Earthquakes in the USA
advertisement

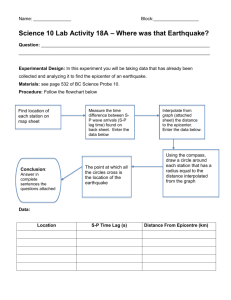
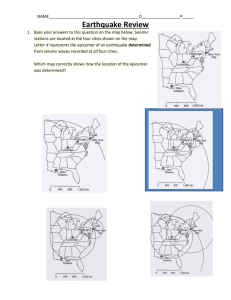
Earthquakes in the USA Question 40D: Data Handling Finding the epicentre of an earthquake In these questions, you will use data received at a seismographic (earthquake sensing) station to work out the distance from the epicentre, where the earthquake started. By using the data from several stations, it is possible to find the actual position of the epicentre. It is a graphical exercise in velocities and displacements. Seattle Boston New York Denver San Francisco Chicago Washington Los Angeles Atlanta El Paso Houston New Orleans 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Miami 3000 Scale (km) The two types of waves created in an earthquake are primary (P) waves, which are longitudinal, and secondary (S) waves, which are transverse. Primary waves, as the name suggests, travel faster than secondary waves, and arrive at a seismograph sooner. 1. P waves travel at 7.8 km s–1, while S waves travel at 4.5 km s–1. Calculate the time taken for each type of wave to travel 200 km. How long will they take to travel 1000 km? 2. Calculate the time lag between the arrival of P waves and S waves that you would observe from an earthquake 200 km away. What will the time lag be from an earthquake 1000 km away? 3. If there is a time lag Δ t between the arrival of primary and secondary waves, write an expression for the distance x to the epicentre of the earthquake in terms of the time lag Δ t and the speeds of P and S waves, 7.8 km s–1 and 4.5 km s–1. 4. A seismograph in Denver, Colorado indicates a 100 second delay between the arrival of P and S waves. How far is the epicentre from Denver? Using a pair of compasses, or a drawing program on the computer, find all the possible places where the epicentre may be. 5. A seismograph in El Paso, Texas indicates a 130 second delay between the arrival of P and S waves from the same earthquake. How far is the epicentre from El Paso? Using a pair of compasses, or a drawing program on the computer, find all the possible places where the epicentre may be. Why can't you tell where the earthquake epicentre was? What else do you need to find the epicentre? 6. A seismograph in San Francisco, California indicates a 40 s delay between the arrival of P and S waves from the same earthquake. Use this information to identify which of the two places that you found in question 5 is the epicentre. 7. If the construction is done carefully, you should find that the three circles do not overlap exactly, but leave a small gap between them at their region of common intersection. Suggest possible explanations for this.