Classification techniques for Creativity & Problem Solving
advertisement

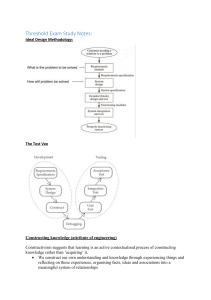
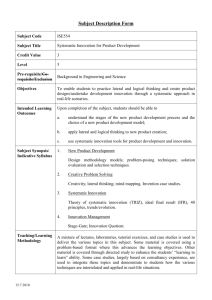
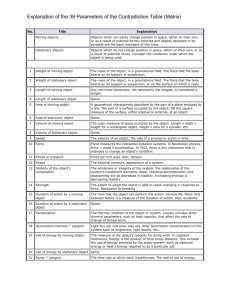
Power Principle of Operation Mechanical Action Chemical Action Electro-magnetic Action Electric Source Nuclear Action Biological Action Non Coordinate Partially Coordinate Coordinate Opposite Future & Innovation Valerio Abate The Innovation Balance • No Problem…. ….No Solution • No Contraddiction . . . . . . . . No Invention Operative Learning "the answer is within the problem“ A.Einstein The Dialectic Paradox Exercise (From “Creative Genius”) This is a 4 four step exercise to learn one principle of “inventing”. How to extract a solution from within the problem itself using the principle: Resolution of Opposites The Dialectic Paradox: Step 1 Goal: Extract & Consolidate Knowledge. Method: Find the word that most describes the problem. Mechanism: Put a problem or issue into one word. Example: If it is a struggle with someone, perhaps the word most descriptive of the problem would be "conflict". If it is a feeling of being unmotivated or stuck, perhaps the word might be "stagnate". Find the best word to describe the negative side of the problem. The Dialectic Paradox: Step 2 Goal: Search & Extract New Knowledge Method: Find the polar opposite word. Mechanism: Choose the word that best describes the ideal resolution of the issue. Example: the resolution of "conflict" could be "harmony" and for "stagnate", it might be "motivated". The Dialectic Paradox: Step 3 Goal: Generate New Concepts Method: Semantic Innovation Mechanism: Put the words into a two word phrase. Example: "motivated stagnation" or "stagnate motivation", or "harmonious conflict" or "conflictual harmony". The Dialectic Paradox: Step 4 Goal: Synthesize New Solution Method: Resonate with these opposites Mechanism: think of some examples of them in an object or process Example: "harmonious conflict" might be mediation, negotiation, symphony, akido, parasites, fever. "Stagnate motivation" might be hibernation, cocoon, meditation, yoga, etc. This step is one that usually takes some time and/or is one that is helpful to brainstorm with other people. The Development of Anything • Human activities needed to innovate: – Creativity This thing has value! – Problem Solving I got the contraddiction! – Representation This is the shape! The Development of the Innovation Development System Knowledge Creativity Problem Solving Design Market Classification techniques for Creativity & Problem Solving Description 1 Conditioning/motivating/organizing techniques (metal blocks) 2 Randomization (psychological inertia) 3 Focusing techniques (Frustration due to lack of guidelines) 4 Systems (Focusing +Random Flows) 5 Pointed techniques (“think in the box”) 6 Evolutionary directed techniques (life of technical systems ) Example Listening to music Brainstorming Attribute listing QFD Problem reversal Utilization of the TRIZ Patterns/Lines of Technological Evolution 7 Innovation knowledge-base techniques Contradiction Table and 40 (lack of knowledge structure) Innovation Principles Creativity & Problem Solving Methods M e t ho d M e t ho d Group Psychological 1 1. Rand o m inp ut 2 . Pro b lem revers