eW/FS/WE/001
The water environment
WATER CYCLE: Condensation
AC3.1
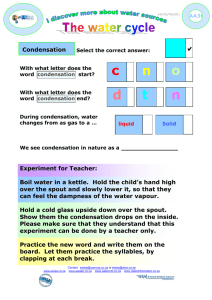
Condensation is the change of water from its gaseous form (water
vapour) into liquid water.
It generally occurs when the
temperature of the vapor decreases.
Condensation occurs in the atmosphere
when warm air rises, cools and looses its
capacity to hold water vapour. As a result,
excess water vapour condenses to form
clouds.
Condensation is very noticeable on plants as
dew in the morning.
( http://www.und.edu/instruct/eng/fkarner/earth.htm)
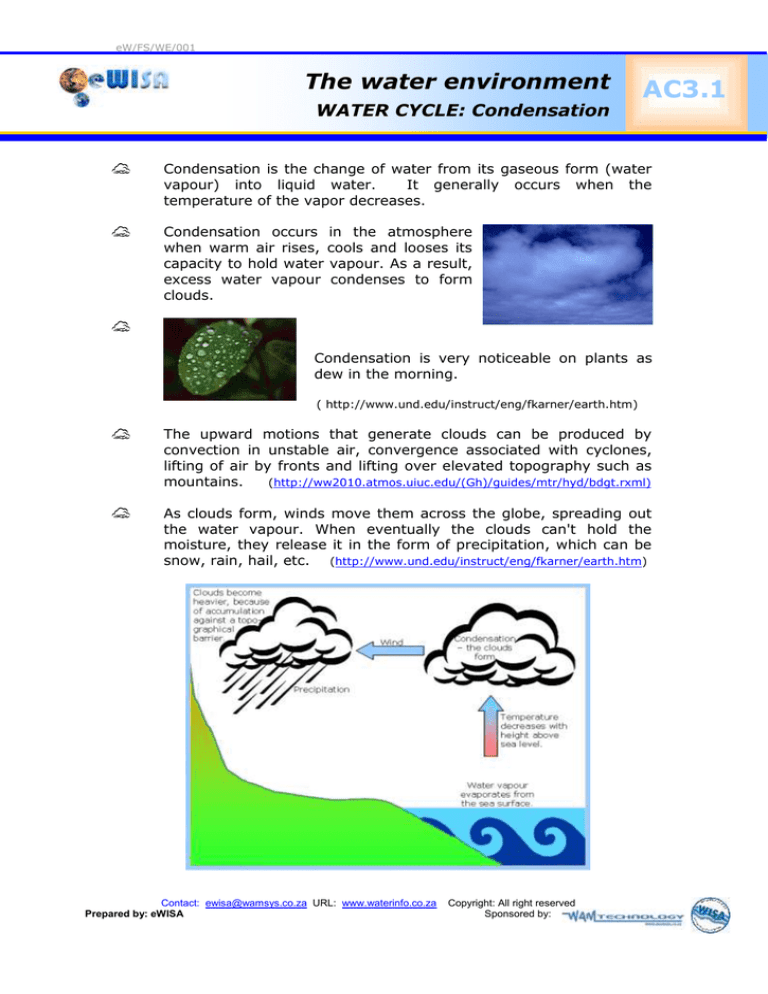
The upward motions that generate clouds can be produced by
convection in unstable air, convergence associated with cyclones,
lifting of air by fronts and lifting over elevated topography such as
mountains.
(http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/hyd/bdgt.rxml)
As clouds form, winds move them across the globe, spreading out
the water vapour. When eventually the clouds can't hold the
moisture, they release it in the form of precipitation, which can be
snow, rain, hail, etc. (http://www.und.edu/instruct/eng/fkarner/earth.htm)
Contact: ewisa@wamsys.co.za URL: www.waterinfo.co.za
Prepared by: eWISA
Copyright: All right reserved
Sponsored by: