Other operators can not negotiate peer
advertisement

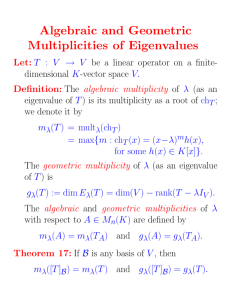
Transit & peering Taiwan Internet Interconnection problem Advisor:Kuang Chiu Huang Group:Ting Wei Lin,Ting Huei Lee, Kuei Chin Fan Outline Background Transit and peering Respect of ISPs Analysis Conclusion Background Development of Taiwan’s telecom industry Telecommunications industry has a typical characteristic of public utilities industries they have exclusive Background 1987~1996 The first time to open to competition in telecom industry 1996~2000 The introduction of infrastructure competition 2000~ Open competition completely Background The first time to open to competition in telecom industry 1987 1989 1994 • Began the liberalization of terminal equipment • liberalization of the circuit using • common data circuit rental released • open value-added network services • Open Digital Low Power Wireless telephone (CT-2) business Background The introduction of infrastructure competition 1996 •Pass the three laws of telecom mobile phone penetration rate of 108% in 2002,it was the highest • open business of mobile phone, Radio rate in the world!! Paging, mobile data and wireless telephone 1997 Background Open competition completely • open international submarine cable 2000 • International Simple Release (ISR) Business 2003 2006 2007 • mobile virtual network operator business • the National Communications Commission was established • Open wireless broadband access services Background Memorabilia April,2009 NCC asked fixed-line operators to discuss coordination August,2009 Chunghwa Telecom reduce the price April, 2013 NCC held the hearing about relevant draft amendments to the network Background Current state 80% UP domestic broadband users first provide bandwidth services Chunghwa Telecom Background Current state Chunghwa Telecom Charge the high rate fees Other ISPs what is reasonable on network interconnection prices? Transit and peering Peering Internet is composed of many ISP's network. Depending on the connection type and pay conditions can be divided. • Public peering • Private peering Transit and peering Transit Passing packets to itself and other downstream domains, in addition, is also responsible for the traffic to other domains Transit and peering Conclusion The Internet and fixed-line market is still only oligopolistic. the authorities should be actively controlled. While others were also thrown free interconnects voice, but this in turn involves fairness and justice. Transit and peering Conclusion The Internet and fixed-line market is still only oligopolistic. the authorities should be actively controlled. While others were also thrown free interconnects voice, but this in turn involves fairness and justice. Respect of CHT Market mechanisms States supervisory authority for network interconnection policy, are "low control; highly consultative; scale quite free interconnection" principle. First mover advantage With unequal business model to control prices, just let small ISPs use resources of CHT in vain. State-owned enterprises Resources put into the construction is tax, if free interconnection, is tantamount to allow the private industry use national resources. Respect of other ISPs If other carriers doesn’t interconnect with CHT, the line must go through oversea, this would appear delay; therefore no other viable alternatives. CHT sets high prices of Internet interconnection. Analysis Monopoly • Other operators can not negotiate peer Other ISP industry can not be commercial negotiations on an equal footing to get a reasonable access fee. • Price squeeze Vertically integrated industry has a monopoly position, to increase the price to the downstream industry competition. • The market can not generate a positive cycle When interconnecting, the net inflow are required to pay to the net outflow.So ISPs will seek great ICP to enhance the customer experience and reduce the.Moreover,ICP get more resources to optimize content But the current situation in Taiwan, small ISPs buy bandwidth of CHT to enhance the customer experience, ICPs do that for the same reason. Government control controversy CHT has gradually cut costs and improve interconnection issues above unfair, but CHT and other operators on interconnection charges are still unable to reach a consensus. Industry self-regulation failure (TWIX inefficient) CHT past only use low bandwidth links to TWIX (only 1G in 2009), resulting in other ISPs need to buy its bandwidth. Now,CHT has increased bandwidth to TWIX about 187G (Oct 2013). Conclusion ISPs In Taiwan It will harm the industry and block the Chunghwa transit fee Free peering development . Telecom Bigger ISPs in the world Government should forma the vertical price squeeze according to the Fair Trade Act Establish relations linked between wholesale price and retail price in the future 1. Enhance the competitiveness of existing business. 2. Subscriber loop circuit fees will thus reduce 3. Attract new entrants into the broadband market