Force Powerpoint
advertisement

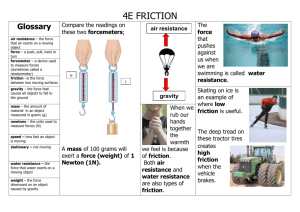
Unit 2 Force Force – push or pull • a force always acts in a certain direction • ex. if you push something, the force is in the direction of the push Forces in Nature • Electric force • ex. lightning • Magnetic force • ex. magnetic poles • Gravity Weight is a force Newton • metric unit of force What is gravity? • Sir Isaac Newton • 1642 – 1727 • The Principia Gravity • force of attraction between all objects in the universe Gravity • the larger an object’s mass, the greater the gravitational force Gravity • the greater the distance between two objects, the smaller the gravitational force • the force of gravity decreases by the amount equal to one divided by the distance (d) squared • 1/d2 What is air resistance? • air resistance • force that opposes the movement of an object in air Air Resistance • a larger surface area usually results in greater air resistance • lighter objects feel more air resistance than heavier objects Terminal Velocity • speed at which air resistance and gravity acting on an object are equal • as an object falls, it’s speed increases at a steady rate until it reaches it’s terminal velocity Vacuum – empty space • in a vacuum, all objects fall at the same speed What is friction? • Friction • force that opposes the motion of an object • the force of friction works in the opposite direction of the force of motion Types of Friction • Sliding Friction • the source of friction is the contact between two surfaces, at least one of which is in motion Types of Friction • Air Resistance • friction results from air pushing on an object as it is moving Types of Friction • Rolling Friction • friction between two surfaces that are not in constant contact • ex. wheels Friction • friction makes motion possible • friction also makes it hard to move objects • reducing friction makes it easier to move objects How can friction be reduced? • by changing sliding friction into rolling friction • by using lubricants • Lubricants – substances that reduce friction What is pressure? • Pressure • force per unit area Pressure • pressure is the amount of force acting on a surface • pressure equals force divided by area • p = f/a Pressure • pressure can be changed by changing the amount of force acting on an area • pressure can be changed by changing the area on which a force acts Fluid Pressure • pressure in gases and liquids Air Pressure • air pressure is caused by the motion of particles in the air • you do not feel the weight of the air because the pressure inside your body is equal to the air pressure around you Air Pressure • air pressure changes with altitude • the higher you are, the lower the air pressure Air Pressure • Barometer • instrument used to measure air pressure Water Pressure • the force of water pressure on an object is the same in all directions • water pressure changes with depth • the deeper you are, the greater the water pressure Water Pressure • Manometer • instrument used to measure pressure in a liquid What is Bernoulli’s principle? • Bernoulli’s Principle • principle that states that as the speed of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases Bernoulli’s Principle • airplane wings are designed to use Bernoulli’s principle • air traveling over the wings moves faster than air underneath • this reduces the pressure on top of the wing, allowing it to be pushed upward Bernoulli’s Principle • three forces combine to help an airplane fly • the upward force on a plane’s wing is called lift • a forward force, or thrust, helps the plane take off and maintain air speed • the air resistance on a plane is called drag