2-4-13 Earth Cycles Vocabulary
advertisement

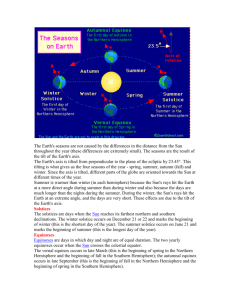
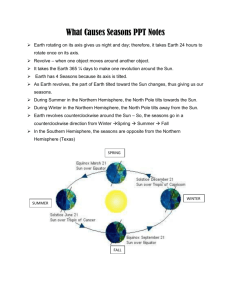
2.04.13 S: Earth Cycles Vocabulary What is your favorite season? Explain. Describe the weather. P: Vocab Stations • Copy all 18 vocabulary words and definitions and draw a picture for each P Rotation • A spinning motion. P Orbit • The path an object follows as it moves around another object. P Revolution • The motion of one object around another object. P Rotational Axis • A line on which an object rotates. P Equinox • A day when Earth's rotational axis is neither toward nor away from the Sun. • Autumnal Equinox-September 22nd • Vernal Equinox- March 21st Solstice P • A day when Earth's rotation axis is the most toward or away from the Sun. • Winter Solstice Dec. 22 • Summer SolsticeJune 22 P Lunar Phases • The different appearances of the moon throughout the month. • Lunar cycle lasts about 28 days. P Waxing The phase where more of the moon’s near side is lit each night. P Waning The phase where less of the Moon’s near side is lit each night. P Gibbous-Moon More than half, but less than fully illuminated. P Crescent-Moon The time at which the moon appears as a narrow waxing or waning crescent. P Solar Eclipse Occurs when the moon goes in front of the sun and blocks most of the sun's light from the Earth. P Lunar Eclipse A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through the shadow of the Earth. P Neap Tides Smallest daily tidal range P Spring Tides Largest daily tidal range P High Tides The tide at its fullest; when the water reaches its highest level. P Low Tides When the tide reaches its lowest water level. P Tidal Range The difference between levels of ocean water at high and low tide. A: Vocabulary Questions On your post-it, write one question for one of the vocabulary words The question can be: Multiple-Choice True or False Fill-in-the-blank Short answer with explanation C: Using your own words, define 3 of the vocabulary words. E: Create one Word Wall. On the front, write the word and draw a picture. On the back, write the definition. 02.06.13 S: Interactive Cycles 1 Draw a picture of how day and night happens? P/A: Interactive Part 1 During the presentation, Answer the questions on the handout in complete sentences in your journal. Pay close attention C: Quiz E: Reading Practice Complete both sides of the handout Justify your answers If you do not finish, take for HW 02.06.13 S: What Sun Cycles P Rotation • A spinning motion. P Orbit • The path an object follows as it moves around another object. P Revolution • The motion of one object around another object. P Rotational Axis • A line on which an object rotates. P Equinox • A day when Earth's rotational axis is neither toward nor away from the Sun. • Autumnal Equinox-September 22nd • Vernal Equinox- March 21st Solstice P • A day when Earth's rotation axis is the most toward or away from the Sun. • Winter Solstice Dec. 22 • Summer SolsticeJune 22 A: Cinch Reading Read the passages carefully C:Answer the questions in complete sentences in your journal. E: Reading Practice C 02.07.13 Day, Night, & Seasons Tell me whether you agree or disagree S: with the following statements. Explain… 1. Day and night occur because the Earth rotates on its axis. 2. The North pole tilts away from the Sun in the Northern Hemisphere’s summer. 3. The Southern hemisphere and the Northern hemisphere experience the same seasons at the same time. P: Day and Night The Earth rotates in a counter clockwise direction from west to east. (Eastern spin) P: Day and Night It takes the Earth ______ to rotate one complete time. P: Day and Night The side of the Earth facing the Sun experiences ______, while the side of the Earth facing away from the sun experiences _______. P: Seasons The seasons change because of the tilt and revolution of the Earth. P: Seasons Earth’s Southern and Northern Hemispheres have opposite seasons. P: Winter NH = Northern Hemisphere SH = Southern Hemisphere NH = tilt away from sunlight Winter SH = tilt toward sunlight Summer NH SH P: NH = Northern Hemisphere SH = Southern Hemisphere Spring NH SH Vernal Equinox: (March 21st) NH = tilt neither away or toward Spring SH = tilt neither away or toward Autumn P: Summer NH = Northern Hemisphere SH = Southern Hemisphere NH SH NH = tilt toward sunlight Summer SH = tilt away from sunlight Winter P: Autumn NH = Northern Hemisphere SH = Southern Hemisphere Autumnal Equinox: (September 22nd) NH = tilt neither away nor toward sunAutumn SH = tilt neither away or toward sun Spring NH SH A: Seasons Investigation Lab Purpose: Investigate why Earth experiences different seasons. Materials: Light bulb Ball on a pencil or skewer A: Seasons Investigation Lab Safety: •Do not touch bulb. •Be careful with pointy objects. Procedures. 1. Follow the procedures on the Seasons investigations handout. 2. Use the Seasons handout diagram in the investigation. 3. Draw the diagram and record your observations in your journal. C: Analysis of Results/Conclusion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Why does the Earth experience seasons? In what direction does the Earth revolve around the Sun and how long does it take? How do the winter and summer seasons in the Northern Hemisphere compare? What is the order of seasons beginning in winter? What is a limitation of the investigation model? E: Lab Summary Write a half page reflection on what you did today in the lab and explain the purpose of the lab. Use vocabulary from our unit on Earth Cycles. 02.08.13 S: Sun Cycles Review Study your Unit 9 Vocabulary words for 5 minutes to prepare for the Quiz PAC: Moon Video Chart As the video is playing, fill in the chart about the Moon What you know (K) (3 things) What you learned (L) (5 things) What you need to know (N) (3 things) E: Exit 1.I already knew ________________________ about the moon. 2.I learned ________________________ about the moon. 3.One thing I still don’t understand about the moon is…