Gilbert_Preecamplsia_3.9.10
advertisement
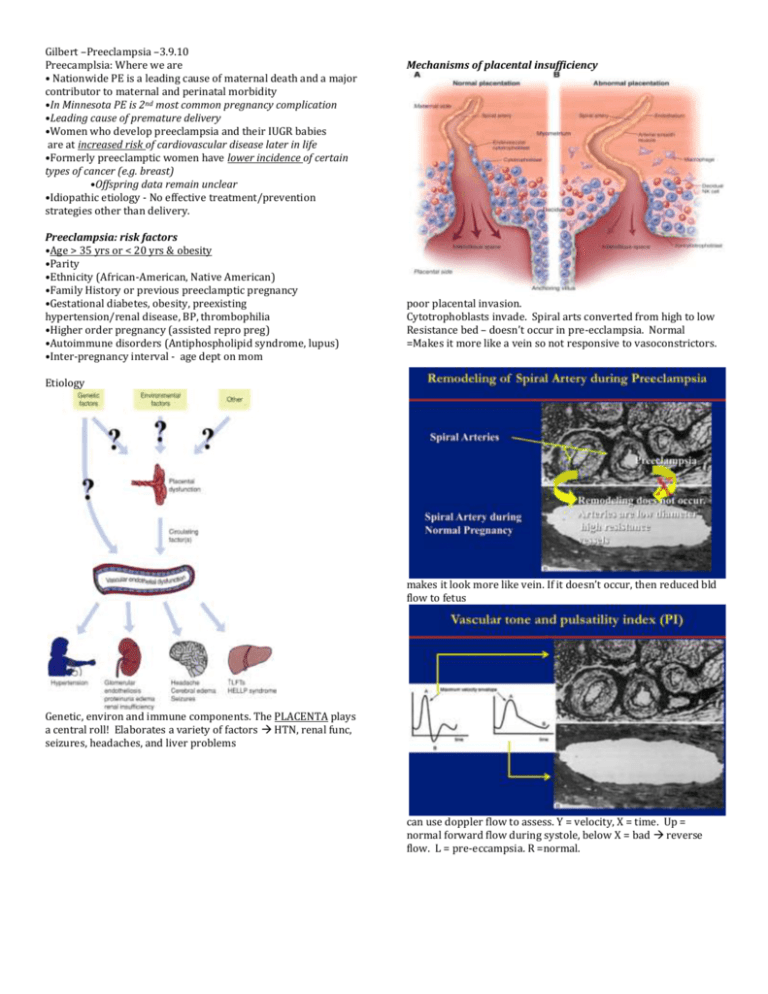
Gilbert –Preeclampsia –3.9.10 Preecamplsia: Where we are • Nationwide PE is a leading cause of maternal death and a major contributor to maternal and perinatal morbidity •In Minnesota PE is 2nd most common pregnancy complication •Leading cause of premature delivery •Women who develop preeclampsia and their IUGR babies are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease later in life •Formerly preeclamptic women have lower incidence of certain types of cancer (e.g. breast) •Offspring data remain unclear •Idiopathic etiology - No effective treatment/prevention strategies other than delivery. Preeclampsia: risk factors •Age > 35 yrs or < 20 yrs & obesity •Parity •Ethnicity (African-American, Native American) •Family History or previous preeclamptic pregnancy •Gestational diabetes, obesity, preexisting hypertension/renal disease, BP, thrombophilia •Higher order pregnancy (assisted repro preg) •Autoimmune disorders (Antiphospholipid syndrome, lupus) •Inter-pregnancy interval - age dept on mom Mechanisms of placental insufficiency poor placental invasion. Cytotrophoblasts invade. Spiral arts converted from high to low Resistance bed – doesn’t occur in pre-ecclampsia. Normal =Makes it more like a vein so not responsive to vasoconstrictors. Etiology makes it look more like vein. If it doesn’t occur, then reduced bld flow to fetus Genetic, environ and immune components. The PLACENTA plays a central roll! Elaborates a variety of factors HTN, renal func, seizures, headaches, and liver problems can use doppler flow to assess. Y = velocity, X = time. Up = normal forward flow during systole, below X = bad reverse flow. L = pre-eccampsia. R =normal. Gilbert –Preeclampsia –3.9.10 Angiogenic factors: the link between placental ischemia and hypertension during preeclampsia as plasma vol expands and vessel converted to low R bed greater diastolic spread. So in late pregnancy, it has smooth high flow low R setting. endothelial dysfunc affects renal func HTN bottom = pre-ecclampsia can be done at 15 wks to ID high risk pts ID markers: COMT = discussed in neuro/psych PAPP-A = preg assoc plasma proteins Oxidative stress = trying to Tx with vitamins never has the desired effect. AT1-AA: Angiotensin Autoantibodies -Some of these markers are also associated in mammary development – may alter differentiation of epithelium and reduced cancer rates seen in these women. L = infarcts in preeclampsia. The fetus is undernourished. Use animal studies: at the beginning of last trimester – place clips on lower abdominal aorta & ovarian art generate preecclampsic model. -See changes in sFLT-1; VEGF dec. Gilbert –Preeclampsia –3.9.10 -VEGF121 reduces high blood pressure associated with placental ischemia – trying to ID factors that can reduce renal & vasc changes. By adding VEGF to rats, we can bring BP back down to normal by improving renal function – better GFR too. -But, fetal weight in RUPP animals Tx with high dose VEGF doesn’t return to normal. Makes us wonder what the appropriate BP targets are – the High BP could be a compensation to get bld to fetus. The placenta lacks the normal autoreg capacity like other organs. -sFlt-1 receptor decreased in RUPP rats by exogenous VEGF121 infusion -ratios of hormones maybe the important factors, it may be enough to keep bp low enough. Could timing of ischemia be important? The timing of reduced bld flow plays a role in if a woman has just a growth restricted baby or a woman who has pre-ecclampsia with growth restricted baby. late preg grp gives you an inc in all the assoc factors -early grp give you growth restriction—bp went up in this grp but not as much as late group. -Timing of Placental ischemia influences maternal sFlt-1 concentrations Long term effects of Preeclampsia •Moms •Decreased cancer incidence •Glucose intolerance (T2DM) •Endothelial dysfunction •Increased risk of CVD, hypertension, etc. •Kids •Increased risk of CVD, hypertension, etc. •Altered incidence of cancer His research: Formerly RUPP rats show no evidence of glucose intolerance (dif than European human studies) -Formerly RUPP rats have endothelial dysfunction in renal microvessels that is attenuated by the antioxidant Tempol -bld vessels don’t relax as much in stim to Ach -this dif may be mediated by oxidants – so admin tempol -Increased breast cancer susceptibility in IUGR (Intrauterine growth rate) offspring -small babies have much greater likelihood for developing cancer. Future Directions •Does exercise training before/during pregnancy prevent hypertension associated with placental ischemia -from animal studies – mix results if it alters fetal growth. -if you already exercise – no need to stop. If you don’t, no need to start. Future treatment of preeclampsia •Prophylatic •Exercise •Symptom suppression = delayed treatment? (concern) •Early identification: Enhanced perinatal care •Symptom Treatment (hydralazine, VEGF, TGF-β, 2-ME, antioxidants?, etc.) •Safely lengthen gestation •Enhance maternal/fetal outcomes Considerations for Preeclamptic Patients •Preeclampsia as an independent risk factor •Lifestyle modifications •Proactive health care -This is his research model – clinical studies, animal models, and in vitro studies to develop effective strategies for prevention/Tx of precclampsia Practice Questions: 1. Describe the pathologic changes in the spiral arteries of pre-ecclamptic patients 2. List 4 risk factors for pre-ecclampsia 3. What effect does VEGF have in pre-ecclampsia? 4. Describe the relationship between pre-ecclampsia and breast cancer. Answers 1. Spiral artery converted from high to low Resistance bed – doesn’t occur in pre-ecclampsia. Normal =Makes it more like a vein so not responsive to vasoconstrictors 2. •Age > 35 yrs or < 20 yrs & obesity •Parity •Ethnicity (African-American, Native American) •Family History or previous preeclamptic pregnancy •Gestational diabetes, obesity, preexisting hypertension/renal disease, BP, thrombophilia •Higher order pregnancy (assisted repro preg) •Autoimmune disorders (Antiphospholipid syndrome, lupus) •Inter-pregnancy interval - age dept on mom 3. educes high blood pressure associated with placental ischemia, but the doesn’t improve birth weight 4. Mom: Some of these markers are also associated in mammary development – may alter differentiation of epithelium and reduced cancer rates seen in these women. Baby: Increased breast cancer susceptibility in IUGR (Intrauterine growth rate) offspring -small babies have much greater likelihood for developing cancer.











