3rd Grade Writing Pacing Guide 11-12
advertisement

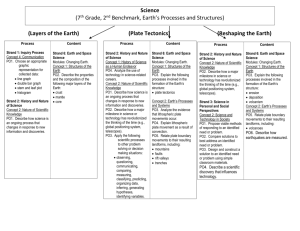
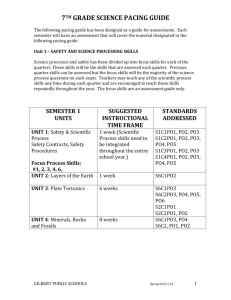
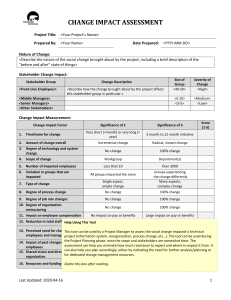
Writing Pacing Guide Third Grade Integrate the Writing Process and Writing Components Throughout the Year Strand 1. Writing Process Strand 2. Writing Components Concept 1: Prewriting Concept 1: Ideas and Content PO1. Generate ideas through a variety of activities (e.g., PO1. Express ideas that are clear and directly related to the topic. prior knowledge, discussion with others, printed material PO2. Provide content and selected details that are well suited to audience and purpose. or other sources). PO3. Use relevant details to provide adequate support for the ideas. PO2. Determine the purpose (e.g., to entertain, to inform, Concept 2: Organization to communicate, to persuade, to explain) of an intended PO1. Organize content in a selected format. (e.g., letter format, narrative, lines of writing piece. poetry). PO3. Determine the intended audience of a writing piece. PO2. Create a beginning that captures the reader’s interest. PO4. Use organizational strategies (e.g., graphic PO3. Place details appropriately to support main idea. organizer, KWL chart, log) to plan writing. PO4. Use transitional words or phrases (e.g., next, then, so, but, while, after that, PO5. Maintain a record (e.g., lists, journals, folders, because) to connect ideas. notebooks) of writing ideas. PO5. Create an ending that provides a sense of resolution or closure. PO6. Use time management strategies, when PO6. Construct a paragraph that groups sentences around a topic. appropriate, to produce a writing product within a set time Concept 3: Voice period. PO1. Show awareness of the audience through word choice and style. Concept 2: Drafting PO2. Convey a sense of originality, sincerity, liveliness, or humor appropriate to the PO1. Use a prewriting plan to develop a draft with main topic and mode of writing. idea(s) and supporting details. Concept 4: Word Choice PO2. Organize writing into a logical sequence that is PO1. Use a variety of specific and accurate words that effectively convey the intended clear to the audience. message. Concept 3: Revising PO2. Use descriptive words and phrases that energize the writing. PO1. Evaluate the draft for use of ideas and content, PO3. Apply vocabulary and/or terminology appropriate to the type of writing. organization, voice, word choice, and sentence fluency. PO4. Use literal and figurative language in a variety of ways. (e.g., imitating, creating PO2. Add details to the draft to more effectively new words, rhyming) (although may be inconsistent or experimental) accomplish the purpose. Concept 5: Sentence Fluency PO3. Rearrange words, sentences, and paragraphs to PO1. Write simple and compound sentences. clarify the meaning of the draft. PO2. Write sentences that flow together and sound natural when read aloud. PO4. Use a combination of sentence structures (i.e., PO3. Vary sentence beginnings, lengths, and patterns to enhance flow of the writing. simple and compound) to improve sentence fluency in the Concept 6: Conventions draft. PO1. Use capital letters for: a. proper nouns d. abbreviations PO5. Modify word choice appropriate to the application in b. titles e. literary titles order to enhance the writing. c. names of places PO7. Apply appropriate tools or strategies (e.g., peer PO2. Punctuate endings of sentences using: review, checklists, rubrics) to refine the draft. a. periods c. exclamation points PO8. Use resources and reference materials to select b. question marks more precise vocabulary. PO3. Use commas to punctuate: Concept 4: Editing a. items in a series c. dates b. greetings and closings of a letter PO1. Identify punctuation, spelling, and grammar and PO4. Use quotation marks to punctuate dialogue, although may be inconsistent or usage errors in the draft. experimental. PO2. Use resources (e.g., dictionary, word lists, PO5. Use colons to punctuate time. spelling/grammar checkers) to correct conventions. PO6. Use apostrophes to punctuate. PO3. Apply proofreading marks to indicate errors in a. contractions b. singular possessives conventions. PO7. Spell high frequency words correctly. PO4. Apply appropriate tools (e.g., peer review, PO8. Use common spelling patterns/generalizations to spell words correctly, including: checklists, rubrics) to edit the draft. a. word families f. CVC words Concept 5: Publishing b. regular plurals g. CCVC PO1. Prepare writing in a format (e.g., oral presentation, c. r-controlled h. CVCC d. diphthongs i. Affixes manuscript, and multimedia) appropriate to audience and e. consonant digraphs purpose. PO9. Spell homonyms correctly in context. PO2. Share the writing with the intended audience. PO10. Use resources (e.g., dictionaries, word walls) to spell correctly. PO3. Use margins and spacing to enhance the final PO11. Use the following parts of speech correctly in simple sentences. product. a. nouns c. personal pronouns PO4. Write legibly. b. action verbs d. adjectives PO12. Use subject/verb agreement in simple and compound sentences. 1 Glendale Elementary School District 3/16/2016 Writing Pacing Guide Third Grade Integrate Literary Response Throughout the Year Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 5: Literary Response PO1. Write a reflection to a literature selection (e.g., journal entry, book review). PO2. Write a book report or review that may identifies the: a. b. c. main idea character(s) setting d. e. sequence of events problem/solution a. text to world PO3. Write a response to a literature selection that connects: a. b. text to self text to text Instructional Period 1 Simple Sentence (Main Sentence Trunk) Vary sentence beginnings a. b. c. d. e. Article + noun = the dog…, Pronoun=It …, Article + adjective + noun = The furry dog Possession pronoun + adjective + noun = my furry dog.., When Phrase = Early in the morning Verb Modifiers (Action Expander) a. b. c. d. e. When phrase (effective at beginning) Where phrase (begin with prepositions) Why phrase (complex sentence) How (adverb, adverbial phrase, simile) Use literal and figurative language where appropriate to purpose Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 2: Expository Defining / Describing PO1. Record information (e.g., observations, notes, lists, charts, map labels and legends) related to the topic. PO2. Write an expository paragraph that contains: a. b. c. a topic sentence supporting details relevant information PO3. Write in a variety of expository forms (e.g., essay, summary, newspaper article, reflective paper, log, or journal). Concept 6: Research PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. 