SPI 0807.Inq.2
advertisement

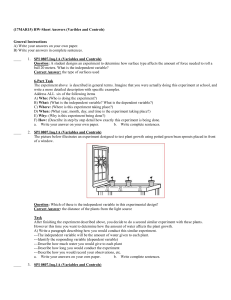
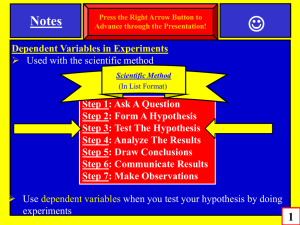
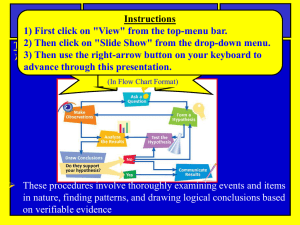
SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION TCAP REVIEW PLICKERS BELLWORK 4-7-15 • Students want to determine which type of plant will best survive in a hot, dry environment. They place four different types of plants in identical pots, and put all of the plants by the same large window. They give each plant the same amount of water every day. • Which of these is the independent variable for the students’ experiment? • a. amount of water c. type of plant • b. health of plant d. amount of sunlight SPI 0807.Inq.2 (Tools and Procedures Tools and Procedures in Science The procedures used in science are called the scientific method Video Clip Scientific Method These procedures involve thoroughly examining events and items in nature, finding patterns, and drawing logical conclusions based on verifiable evidence SPI 0807.Inq.2 (Tools and Procedures Tools and Procedures in Science The procedures used in science are called the scientific method Scientific Method (In List Format) Step 1: Make Observations Step 2: Ask A Question Step 3: Form A Hypothesis Step 4: Test The Hypothesis By doing experiments Step 5: Analyze The Results Step 6: Draw Conclusions Step 7: Communicate results A key procedure is when test your hypothesis by doing detailed and thorough experiments (step 4 shown above) Experiments In an experiment you measure a quantities and/or qualities In an experiment you should conduct multiple trials Experiments should include independent variables, dependent variables, constants, and controls. Example: Scientists could be testing a new vaccine for the flu virus to determine how effective it is Scientists could be measuring how air pollution damages plants and animals Scientists could be measuring the output of solar flares to determine how they might damage our communication satellites SPI 0807.Inq.1 Experiments (Variables and Controls) In an experiment… …you should only test for ONE key thing at a time This is called the… …after you introduce the independent variable, you observe what happens. This response/result is called the… Items or events that are repeated exactly the same way each time you duplicate an experiment are called… NOTE: You should also conduct a control experiment where you either eliminate out the independent variable or use a neutral independent variable (called a placebo) SPI 0807.Inq.2 Experiments (Tools and Procedures In an experiment… …you use scientific tools such as… …a spring scale -measures force (weight) …a graduated cylinder-measures volume …a triple beam balance -measures mass …a metric ruler or meter stick -measures length …a microscope -allows you to observe very small things …a metric thermometer-measures temperature …a stop watch -measures time …a pH indicator -measures acidity and basicity …a galvanometer -measures electrical current (strength and direction) SPI 0807.Inq.2 (Tools and Procedures Scientific Tools SPI 0807.Inq.2 (Tools and Scientific Procedures Tools In an experiment… …you could measure the strength of an acid or base with a… -measures acidity and basicity …pH Indicator -unit of measure: pH scale reading from 0 to 14 SPI 0807.Inq.2 Scientific Tools (Tools and Procedures In an experiment… …you also might use a galvanometer to measure electrical current …measures both the strength & direction of electrical current SPI 0807.Inq.2 Scientific Tools (Tools and Procedures In an experiment… …you also might use…… …beakers beaker …test tubes Test tubes …flasks flask SPI 0807.Inq.2 Scientific (Tools and Procedures In an experiment… …you also might use…… …a hot plate hot plate Tools …a Petri dish Petri dish …a Bunsen burner Bunsen burner Scientific Method (In List Format) Step 1: Make Observations Step 2: Ask A Question Step 3: Form A Hypothesis Step 4: Test The Hypothesis By doing experiments Step 5: Analyze The Results Step 6: Draw Conclusions Step 7: Communicate results Use independent variables when you test your hypothesis by doing experiments (see step 4 above) SPI 0807.Inq.1 (Variables and Controls) Experiments In an experiment you should conduct multiple trials How many? More is better! Experiments should include independent variables, dependent variables, constants, and controls. SPI 0807.Inq.1 (Variables and Controls) Experiments: In an experiment you test or measure a quantity and/or quality of something. Example: Measuring Quantity: Scientists could be testing a new cell phone battery to determine how long it will last when you are text messaging. Example: Measuring Quality: Scientists could be testing new IPod ear buds to determine