The Power of the Situation
advertisement

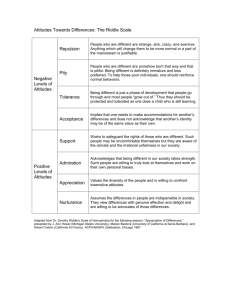
Behavior and Attitudes Chapter 4 David Myers Behavior and Attitudes How well do attitudes predict behavior? When does behavior affect attitudes? Why does behavior affect attitudes? Behavior and Attitudes Attitudes – evaluative reactions toward an entity that are exhibited in your beliefs, feelings, and/or actions ABC’s of Attitudes - Affect, Behavior, Cognition Do Attitudes Determine Behavior? Do Attitudes Determine Behavior or Are We Hypocrites? Most incorrectly feel that to change behaviors you must first change attitudes Studies show that people’s attitudes don’t predict their actions very well Politicians (2008 Election) Religion Honesty Race Sex (Abstinence Only Programs) When Do Attitudes Predict Behaviors? Minimizing Social Influences When Social Influences are Minimal (e.g. conformity) Bogus Pipelines, Implicit Association Tests When Situational Influences are Minimal– attitudes are better predictors of average behaviors rather than isolated acts Specific Attitudes - are better predictors of behavior than general ones Potent Attitudes – stronger accessible attitudes are better predictors of behavior Do Behaviors Determine Attitudes? Festinger’s Attitude Theory – changing one’s behaviors will lead to changes in attitudes Roles - can lead to dramatic changes in attitudes Do Behaviors Determine Attitudes? Stanford Prison Experiment Do Behaviors Determine Attitudes? Saying Becomes Believing Effect – we adjust our message to the audience and then believe it more ourselves Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon – the tendency to comply with a larger request after having previously agreed to a small request Cialdini’s Low-Ball Technique – people who agree to an initial request will still agree when the stakes are higher Evil and Moral Acts and Attitude Change Harmful/Evil Acts – minor acts of harm makes it easier to commit larger acts later on Moral Acts - chosen moral action also leads to attitude change Interracial Attitudes & Behaviors Social Movements Why Do Actions Affect Attitudes? Self Presentation Theory: Impression Management we express attitudes that match our actions in order to appear consistent Self-monitoring - attention one gives to situations and corresponding self-presentations Why Do Actions Affect Attitudes? Self-justification Theory: Cognitive Dissonance – we are motivated to maintain cognitive consistency Festinger ‘s Cognitive Dissonance Theory – we feel tension when two thoughts or beliefs are inconsistent with one another Insufficient Justification – altering one’s attitude when there is a lack of justification for a behavior dee Self-justification Theory: Cognitive Dissonance Dissonance & Decisions – choosing between equally appealing options causes dissonance Reduce dissonance by upgrading your choice and downgrading the unchosen option Why Do Actions Affect Attitudes? Self-Perception Theory - when unsure of our attitudes we infer them by self-observation Expressions and Attitudes – manipulating facial muscles causes students to report anger or happiness Mimicry -Mirroring others allows us to experience their feelings Overjustification Effect – rewarding someone for doing something they like will cause them to lose interest Unanticipated rewards or rewards that make one feel good don’t diminish intrinsic appeal or motivation Self-Justification or Self-Perception? Dissonance Theory appears to explain attitude change Self-perception Theory explains attitude formations.