PPT
advertisement

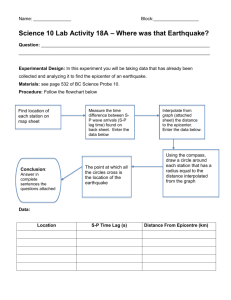
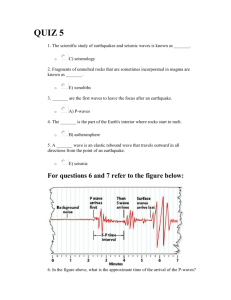
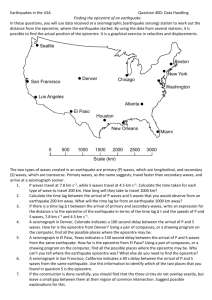
1. Causes: A. plate tectonics (elastic rebound theory) faults “stick” buildup of energy when they slip lots of energy is released = EARTHQUAKE B. glacial rebound theory heavy glacier compresses ground ground springs back up = EARTHQUAKE 2. Earthquake terms: Focus: origin of energy release (deep underground) Epicentre: point on surface above the focus Liquifaction: when land turns to mud when shaken Tsunami: giant wave resulting from earthquake in ocean low in ocean, but fast moving friction slows it down as it nears shore grows up to 80 m high!! Diagram of science! Aftershocks: minor faults nearby breaking loose follow major quakes Seismic waves: 3 types of waves emitted from earthquakes 1. P – wave (primary) push / pull (compressional wave) moves fast 3. L – wave (Love) 2. S – wave (secondary) side-to-side motion (“shear” wave) moves more slowly rolling motion last to arrive travels along surface of Earth most damaging 3. Finding the Epicentre of an Earthquake: The distance between the P & S – waves increases as waves travel outward from the epicentre. How much time that passed between the detection of the P & S – waves can be used to determine how far away the epicentre was. With 3 stations calculating distances to the epicentre of the earthquake, the epicentre can be pinpointed. Homework: Textbook Page 531, “Reading Check”, Questions 1-3 Virtual Seismologist Activity 2 Earthquake Certificates must be printed / emailed with your name on them (can’t do San Francisco) http://nemo.sciencecourseware.org/VirtualEarthquake/VQuakeExecute.html