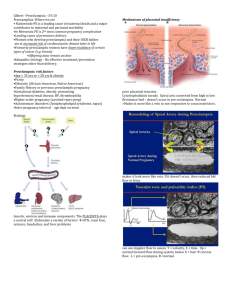
Complications: Placental problems,
Postpartum bleeding, high risk pregnancy, high risk neonate
Lets review…
High-risk pregnancy
Maternal age
Maternal parity
Maternal obstetric and gynecologic history
Maternal medical history
Maternal lifestyle
Cultural background
Family history
Bleeding disorders
Spontaneous abortion
Ectopic pregnancy
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Placenta previa
Abruptio placenta
Postpartum hemorrhage
Hematomas
Retained placenta
Uterine involution
High risk obstetrics
Amniotic fluid embolism
Umbilical cord prolapse
Oligohydramnios
Polyhydramnios
Inductions
Shoulder dystocia
Forceps/vacuum
Version
Cesarean births
Preterm Labor
Incompetent cervix
PPROM
Multiple gestation
High Risk Neonate
Resuscitation
Stabilization
Hypertension
BP
Systolic 140 mmHg or greater
Diastolic 90 mmHg or greater
Hypertensive disorders classified into four categories:
-Preeclampsia/eclampsia syndrome
-Preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension
-Gestational hypertension
-Chronic hypertension
Gestational hypertension
Vasospasm
Increased blood pressure
Decreased circulating volume
Increased extravascular fluid
Decreased organ perfusion
Vascular damage
How does this affect organs?
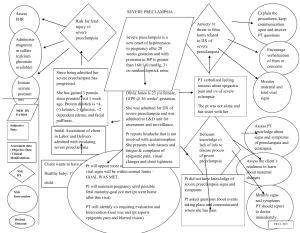
Preeclampsia
hypertensive, multisystem disorder of pregnancy
Etiology unknown
Pregnancy specific syndrome of reduced organ perfusion secondary to vasospasm and endothelial activation
Preeclampsia and liver function
In preeclampsia there is an increase in micro vascular fat deposits in liver- can cause epigastric pain.
Liver damage may be mild or it can progress to HELLP syndrome
(Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and
Low Platelets)
Preeclampsia and Kidney function
Glomerular endothelial damage, fibrin deposits resulting in ischemia reduce renal blood flow and decrease glomerular filtration rate
Protein excreted in urine
Oliguria sign of severe preeclampsia and kidney damage
Preeclampsia and coagulation system
Thrombocytopenia
Platelet count < 100,000 cells/mm3 indicates severe preeclampsia
Preeclampsia and the brain
Edema
Cerebral hemorrhage
Can lead to hyperreflexia
Severe headaches
Can progress to eclamsia
Retinal arterial spasms can cause blurring or double vision, spots before the eyes
Treatment
Depends on severity
Magnesium sulfate- a CNS depressant
Helps reduce seizure activity without long term adverse effects to woman and fetus
Do need to monitor for magnesium toxicity
Intrauterine resuscitation
Left lateral side (see which position fetus tolerates best)
IV Fluids
Oxygen 8-10L per mask
Stop Pitocin if infusing
Palpate uterus for tachysystole
References
Durham, R.F., Chapman, L. (2014). Maternal-Newborn Nursing:
The critical components of Nursing Care. F.A. Davis Co:
Philadelphia.
Luxner, K.L. (2004). Delmar’s Maternal-Infant Nursing Care Plans,
2 nd Ed. Delmar Cengage Learning: Clifton Park: NY.