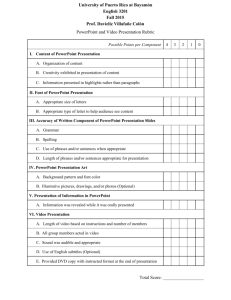
construction

PowerPoint Presentations
Why use PowerPoint?
Amount of information
Font
Color
Extras
Examples
Why use PowerPoint?
Reach different learning styles
Reinforce key information
Give clear prompts for assignments
Move presentation directly to your web site
Keeps instructor organized and on task
Serves as Ockham’s razor
Amount of information
Ockham’s razor: “entities are not to be multiplied beyond necessity”
Less is more A good rule of thumb:
No more than 6 words per line.
No more than 6 lines per slide.
What do I really want them to know?
What can they see / read / take in?
Why use PowerPoint?
PowerPoint allows me to reach students of different learning styles because it adds a visual element to my oral presentation.
This is especially important because today’s students seem to be more visual than other generations.
It helps reinforce the key information in my presentation and keeps student interest focused on the front of the room.
It allows me to give students clear prompts for their assignments, especially in-class assignments. They can always look up to refocus their attention to the assigned task.
A PowerPoint presentation can be moved directly to your web site so that students can look at it again after class and as many times as they want.
PowerPoint forces an instructor to organize his or her lecture and presentation material and keeps them on track and focused.
It serves as Ockham’s razor by helping me structure my thoughts.
Why use PowerPoint?
Reach different learning styles
Reinforce key information
Give clear prompts for assignments
Move presentation directly to your web site
Keeps instructor organized and on task
Serves as Ockham’s razor
Font
Choose font size and type for your particular context.
Use same font for continuity.
Use 2 contrasting fonts to organize information, for emphasis
.
--
Comic Sans &
Arial --
Font Legibility
ALL CAPS vs.
Upper & Lower case
Font Style
Serif
Which of these is easier to read?
(Times New Roman 36)
Sans Serif
Which of these is easier to read?
(Arial 32)
Font Size
12: Read this.
20: Read this.
32: Read this.
36: Read this.
40: Read this.
44: Read this.
60: Read this.
Color
Uses: contrast, emphasis , interest
Contrast between text & background
-- computer projection: dark background, light text
-- overhead projector: light background, dark text
With newer computer projectors, this difference is minimal
Color
Uses: contrast, emphasis, interest
Contrast between text & background
-- computer projection: dark background, light text
-- overhead projector: light background, dark text light background, dark text
Color
Use a consistent color scheme for continuity.
Avoid reds & greens .
Use color sparingly for emphasis.
Don’t get carried away!
Slide Transitions
Chose one transition and use for all sides
Transition should be (almost) transparent
Used to draw viewer to the next slide
Extras:
Pictures & Animation
Group Discussion
How do maps influence our thinking about the world?
Individual Midterm Grades
50
40
30
20
10
0
A B C D F
16 41 49 43 22
C
D
A
B
F
Images
Generate interest
Illustrate points
Decorate
Visual Literacy
Font Color
Content
Amount Extras
Visual Literacy
Russia:
From Empire to Federation
Russia:
From Empire to Federation
Russia:
From Empire to Federation
Russia:
From Empire to Federation
Public Speaking Rule 1:
Know Your Subject
Public Speaking Rule 2:
Know Your Audience
It is a period of peace,
A long time ago in a galaxy far, far away. . . .
‘ nirvana ’ there.
Group Writing
With your group, list things in the picture that help us determine the location of this picture.
What does this scene suggest?
Make your own!
Create your own presentation on one of the articles from the Learning section of your notebook or your class material
--a minimum of 2 slides
--design for this room