al 3 . Ques tio ns As k 4 . Ques tio n Summary 5. Lateral Thinking 6 . The Dis co ntinuity Princip le 7. Thinkerto ys 8 . Brains to rming 9 . Fo rced Analo g y 10 . Attrib ute Lis ting 11. M o rp ho lo g ical Fo rced Co nnectio ns 12 . M o rp ho lo g ical Analys is 13 . Imitatio n 14 . M ind M ap s * 15. Sto ryb o ard ing 16 . Synectics ** 17. Lo tus Blo s s o m Techniq ue 18 . In the Realm o f the Sens es 19 . Drawing and Vis ual Thinking 2 0 . Camelo t 2 1. Checklis ts 2 2 . Limericks and p aro d ies 2 3 . Ro le p laying 2 4 . Wo rko ut/retreats 2 5. Kep ner-Treg o e 2 6 . Draw a p icture 2 7. Exp erience kit 2 8 . Fis hb o ne d iag ram 2 9 . King o f the mo untain 3 0 . Red efining a p ro b lem/o p p o rtunity 3 1. Sq ueeze and s tretch 3 2 . What p atterns exis t? 3 3 . Why-why d iag ram 2 3 X X X X X X X X 4 5 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Group Psychological X X X X X X X X M e t ho d Group X X X X 6 7 1 3 3 . Why-why d iag ram 3 4 . As s ump tio n revers al 3 5. As s o ciatio ns 3 6 . Circle o f o p p o rtunity 3 7. Dead lines 3 8 . Fres h eye 3 9 . Id ea b its and racking 4 0 . Id ea no teb o o k 4 1. Inp ut-o utp ut 4 2 . Lis tening to mus ic 4 3 . Name p o s s ib le us es 4 4 . The Nap o leo n techniq ue 4 5. Pro d uct imp ro vement 4 6 . Related nes s 4 7. Relatio nal wo rd s 4 8 . Revers al – d erevers al 4 9 . 7x7 techniq ue 50 . Sleep ing /d reaming o n it 51. The two -wo rd s techniq ue 52 . Vis ualizatio n 53 . What if? 54 . Go rd o n/Little 55. Gro up d ecis io n s up p o rt 56 . Id ea b o ard 57. Id ea trig g ers 58 . Inno vatio n co mmittee 59 . Interco mp any inno vatio n 6 0 . Lio n’s d en 6 1. NHK metho d 6 2 . No minal g ro up techniq ue 6 3 . Phillip s 6 6 6 4 . Pho to excurs io n 2 Psychological 3 4 5 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X 6 7 1 6 5. Scenario writing 6 6 . SIL metho d (co mb ining ) 6 7. TKJ 6 8 . Delp hi 6 9 . (NLP) 70 . As s ump tio n Smas hing 71. DO IT 72 . LARC 73 . Unco ns cio us Pro b lem So lving 74 . Bas ad ur Simp lex p ro ces s 75. Fuzzy Lo g ic (Fuzzy Thinking ) 76 . SERENDIPITY 77. Wallas ’ mo d el 78 . Ro s s man creativity mo d el 79 . Wo rking Pap er: M o d els fo r the Creative 8 0 . Barro n’s Ps ychic Creatio n M o d el 8 1. Creative Pro b lem So lving (CPS) 8 2 . Univers al Traveler M o d el 8 3 . Ro b ert Fritz’s Pro ces s fo r creatio n 8 4 . Seven Step s b y Ro g er vo n Oech 8 5. TRIZ Co ntrad ictio n Tab le and 4 0 8 6 . TRIZ Id eality Co ncep t 8 7. TRIZ Sys tem Ap p ro ach 8 8 . TRIZ Patterns /Lines o f Evo lutio ns 9 1. TRIZ ARIZ 9 2 . TRIZ Sub s tance-Field Analys is 9 3 . TRIZ 76 Stand ard So lutio ns 9 4 . TRIZ Sys tem o f Op erato rs X X X 2 3 X X X X 4 5 X X X X 6 7 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Innovation of Systems Subset of Laws of System Evolution Laws of Dialectics The Law of the Unity of Opposites Key Concept:Contraddictions The Laws of Trasformation of Quantity into Quality Key Concept: S-Curve The Law of the Negotiation of the Negotiation Key Concepts: Spiral Shaped Evolution Contraddiction Transition To Supersystem Time Separation Space Separation Transition To Subsystem Phase Space Separation S-Curves Parameter P Life Time S-Curve Jump Spiral Shaped Innovation m a t r i a l s Fashion