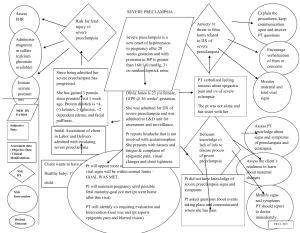
1. What are the major differences between gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia? Gestational hypertension develops halfway through pregnancy around 20 weeks and is most common in women pregnant for the first time. Diagnosed when blood pressure is higher than 140/90/ Preeclampsia – is also high blood pressure during pregnancy but can be fatal to the baby and mother. It also causes damage to other organs. Also there is protein in he urine. Eclampsia – is a complication preeclampsia characterized by seizures and coma. 2. What is the pathophysiology that leads to these conditions? Gestational hypertension is caused by unknown factors. Preeclampsia – This is cause by abnormal blood vessels in the placenta which cause insufficient blood supply to the uterus and damaged blood vessels. Eclampsia – Chromosome abnormality, immunologic defects, and placental infraction are all possible causes. 3. What is HELLP syndrome and how does it differ from preeclampsia? HELLP syndrome is a highly fatal liver disorder which is a type of preeclampsia. It stands for Hemolysis elevated liver enzyme and low platelet count. Your bp can remain normal with HELLP syndrome. 4. What are the common medications used to treat preeclampsia and what risks do they carry? Labetalol - it slows down the heart rates, making it easier for the heart to pump blood around the body and can not be discontinued abruptly. Magnesium sulfate – prevents seizures. Can cause breathing difficulties and lower bp Methyldopa – headaches vomiting edma. 5. What is the nursing management for each? Methyldopa – Monitor VS, Is/Os, monitor for hypotension. Labetalol- monitor Bp, educate pt about not standing up to quickly, the nurse should take the blood pressure immediately before the administration. Magnesium sulfate – Test reflexs, Monitor magnesium levels, and encourage fluids. 6. What assessments need to be conducted frequently for the patient with preeclampsia? Weighing the patient regularly, check for edma, monitor Is and Os, checking lung sound, monitoring vitals, LOC, deep tendon reflex, and urinalysis. 7. Describe deep tendon reflexes and how they are graded. Grade 0 = No Resonse Grade 1+ = Diminished/depressed response Grade 2+ = Active normal response Grade 3 = Brisk/exaggerated response Grade 4+ = Very brisk/hyperactive; abnormal response 8. Discuss why a patient with preeclampsia is at risk for seizures. What are seizure precautions and how are they instituted? When arteries are damaged, there is a restriction in the blood flow. It can produce swelling in the blood vessels in the patient's brain and in the growing baby. If this abnormal blood flow through vessels hinders the brain's ability to function, seizures may occur. 9. Describe the nursing care involved with seizure activity. Note when the seizure began, turn pt to side, maintain patent air way, pad bed rails, and monitor the fetus. 10. What are the signs of magnesium toxicity in the mother and the baby? The most common signs of developing magnesium toxicity include respiratory depression, nausea, muscle weakness, loss of reflexes, and decrease in BP or pulse. Also low urine output. 11. What are the risks to the mother and fetus in states of hypertension or magnesium sulfate toxicity? abruptio placenta, preterm birth/premature delivery, and pregnancy loss or stillbirth. 12. What is the definitive treatment and why? The definitive treatment of preeclampsia/eclampsia is delivery of the fetus. This is to prevent the development of maternal or fetal complications from disease progression. Delivery leads to the ultimate resolution of the disease. 13. Identify the common lab tests indicated for the patient with preeclampsia and discuss the cause of abnormal findings. In addition, describe L/S ratio and phosphatidylglycerol and identify why these tests are important prior to delivery of the baby. Urine analysis. measurement of the amount of protein in the urine. Uric acid. Increased uric acid in the blood is often the earliest laboratory finding related to preeclampsia. Hematocrit. A high hematocrit value can be a sign of preeclampsia. The focus of testing the L/S ratio is to determine fetal lung maturity to decrease the risk of delivering a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome. Amniotic fluid phosphatidylglycerol is an early indicator of fetal lung maturity.