if they are more comfortable or not. Example 03: A student conducts an experiment with ten 8th grade students. He uses 3 similar types of sour candy in a series of 4 trials. (Sour Patch Kids, Sour Skittles, and Warheads) He gives 1 piece of candy to each student and records their facial expressions to determine how sour each candy is. What is the independent variable in this example? In other words, what is the one thing being tested for or changed? The independent variable is the type of sour candy Example 05: A student conducts an experiment to determine which ink color in ballpoint pens will last the longest before running out. She copies text from her science book. She copies the same text over and over. She writes at the same speed. The room temperature remains the same. She writes on the same kind of paper each time.. She uses 3 ink colors in 3 ballpoint pens in a series of experiments. (1) Black ink pen, (2) Blue ink pen, (3) Red ink pen) What is the independent variable in this example? In other words, what is the one thing being tested for or changed? The independent variable is the color of ink SPI 0807.Inq.3: (Interpret Data) Different types of charts, tables, and graphs Tables Tables/charts are used to organize exact amounts of data and to display numerical information. Tables do not show visual comparisons. SPI 0807.Inq.3: (Interpret Data) Different types of charts, tables, and graphs Pie Charts A pie chart is a circular chart divided into sectors Best used for comparing parts to a whole Works well for comparing 6 or fewer items, but more than six items becomes difficult to view and interpret The total amount should equal 100% SPI 0807.Inq.3: (Interpret Data) Different types of charts, tables, and graphs Bar Graph Bar graphs are used to compare facts. The bars provide a visual display for comparing quantities in different categories Bar graphs help us to see relationships quickly. SPI 0807.Inq.3: (Interpret Data) Different types of charts, tables, and graphs Line Graph Line graphs are used to display data or information that changes continuously over time. Line graphs allow us to see overall trends such as an increase or decrease in data over time. SPI 0807.Inq.4: Cause and Effect What is cause and effect? Cause and effect refers to a connection or relationship between two actions or events Here is a way to think about this topic: ..if you do this one action then this other action will occur -The cause: is the first action or event -The effect: is the resulting consequences Example: In first period a student has a headache and is sleepy. The night before they stayed up late watching a funny TV show until 1:00 A.M. Identify the cause and effect in this situation. (see next slide) SPI 0807.Inq.4: Cause and Effect Example: In first period a student has a headache and is sleepy. The night before they stayed up late watching a funny TV show until 1:00 A.M. Identify the cause and effect in this situation. The cause (first action): was staying up late until 1:00 A.M. The effect (resulting consequences): headache & being sleepy SPI 0807.Inq.5: Bias and Error Bias and Error in Science Bias: this means you are prejudiced towards or against something and that you allow your views to affect the results of your experiment. Science is about obtaining accurate results so bias should NEVER be allowed to influence your experimental results! Bias Is Bad! Bias Bias SPI 0807.Inq.5: Bias and Error Solutions to Bias in Science Humans are imperfect, so bias happens both intentionally and unintentionally Ways to Reduce and/or Eliminate Bias Be aware that bias can and does happen Strive to recognize it, and eliminate it from your experiments. Follow the steps and principles of the scientific method Make sure that others rigorously review your work looking for bias Errors in Science Avoid Mistakes: One small error can result in all your experimental data being wrong So scientists work very hard to avoid making mistakes Peer Review: One key way scientists deal with this issue is by having other scientists review their work to check for mistakes This very common practice is called peer review To Avoid Mistakes: Make sure you are following the steps of the scientific method Make sure you have only one independent variable at a time Make sure you correctly identify your dependent variables Make sure you include valid control experiments Make sure you record in detail every step of your experiment Ask someone else to review all your work (peer review) In your TCAP packet, complete Chapter 1: scientific Inquiry questions. Answer on the sheet provided. Do not loose this sheet. This will be counted as a classwork grade. We will go over the answers today in class.