MRP Practice Problems: BOM, Lead Time, Net Requirements
advertisement

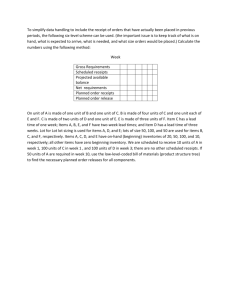
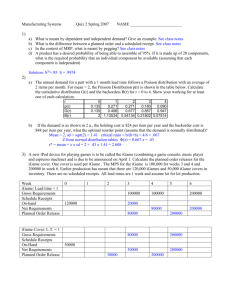
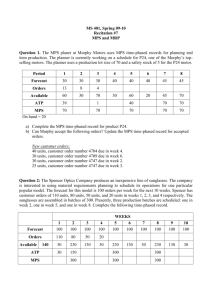
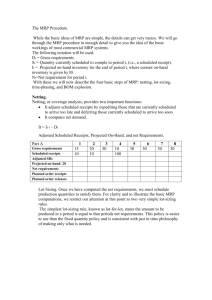
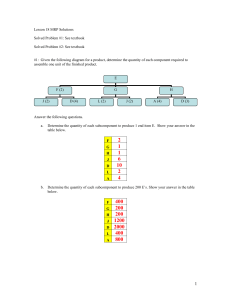
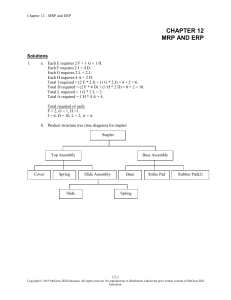
Practice Problems: Chapter 14, Material Requirements Planning Problem 1 (page 513): a. Prepare a Bill-of-materials tree b. Revise the BOM according to low-level coding. Problem 2: Determine the overall lead time for the two end products TOL and HQ. Item X A B C D E F G Lead time Chair Leg assembly Seat Back assembly Legs Cross bar Slide rails Back supports 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 3 Problem 3: Suppose that the production of 200 Chair X is planned. Further suppose that the following inventories are available. Determine the net requirements for all the component items. Item X A B C D E F G Item Available 20 50 250 40 60 50 150 400 Gross requirement Available Net requirement MRP Formulas: Gross requirements (GR) The total expected demand for an item or raw material during each time period without regard to the amount on hand. (For end items it is MPS; for components, these quantifies are derived from the planned-order releases of their immediate “parents.” Scheduled receipts (SR) Open orders that have been placed and are scheduled to arrive from vendors or elsewhere in the pipeline by the beginning of a period. Projected on hand (POH) Expected inventory available on hand at the beginning of each time period Net requirements (NR) The actual amount needed in each time period. Planned-order receipts (PORT) The quantity expected to be received by the beginning of the period in which it is shown. Planned-order releases (PORL) Equals planned-order receipts offset by lead time. This amount generates gross requirements at the next level in the assembly or production chain. When an order is executed, it is removed from “planned-order releases” and entered under “scheduled receipts." GR Planned-order releases of immediate “parents” x No. required per unit SR Given POH POH of previous period + SR + PORT – GR NR GR – (POH + SR + PORT) if positive, otherwise zero PORT NR, in the case of Lot for Lot PORL PORT offset by lead time Problem 4: Develop a net material requirements plan for Chair X. Available Lead time Item Scheduled Receipts X A B C D E F G Week #1 = 100 Week #1 =120, Week #2 = 120 Week #1 =250 Week #1 =80, Week #2 = 100 20 50 250 40 60 50 150 400 Week #1 = 300 Week #1 = 500 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 3 MPS: (Quantities must be made available in the given week) Week: MPS for X 1 80 2 120 3 100 4 120 5 120 6 100 Item LT = Week: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases Item LT = Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases Item Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT = Item LT = Week: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases Item LT = Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases Item Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT = Item LT = Week: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases Item Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT =