Organic Chemistry: Alkanes, Alkenes, Functional Groups
advertisement
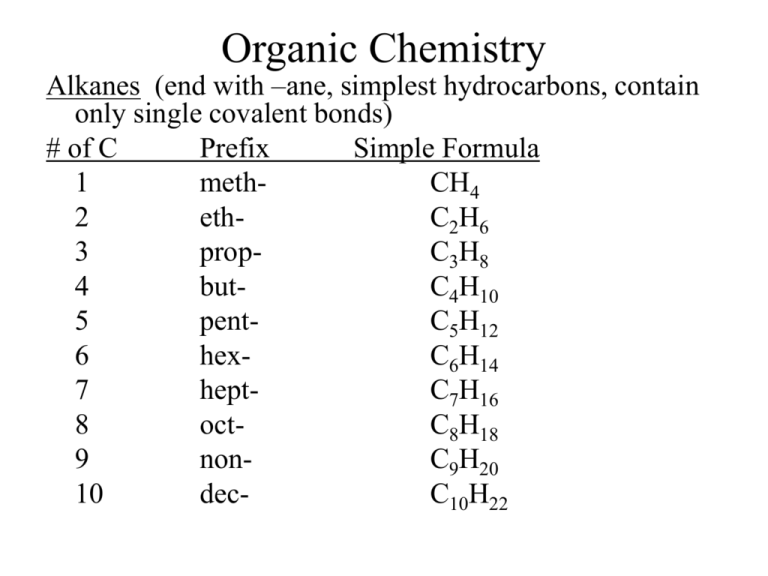
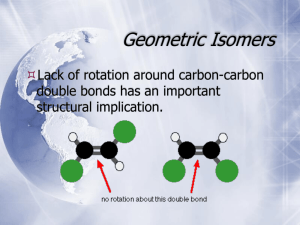
Organic Chemistry Alkanes (end with –ane, simplest hydrocarbons, contain only single covalent bonds) # of C Prefix Simple Formula 1 methCH4 2 ethC2H6 3 propC3H8 4 butC4H10 5 pentC5H12 6 hexC6H14 7 heptC7H16 8 octC8H18 9 nonC9H20 10 decC10H22 -all alkanes that are straight chains are named n-alkane (means normal) C4H10 = n-butane -look at pg 1010 *iso-, and neo- Branched Chain Alkanes -alkane group takes the place of a H atom -called a substituent alkyl group- hydrocarbon substituent -ends with –yl (take away -ane) -contains one less H -look at # of C to name ex- CH3 = methyl C2H5 = ethyl Naming Branched Chain Alkanes 1) Find the longest chain = parent molecule ex- heptane 2) # the C’s in the chain, making sure alkyl groups have lower numbers, can count backwards ex- 2,3,4 instead of 4,5,6 3) Add #’s to names of alkyl groups, with a dash in between ex: 2-methyl 3-methyl 4-ethyl 4) Use prefixes to denote multiples of the same alkyl groups, commas between #’s ex- 2,3-dimethyl 5) Put alkyl groups in alphabetical order ignoring prefixes ex- 4-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl 6) **Use proper punctuation -commas separate #’s -hyphens separate #’s and letters -no spaces 7) Add parent chain name ex- 4-ethyl-2,3-dimethylheptane *Remember prefixes* 2 = di3 = tri4 = tetra5 = penta6 = hexa7 = hepta8 = octa9 = nona10 = deca- Drawing Structural Formula From Name 1) Find parent chain and draw 2) # C’s on parent chain 3) Identify substituents and attach to proper C 4) Add hydrogen as needed Try These!! 1) 3-ethylhexane 2) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane 3) 3-ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane saturated compounds- contain max # of H -all alkanes, all single C-C bonds unsaturated compounds- do not contain max # of H -contain double or triple C-C bonds -alkenes and alkynes Alkenes -contain at least one double C═C bond Naming Alkenes 1) Find longest chain containing double bond -this is parent chain -gets –ene ending ex- butene 2) # so that C atoms of the double bond get the lowest #’s, then look at alkyl groups to get lowest # -double bond gets numbered in the name ex- 2-butene 3) Substituents get named the same as alkanes ex- 2-methyl 4) Put all together ex: 2-methyl-2-butene Alkynes -named same way except end in –yne http://www.chembio.uoguelph.ca/educmat/chm1 9104/organic_nomenclature_quizzes.htm Structural Isomers -compounds that have the same simple formula, but different structural formulas Ex- C4H10 n-butane 2-methylpropane Try This!! Write the structural formulas/skeleton formulas and names for the nine isomers of heptane Cyclic Hydrocarbons-contain a hydrocarbon ring -all single bonded cyclic hydrocarbons are named with the prefix cycloexcyclopropane -if have subgroups, name just like before Try these!! 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons/aromatic hydrocarbons -contain 6 carbon with 3 double bonds -called benzene = -benzene can have subgroups coming off of it 1-ethyl-2,3-dimethylbenzene methylbenzene -if benzene is a substituent it is called phenyl 2-phenylpropane -or isopropylbenzene Functional Groups **R represents C chain attached to functional group Halocarbons R-X X= a halogen functional group = halogen -use root of halogen to name exchloromethane 1,4-dibromobenzene Alcohols R-OH functional group = OH (hydroxyl) -name same as others except ending on parent chain drops the –e and gets an –ol -must number where the -OH is located -alcohols containing 2, 3 or 4 –OH get prefix (diol, triol, tetrol) after parent chain exmethanol 1,2-ethanediol 2-methyl-2-propanol Ethers R-O-R functional group = ether -name R groups then add ether (space between) exethylmethyl ether diphenyl ether Aldehydes functional group = carbonyl group -name same as others, but gets the –al ending * ═O is always on the terminal carbon, so no need to number expropanal 3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-methylbutanal Ketones functional group = carbonyl group -to name, drop –e on parent chain and add –one -number so ═O gets lowest # expropanone 2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanone diphenylmethanone Carboxylic Acids functional group = carboxyl -ends with –oic acid exethanoic acid 4-methyl-3-pentenoic acid Esters functional group = ester -get –oate ending, with space between, parent chain is where ester group is located -esters have fruity, pleasant odors exethyl ethanoate butyl propanoate ethyl pentanoate Amines functional group = amine group -named by groups attached and end with amine exethylamine trimethylamine ethylmethylamine Summary Type halocarbon alcohol ether aldehyde ketone Structure R-X R-OH R-O-R *on terminal carbon carbonyl carboxylic acid -COOH ester amine Group X=halogen hydroxyl ether carbonyl NR3 carboxyl Ending root of halogen -ol ether -al -one -oic acid ester -oate amine amine