Calculating Formal Charges
advertisement

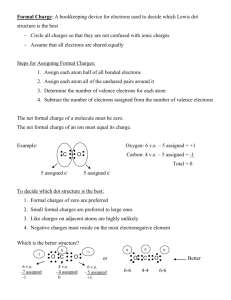
Calculating Formal Charges Simple but significant What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • The Formal Charge is a mathematical summation of the number of actual electrons associated with an atom in a molecule. “Electronic Bookkeeping” • The Formal Charge is all determined relative to the number of valence electrons an atom would have in the ground state. • Remember, valence electrons are those found in the outermost unfilled shell. What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • Anytime you see a charge in a molecule, it tells you that the atom with the charge has more or less electrons than it normally would. • A -1 charge equals one extra electron on an atom. • A +1 charge equals one less electron on an atom. What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • Charges can be found on all sorts of atoms common to organic chemistry, including carbons, oxygens, nitrogens and halides. • Remember that carbon typically has four covalent bonds. If it has only three, then it will be a charged atom, depending on whether it has a lone pair or O not. H C H C What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • Oxygen atoms, when neutral, have two covalent bonds and two lone pairs, like in water. Often though oxygen atoms may have negative or positive charges. • Nitrogen atoms, when neutral, have three covalent bonds and one lone pair. These can also have negative or positive charges, depending on what is bonded. What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • The presence of more or less electron density in a molecule dictates the flow of electrons in a process so this is really helpful information. • So – how do you calculate the Formal Charge on an atom? What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • The equation to determine the Formal Charge on an atom: FC = (The number of valence electrons on the atom in the ground state) – ½ (total number of electrons in covalent bonds attached to the atom, with each covalent bond having two electrons) – (all electrons in lone pairs on an atom, with each lone pair equal to two electrons). • So: FC = #Valence – ½ (bonding) – (all lone pair electrons) What is the Formal Charge of an Atom? • Keep in mind that Formal Charge is for a specific atom so you have to know exactly which atom you are doing the calculation for. • Determine the Formal Charge on the nitrogen atom in the following: H H N H Calculating some Formal Charges • Nitrogen is in Group V and has 5 valence electrons H H in the ground state. N H • FC = #Valence – ½ (bonding) – (all lone pair electrons) • FC(N) = 5 – ½ (6) – (2) = 5 – 3 – 2 = 0 • Nitrogen has no charge – its neutral. Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on oxygen in the hydronium ion shown: H H O H • Oxygen is in Group VI and has 6 valence electrons in the ground state. • FC = #Valence – ½ (bonding) – (all lone pair electrons) Calculating some Formal Charges • FC = #Valence – ½ (bonding) – (all lone pair electrons) • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (6) – (2) = 6 – 3 – 2 = +1 H H O H Calculating some Formal Charges • Every time you see that positive charge on an atom, it technically means the atom is missing one entire electron. H H O H • In this case, the oxygen only has five electrons, not six. Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on oxygen in the molecule shown: O • Again, oxygen is in Group VI and has 6 valence electrons in the ground state. Calculating some Formal Charges • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (2) – (6) = 6 – 1 – 6 = -1 • As in this sodium salt: O Na Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on oxygen in the molecule shown: H O • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (6) – (2) = 6 – 3 – 2 = +1 H O Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on oxygen in the molecule shown: H O Calculating some Formal Charges • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (6) – (2) = 6 – 3 – 2 = +1 H O Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on nitogen in the molecule shown: H N Calculating some Formal Charges • FC(O) = 5 – ½ (8) – (0) = 5 – 4 – 0 = +1 H N Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on the (highlighted in red) in the molecule shown: O S H3C H C H carbon Calculating some Formal Charges • Carbon is in Group IV. • FC(O) = 4 – ½ (6) – (2) = 4 – 3 – 2 = -1 O S H3C H C H Calculating some Formal Charges • Calculate the formal charge on the (highlighted in red) in the molecule shown: O S H3C CH3 sulfur Calculating some Formal Charges • Sulfur is in Group IV. • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (6) – (2) = 6 – 3 – 2 = +1 O S H3C CH3 Calculating some Formal Charges • Final Problem: Calculate the formal charge on the oxygen (highlighted in red) in the molecule shown: O S H3C CH3 Calculating some Formal Charges • Oxygen is in Group IV. • FC(O) = 6 – ½ (2) – (6) = 6 – 1 – 6 = -1 O S H3C CH3 Formal Charges • Just remember: Valence Electrons minus half the bonding electrons (two per bond) minus all of the lone pair electrons (two per pair)… • Thanks for reading…