2 Instructional Period 2 Instructional Period 3 Instructional Period 4 Instructional Period 5 Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 2: Expository Problem/Solution PO1. Record information (e.g., observations, notes, lists, charts, map labels and legends) related to the topic. PO2. Write an expository paragraph that contains: Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 2: Expository Comparison PO1. Record information (e.g., observations, notes, lists, charts, map labels and legends) related to the topic. PO2. Write an expository paragraph that contains: a. b. c. a. b. c. Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 2: Expository Integration of Paragraph Organizations PO1. Record information (e.g., observations, notes, lists, charts, map labels and legends) related to the topic. PO2. Write an expository paragraph that contains: Verb Modifiers (Action Expander) Predicates (3 Action) a. a. b. b. c. d. e. When phrase (effective at beginning) Where phrase (begin with prepositions) Why phrase (complex sentence) How (adverb, adverbial phrase, simile) Use literal and figurative language where appropriate to purpose Noun modifiers (Surround-the-Noun) a. Adjective before noun ‘With” phrase after the noun Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 2: Expository Chronological and Sequential Order PO1. Record information (e.g., observations, notes, lists, charts, map labels and legends) related to the topic. PO2. Write an expository paragraph that contains: a. b. c. a topic sentence supporting details relevant information PO3. Write in a variety of expository forms (e.g., essay, summary, newspaper article, reflective paper, log, or journal). Concept 6: Research PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. Glendale Elementary School District 3/16/2016 c. d. Begin with a verb Construct sentences with subject/verb agreement Use action verbs with the same verb tense Use specific nouns and action verbs Context Sentences Context proves meaning of word (i.e., synonyms, antonyms, examples, restatement, definition, and explanation) Compound Sentences and Complex a topic sentence supporting details relevant information PO3. Write in a variety of expository forms (e.g., essay, summary, newspaper article, reflective paper, log, or journal). Concept 6: Research PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. a topic sentence supporting details relevant information PO3. Write in a variety of expository forms (e.g., essay, summary, newspaper article, reflective paper, log, or journal). Concept 6: Research PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. a. b. c. a topic sentence supporting details relevant information PO3. Write in a variety of expository forms (e.g., essay, summary, newspaper article, reflective paper, log, or journal). Concept 6: Research PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. Writing Pacing Guide Third Grade Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 1: Expressive Personal Narrative PO1. Write a narrative based on imagined or real events, observations, or memories that includes: a. b. c. d. e. f. characters setting plot sensory details clear language logical sequence of events Poetry PO2. Write in a variety of expressive forms (e.g., poetry, skit) that may employ: a. b. c. figurative language rhythm appropriate format Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 1: Expressive Poetry PO2. Write in a variety of expressive forms (e.g., poetry, skit) that may employ: a. b. c. figurative language rhythm appropriate format Narrative PO1. Write a narrative based on imagined or real events, observations, or memories that includes: a. b. c. d. e. f. characters setting plot sensory details clear language logical sequence of events Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 3: Functional Friendly Letter PO2. Write communications, including: thank-you notes, friendly letters, messages and invitations. PO3. Address an envelope for correspondence that includes: an appropriate return address and an appropriate recipient address. Concept 4: Persuasive Persuasive PO1. Write persuasive text (e.g., advertisements, paragraph) that attempts to influence the reader. Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 4: Persuasive Persuasive PO1. Write persuasive text (e.g., advertisements, paragraph) that attempts to influence the reader. Concept 3: Functional Formal / Business Letter PO2. Write communications, including: a. formal letters PO3. Address an envelope for correspondence that includes: an appropriate return address and an appropriate recipient address. Concept 3: Functional PO1. Write a variety of functional texts (e.g., directions, recipes, procedures, rubrics, labels, posters, graphs/tables). 3 Glendale Elementary School District 3/16/2016 Strand 3: Writing Applications Concept 6: Research Informational Report PO1. Paraphrase information from a variety of sources (e.g., Internet, reference materials). PO2. Organize notes in a meaningful sequence. PO3. Write an informational report that includes main ideas and relevant details. Concept 3: Functional PO1. Write a variety of functional texts (e.g., directions, recipes, procedures, rubrics, labels, posters, graphs/tables).