Sexually Transmitted Infections
advertisement

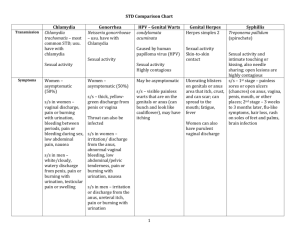
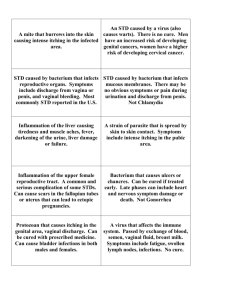
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Its your health. Protect yourself. Why Should I get Tested for STDs? Sexually transmitted diseases are common. Think it can’t happen to you? Think again. By age 25, one in two sexually active young people will get an STD. Some STDs show no symptoms, and many of those infected don’t know it. The only way to “know for sure” is to get tested! STDs are treatable, and most are curable. Putting off treatment can lead to irreversible health effects such as infertility, increased risk for cancer, and even death. Before you start a new sexual relationship, talk with your partner about getting tested for STDs. After all, you aren’t just having sex with your partner but with everyone they’ve had sex with….and everyone they had sex with…. How can I get Tested for STDs at the WCU Student Health Center? Students should call 227-7640 to schedule an appointment. If you are concerned about privacy when making the appointment, simply state that you wish to see a health care provider for a “personal reason”, instead of saying an STD screening. You may also request to see a male or female provider at this time. (These requests will be honored but not guaranteed depending on schedule availability.) What Will Happen on the Day of My Appointment? The Talk Be prepared to address topics concerning your sexual history, current sexual behavior, methods of contraception and STD risk reduction, and any current symptoms that you may be experiencing. These questions may seem really personal, but its important to be honest with your health care provider. All information is confidential. Based on your conversation, your provider will determine appropriate tests for you. What Will Happen on the Day of My Appointment? The Exam There is no single test that will screen for all STDs. Your exam may include: Physical exam – your health care provider may look at your genital and/or your anus for any signs of an infection, such as a rash, discharge, sores, or warts. For women, this exam can be similar to a yearly pelvic exam. Urine sample – you may be asked to urinate into a cup. Discharge, tissue, cell or oral fluid sample – your provider will use a swab to collect samples that will be looked at under a microscope. Blood sample – your provider may take a small blood sample Sometimes your diagnosis can be made based on your symptoms or a physical exam. Treatment could be prescribed right away. Other times, your health care provider may need to send a sample away to a lab. In that case, the results may not be available for several days. Always follow up! Signs and Symptoms of Chlamydia Most of those infected have no symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 1 to 3 weeks of exposure. Women: abnormal vaginal discharge, a burning sensation when urinating, lower abdominal pain, nausea, fever, pain during intercourse, or bleeding between menstrual periods. Men: discharge from the penis, burning sensation when urinating, or burning and itching around the opening of the penis. How is Chlamydia Treated? Chlamydia can be easily treated and cured with a single antibiotic dose. Both partners must be treated at the same time to prevent passing the infection back and forth. Pts with chlamydia should abstain from sexual intercourse until 7 days after their partner has completed treatment. Signs and Symptoms of Gonorrhea Most of those infected show no symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 2 days to 4 weeks of exposure. Women: a painful or burning sensation when urinating, increased vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding between periods. Men: a burning sensation when urinating, or a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis. Sometimes men with gonorrhea get painful or swollen testicles. How is Gonorrhea Treated? Gonorrhea can be easily treated and cured with a single dose of an antibiotic. Both partners must be treated at the same time to prevent passing the infection back and forth. Because many people with gonorrhea also have chlamydia, antibiotics for both infections are usually given together. Signs and Symptoms of Genital Herpes Most people have no symptoms. The first outbreak typically occurs 2 weeks after exposure. The virus stays in the body forever and may cause recurrent outbreaks. Men and Women: small painful blisters or ulcers on the genitals, flu-like symptoms: fever, headaches, tender swollen glands. How is Genital Herpes Treated? There is no treatment that can cure the herpes virus itself. Antiviral medications (Acyclovir) can help reduce the pain and itching as well as the frequency of recurrent outbreaks. Daily suppressive therapy with antiviral medications can reduce the likelihood of spreading the virus to sex partners. Signs and Symptoms of HPV (Genital Warts) Most people with HPV do not develop symptoms. Certain types of HPV can cause genital warts in men and women, while others can cause cervical cancer in women. Genital warts usually appear as small bumps or groups of bumps, usually in the genital area. They can be raised or flat, single or multiple, small or large, and sometimes cauliflower shaped. Cervical cancer does not have symptoms until it is quite advanced. For this reason, it is important for women to get Pap test annually. How is HPV Treated? There is no treatment that can cure the virus itself. Visible genital warts can be removed by topical medications prescribed by your clinician, or by chemical treatments performed by your clinician in the office. Should I be Concerned About HIV? Many people infected with HIV do not have any symptoms at all for many years after exposure. One quarter of the HIV-infected persons in the United States do not know that they are infected. HIV is spread through unprotected vaginal, oral, and anal sex with someone who has HIV; through sharing contaminated needles or drug works; and during pregnancy or breast- feeding with an HIV-positive mother. There is no treatment that can cure HIV or AIDS. Antiretroviral medications can slow the progression and delay the onset of AIDS. How Do I get Tested for HIV? Free HIV Testing is provided by the Jackson County Department of Public Health at the WCU UC on the following dates: 4/15, 9/15, 12/1 from 4pm-8pm You may also contact Jackson County Department of Public Health to schedule an appointment at their facilities located on Scotts Creek Rd. 828-586-8994 The American Red Cross screens all donated blood for HIV/AIDS. How Do I Protect Myself? Get tested Ask your partner to get tested Use condoms Limit your number of sexual partners Do not inject illicit drugs If consuming alcohol, do so moderately Condoms…am I Using Them Correctly? Use a new condom each and every time you have sex (including oral sex)— throughout the entire sex act (from start to finish). Before any genital contact, put the condom on the tip of the erect penis with the rolled side out. If the condom does not have a reservoir tip, pinch the tip enough to leave a halfinch space for semen to collect. Holding the tip, unroll the condom all the way to the base of the erect penis. After ejaculation and before the penis gets soft, grip the rim of the condom and carefully withdraw. Then gently pull the condom off the penis, making sure that semen doesn't spill out. If you feel the condom break at any point during sexual activity, stop immediately, withdraw, remove the broken condom, and put on a new condom. Ensure that adequate lubrication is used during vaginal and anal sex, which might require water-based lubricants such as K-Y JellyTM or AstroglideTM. Oil-based lubricants (petroleum jelly, massage oils, body lotions) should not be used because they can weaken latex, causing breakage. References Center for Disease Control www.cdc.gov UpToDate www.uptodate.com