The 451 Group
advertisement

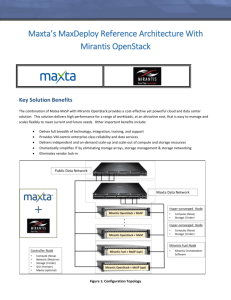
A Journey to OpenStack Lessons Learned from Early Adopters Agatha Poon Research Manager, Global Cloud Computing The 451 Group Today 260+ Staff One company with 3 Go to Market brands Syndicated research, certification, and accreditation services Global Events 1,400+ client organizations: enterprises, vendors, service providers, and investment firms Organic and growth through acquisition Advisory Services 2 Agenda Why should we care? Where is the opportunity? What can OpenStack do? Key takeaways 3 OpenStack regional snapshot Fast Growing China and India Strong government support for innovation and balanced growth A wealth of talent-strong engineering and technical skills Chinese providers are eager to productize OpenStack-based services and technologies. OpenStack initiatives in India are backed by global technology giants and US-based vendors. Early adopters – Academia, Government Well Developed East Asia & Pacific Countries Emerging ASEAN and other South Asian economies Growing choice in outsourcing locations, with Malaysia, Philippines, and Vietnam building credentials Sri Lanka leads the South Asian region in terms of human development indicators In learning phase Vendor-driven projects and training programs Early adopters-tech-savvy IT segment Investment attention focusing on transformational markets of Japan, Korea, Australia, and New Zealand. Consolidation opportunities ongoing in IT savvy economies (Australia, Japan, Korea) The learning curve remains steep, but commercial deployments exist, driven by local cloud/hosting/managed service providers OpenStack is used by academia for the deployment of public/private/hybrid clouds Enterprise cloud journey 83% Cisco UCS NetApp FlexPod VCE Vblock HP CloudSystem Matrix IBM PureSystems Dell Active System Source: InfoPro cloud computing, Wave 5 Exciting Vendors, Technologies and Initiatives Growth catalysts Microsoft 29% Trustworthy Visibility VMware 25% Security No vendor lock-in Amazon.com 24% OpenStack “OpenStack is very exciting. We continue to use VMware for traditional environment.” 16% IBM Large Enterprise, Services: Business/Accounting/Engineering 8% EMC “We use Chef for the orchestration layer……..and a bunch of other stuff. OpenStack is being examined to convert to at some layers.” 5% 0% 5% 10% Source: InfoPro cloud computing, Wave 5 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% Large Enterprise, Financial Services On-premise, Private Cloud Platform, Management and Automation Roadmap Automated Server Provisioning 47% Cloud Performance Management/Monitoring 36% Cloud Platform/Orchestration Stack Automated Middleware Provisioning Automated Network Provisioning In Use Now 8% 34% Automated Storage Provisioning Metering/ Billing Across Internal/ External/ Hybrid Clouds 11% 18% 24% 6% 20% 16% 12% Short-term Plan 5% 15% 17% Longer-term Plan 27% 52% 16% 12% 26% 2% 39% 13% 5% 6% 6% 13% 2% 5% 5% 57% 67% 60% Not in Plan 3% 6% 9% Don't Know Source: InfoPro cloud computing, Wave 5 7 An evolving landscape of OpenStack vendor ecosystem OpenStack Service Providers IT Services & Turnkey Solutions DevOps PaaS on OpenStack Opportunities exist to test, secure, integrate, and orchestrate disparate cloud assets – for enterprises and service providers. OpenStack Distributors NSPs/SIs Hardware/ Software vendors OpenStack with other clouds Global OpenStack market sizing ($m) OpenStack service providers segment is the top revenue generator (E2013: $486m) Strong uptick in revenue is expected from OpenStack distributors (8.4% in 2014 from 3.5% in 2012) 2012-2016 CAGR: 43% $1,671 $1,237 $895 $622 $399 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Source: 451 Research Market Monitor, October 2013 9 Projected revenue in 2013: By vendor type OpenStack IT Services & distributors turnkey solutions 8% 5% Vendor by category Vendor count PaaS on OpenStack 7 OpenStack service providers 14 DevOps 5 OpenStack with other clouds 3 Network service/Equipment providers 7 OpenStack distributors 4 IT Services & Turnkey solutions 8 OpenStack Service Providers 78% Source: 451 Research Market Monitor, October 2013 10 OpenStack-based private cloud, bespoke deployment and consulting It took over a year to productize OpenStack- based offerings It’s an ongoing efforts due to a very long development cycle Implementation challenges Overcoming product immaturity and lack of real testing performed on the code base Making sure patches run against production sites and not devstack is paramount Key lessons learned “You are insane to blindly follow release” Tristan Goode, CEO at Aptira Customers/ Use cases 10 deployments (6 of them are based on existing offerings, 4 deployments are based on a mix of in-house expertise and thirdparty OpenStack products Dev/ test PoC for scalability and federation Collaborative research Data analytics Aptira has been self-funded, but is looking to raise external funding to grow and own the OpenStack service provider space in India and across Asia-Pacific. 11 OpenStack-compatible product FusionSphere R3C10, the virtualization platform within Fusion Cloud Next release-FusionSphere R5-will be based on all OpenStack components: compute, network, storage, and management services >1,000 engineers are involved in Fusion Cloud project Implementation challenges Not enterprise-ready yet Incorporating all existing enterprise-level features into OpenStack, along with enhancing the compatibility of underneath virtualization platform Key lessons learned The ability to understand the disadvantages/ weaknesses of OpenStack is instrumental in driving successful deployments Addressing issues related to software upgrade and business migration Customers Gaining traction in the telecom and entertainment sectors, working with the top three Chinese telecom carriers More than a dozen POCs around the globe Huawei will first bring OpenStack to enterprises and telecom customers. The ultimate goal is to become the Openstack enterprise solution provider. NTT Communications Product verification based on OpenStackcomponents • ~80 engineers and 450 patches • Use cases - office migration and flexible virtual office environment • Targeting Arcstar Universal One (VPN) users, the company has recently released a cloud service based on OpenStack. Key lessons learned •Community-based OpenStack lacks error processing function, which is indispensable for service providers •Community-based development effort is crucial to minimize development costs Customers • It was released less than a week. Implementation challenges • Error handling and transaction processing • Multi-plugin for Neutron to address issues associated with concurrent use of multiple modules • Constant bug-fixing during internal testing NTT Communications will focus on enhancing service functions to support intranet users within and between business organizations. 13 eNoCloud •The continuous delivery of new features could be challenging- it took approximately three months to setup eNocloud, but one year to reorganize engineering around the notion of continuous delivery •Entire development team (~25) involved in various OpenStack projects •One of the top ten contributors to OpenStack for the past three releases Implementation challenges •OpenStack feature gaps still exist •Managing growth while maintaining core values, and being able to evolve at its own pace Key lessons learned Stay agile Think out of the box - enforce its belief in open source without becoming just another service company Customers • Some 200 clients ( consulting, managed services, and hosting) • Safran/Morpho-OpenStack private cloud • Cloudwatt-Openstack public cloud • Consider eNoCloud as the demonstrator of its technology know-how, and a way to validate its development eNovance are currently expanding its operations worldwide, replicating business processes in many different geographies. Primary focus for 2014 is to grow its existing customer base outside of Europe. 14 The missing links: Who should take the lead? Industry consortia? The Foundation? Large Enterprises? Individual community users? Leading vendors/service providers? Missing links OpenStack Talent Limited functionality Fragmentation within the OpenStack community Proven productions are scarce Accelerating the commercial use of OpenStack using a well-defined, secure framework and standardized management processes. 15 Key takeaways Enterprise interest and demand have emerged as a main drivers for new projects. The crossover and convergence of enterprises and service providers offers vendors an opportunity to serve both markets. There are a handful of commercial deployments in Asia-Pacific, and the market for OpenStack is still defining itself. Global revenues for OpenStack-based offerings are relatively small today, but we expect them to grow rapidly. Demand for OpenStack expertise and experience presents itself as a major challenge. Publications Long-form report: The OpenStack Tipping Point, April 2013 Market Insight report: OpenStack-related business revenue to exceed $1bn by 2015 as commercial models evolve, October 22, 2013 16 Questions? Comments? agatha.poon@451research.com