Indicators, Neutralizations & Titrations Revisited
advertisement

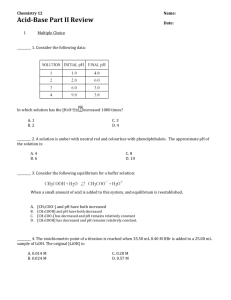
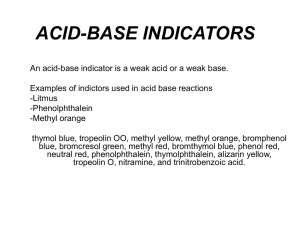
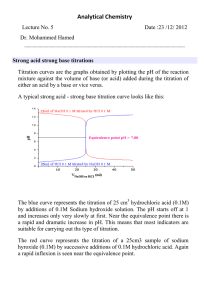
Pre-Lab Quiz When you’re done: Make sure to make your DAY 2 observations for the Egg-tastic Class Inquiry https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kxPwbhFeZSw 4.3 Homework Questions 4. What is the pH of an aqueous solution containing 0.00200 M barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 7. A 2.67g sample of hydrogen fluoride gas (HF) is dissolved in sufficient water to make 1.05L of solution at 25C to form an acidic solution. Hydrogen fluoride is a weak acid with Ka= 6.6x10-4 a. Calculate the pH of the solution b. Calculate the pOH of the solution Indicators, Neutralizations & Titrations Revisited Indicators Indicators are dyes that change colour under varying conditions of acidity. Although not as accurate as instruments such as pH meters in determining acidity, indicators can be used to give less precise measure of acidity. Litmus is a very commonly used indicator which is red in acids and blue in bases. Litmus is an indictor that changes colour from red to blue in the pH range of 5.5 to 8.0. Indicators Indicators are coloured compounds that exist in both acidic and basic forms. A general formula may be used for indictors - HIn - and a reaction written: HIn acidic form colour 1 ↔ H+ + Inbasic form colour 2 Indicators may be in solution form or paper form. pH paper is prepared by treating the paper with the indictor solution. When the paper is then dipped into the solution you are testing, it will change colour depending on the acidity of the solution. Find my pH Activity Indicator used: Purple cabbage Purple cabbage contains colored pigments (one of which is anthocyanin) that change colors when they meet an acid or a base. Acids make purple cabbage juice turn pink. Bases make the juice turn blue or greenish. Indicator Examples Indicator pH range Colour change methyl orange 3.2 - 4.4 red to yellow litmus 5.8 - 8.0 red to blue phenolphthalein 8.2 - 10.0 colourless to pink 1. A given solution turns methyl orange yellow, litmus blue, and phenolphthalein pink. What is the approximate pH of the solution? Methyl orange in yellow when pH is above 4.4 Litmus is blue when pH is above 8.0, and Phenolphthalein is red when pH is above 10.0. Therefore the solution would have to have a pH above 10.0 Indicator Examples Indicator pH range Colour change methyl orange 3.2 - 4.4 red to yellow litmus 5.8 - 8.0 red to blue phenolphthalein 8.2 - 10.0 colourless to pink 2. What color would methyl orange, litmus, and phenolphthalein turn when testing: a. vinegar (pH = 3) Methyl orange: red Litmus: red Phenolphthalein: colorless b. sea water (pH = 8) Methyl orange: yellow Litmus: blue Phenolphthalein: colorless Neutralization Reactions What happens when an acid such as HCl is mixed with a base such as NaOH: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than H+ and a negative ion other than the hydroxide ion, OH-. Double displacement reactions of this type are called neutralization reactions. We can write an expanded version of this equation, with aqueous substances written in their longer form: H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + H2O(l) Removing the spectator ions we get the net ionic equation: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l) Titrations A titration is a laboratory procedure used to determine the concentration of a solution. During an acid-base titration an acid with a known concentration (standard solution) is added to a base with an unknown concentration (or vice-versa). An indicator is also added to the solution which will signal (by a color change) when the base has been neutralized. Titrations Note that as soon as you see a color change the titration is complete and the [H+] and [OH-] are equal. At this equivalency point the titration is stopped. By knowing: the initial volume of the base, the volume of acid added, and the initial concentration of the acid we can calculate the concentration of the base. Titration Examples 1) During a titration 75.8 mL of a 0.100 M standard solution of HCl is titrated to end point with 100.0 mL of a NaOH solution with an unknown concentration. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution? 2) A 20.0 mL solution of strontium hydroxide, Sr(OH)2, is placed in a flask and a drop of indicator is added. The solution turns colour after 25.0 mL of a standard 0.0500 M HCl solution is added. What was the original concentration of the Sr(OH)2 solution?