18.2_cloud_formation
advertisement

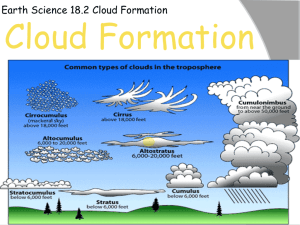
Name: _________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _______ 18.2 Cloud Formation I. Air Compression & Expansion Adiabatic Temperature Changes: – Occur when ______________________________________________________________________ – Done by _________________________ change: air expands or contracts Expansion = __________________________ Compression = _________________________ Expansion and Cooling: – Air pressure ____________________________ as you____________________________ elevation – Dry adiabatic rate: for _____________________ air Temp. ___________________ 10°C for every 1000 m it moves _______________________ (______________________________________) Temp. ____________________ 10°C for every 1000 m it moves ______________________ (______________________________________) – Wet adiabatic rate: for ___________________________ air Temp. changes _______________________ per 1000 m Slower because of ______________________________ – Air at the _________________________ will release latent heat as it ____________ and water ________________________; this works against the cooling. – Rate varies because amount of moisture in the air varies Important for determining _____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. II. Processes That Lift Air Orographic Lifting: occurs when __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ – The forced rise causes adiabatic ___________________ that generates clouds and precipitation – The air ____________ adiabatically as it _______________ down the other side, making condensation and precipitation less likely. This is why the __________________________ sides of mountains are some of the _____________________________ places on earth while the ____________________ sides are some of the _________________ (“_________________________________________”). Frontal Wedging: occurs when ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ – The __________________________________________ air acts as the barrier that forces the ________________________________ air to rise. Convergence: occurs when _______________________________________________________________ – Rising air ___________ adiabatically, possibly forming clouds – Common over _________________________ like Florida: air from the Gulf meets air from the Atlantic over land Localized Convective Lifting: occurs when __________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ – _____________ use them to gain altitude; people use them for _____________________________ – When the pockets ___________, they often form _________________________ III. Stability Stable air: a pocket of air _______________ and __________________ than the surrounding air that resists ________________________________________ Stable air tends to _______________________________________________________, while unstable air (warmer than the surrounding air) tends to ______________ – This is how ____________________________________ work. Normally, air temperature ___________________________ gradually with ________________________ altitude; when the temperature increases with height, it is called a ________________________________ __________________________. – This is when the most _______________ conditions happen. – Usually happens on ______________________________ Clouds associated with stable air are ____________________________________________________, with little if any precipitation. Clouds associated with unstable air masses often generate ___________________________________ and the occasional ____________________________. IV. Condensation For any form of ________________________________ to occur (dew, fog, or clouds), the air must be _____________________________. – Usually when air is cooled to its _________________________ Water vapor must have a ____________________ to condense upon. – In the air, tiny bits of particulate matter called __________________________________________ serve as the surfaces for water vapor condensation. Ex: _______________________________________________ Without them, relative humidity over 100% would be necessary for clouds.