ISE554: Systematic Innovation for Product Development
advertisement

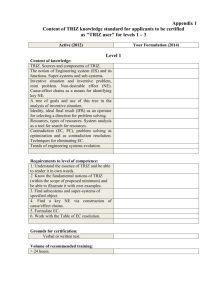
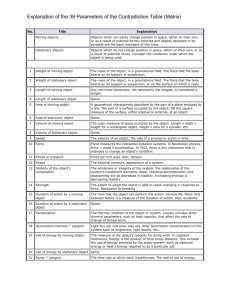
Subject Description Form Subject Code ISE554 Subject Title Systematic Innovation for Product Development Credit Value 3 Level 5 Pre-requisite/Corequisite/Exclusion Background in Engineering and Science Objectives To enable students to practice lateral and logical thinking and create product designs/undertake development innovation through a systematic approach in real-life scenarios. Intended Learning Outcomes Upon completion of the subject, students should be able to Subject Synopsis/ Indicative Syllabus a. understand the stages of the new product development process and the choice of a new product development model; b. apply lateral and logical thinking to new product creation; c. use systematic innovation tools for product development and innovation. 1. New Product Development Design methodology models; problem-posing techniques; solution evaluation and selection techniques. 2. Creative Problem Solving Creativity; lateral thinking; mind mapping. Invention case studies. 3. Systematic Innovation Theory of systematic innovation (TRIZ), ideal final result (IFR), 40 principles, trends/evolution. 4. Innovation Management Stage-Gate; Innovation Quotient. Teaching/Learning Methodology 15.7.2010 A mixture of lectures, laboratories, tutorial exercises, and case studies is used to deliver the various topics in this subject. Some material is covered using a problem-based format where this advances the learning objectives. Other material is covered through directed study to enhance the students’ “learning to learn” ability. Some case studies, largely based on consultancy experience, are used to integrate these topics and demonstrate to students how the various techniques are interrelated and applied in real-life situations. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Intended Learning Outcomes Specific assessment methods/tasks % weighting Intended subject learning outcomes to be assessed a b c 1. Assignments/Tutorials/Laboratories 40% 2. Case studies 30% 3. Test 30% Total 100% The assignments, which are administered throughout the course, are designed to facilitate students to reflect on and apply the knowledge learnt. Continuous assessment comprises laboratories, tutorials, assignments, one miniproject with individual and group assessment components, and a final examination. All assessment components require students to apply what they have learnt to realistic work scenarios. Student Study Effort Expected Class contact: Lectures 2 hours/week for 8 weeks 16 Hrs. Tutorials 3 hours/week for 6 weeks 8 Hrs. Laboratory work 9 Hrs. Case studies 9 Hrs. Other student study effort: Preparation for assessment and case studies Total student study effort Reading List and References 15.7.2010 84 Hrs. 126 Hrs. 1. Masahiro Takahashi 1999, From Idea to Product – The Integrated Design Process, Hong Kong Productivity Council 2. Altshuller, G.; et al. 1997, 40 Principles: TRIZ Keys to Technical Innovation, Technical Innovation Center 3. Altshuller, G. 1999, The Innovation Algorithm: TRIZ, Systematic Innovation and Technical Creativity, Technical Innovation Center 4. Buzan, Tony & Buzan, Barry 1995, The Mind Map Book, BBC Books 5. de Bono Edward 1977, Lateral Thinking, Penguin Books 15.7.2010 6. Mann, D. 2002, Hands-On Systematic Innovation, CREAX Press 7. Pugh, S. 1999, Total Design: Integrated Methods for Successful Product Engineering, Addison Wesley/Longman 8. Rantanen, K. and Domb, E. 2000, Simplified TRIZ, Saint Lucie Press 9. Savransky, S. D. 2000, Engineering of Creativity: Introduction to TRIZ Methodology of Inventive Problem Solving, CRC Press 10. Terninko, J.; et al. 1998, Systematic Innovation: An Introduction to TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving), Saint Lucie Press