Food Safety is Risky Business - National Ag Risk Education Library
advertisement
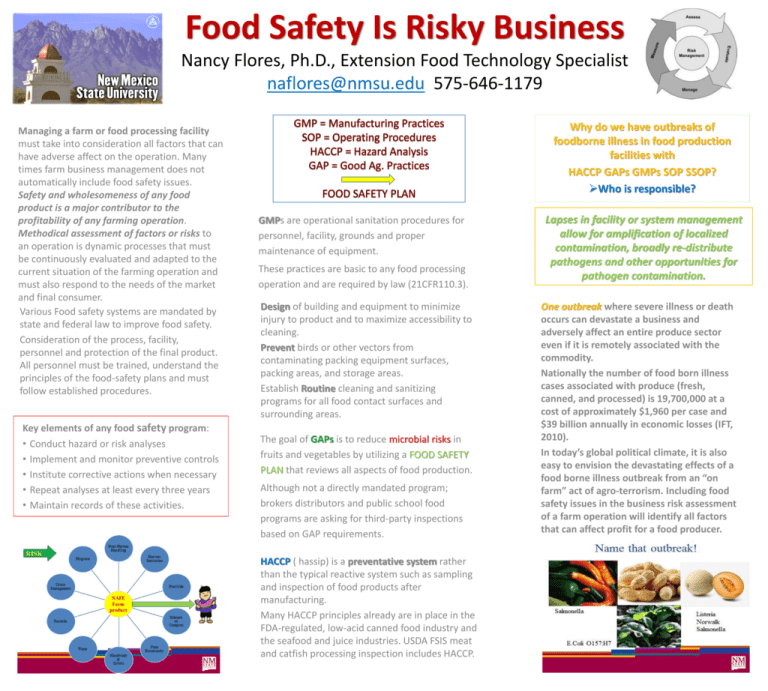
Food Safety Is Risky Business Nancy Flores, Ph.D., Extension Food Technology Specialist naflores@nmsu.edu 575-646-1179 Managing a farm or food processing facility must take into consideration all factors that can have adverse affect on the operation. Many times farm business management does not automatically include food safety issues. Safety and wholesomeness of any food product is a major contributor to the profitability of any farming operation. Methodical assessment of factors or risks to an operation is dynamic processes that must be continuously evaluated and adapted to the current situation of the farming operation and must also respond to the needs of the market and final consumer. Various Food safety systems are mandated by state and federal law to improve food safety. Consideration of the process, facility, personnel and protection of the final product. All personnel must be trained, understand the principles of the food-safety plans and must follow established procedures. Key elements of any food safety program: • Conduct hazard or risk analyses • Implement and monitor preventive controls • Institute corrective actions when necessary • Repeat analyses at least every three years • Maintain records of these activities. Why do we have outbreaks of foodborne illness in food production facilities with HACCP GAPs GMPs SOP SSOP? Who is responsible? GMPs are operational sanitation procedures for personnel, facility, grounds and proper maintenance of equipment. These practices are basic to any food processing operation and are required by law (21CFR110.3). Design of building and equipment to minimize injury to product and to maximize accessibility to cleaning. Prevent birds or other vectors from contaminating packing equipment surfaces, packing areas, and storage areas. Establish Routine cleaning and sanitizing programs for all food contact surfaces and surrounding areas. The goal of GAPs is to reduce microbial risks in fruits and vegetables by utilizing a FOOD SAFETY PLAN that reviews all aspects of food production. Although not a directly mandated program; brokers distributors and public school food programs are asking for third-party inspections based on GAP requirements. HACCP ( hassip) is a preventative system rather than the typical reactive system such as sampling and inspection of food products after manufacturing. Many HACCP principles already are in place in the FDA-regulated, low-acid canned food industry and the seafood and juice industries. USDA FSIS meat and catfish processing inspection includes HACCP. Lapses in facility or system management allow for amplification of localized contamination, broadly re-distribute pathogens and other opportunities for pathogen contamination. One outbreak where severe illness or death occurs can devastate a business and adversely affect an entire produce sector even if it is remotely associated with the commodity. Nationally the number of food born illness cases associated with produce (fresh, canned, and processed) is 19,700,000 at a cost of approximately $1,960 per case and $39 billion annually in economic losses (IFT, 2010). In today’s global political climate, it is also easy to envision the devastating effects of a food borne illness outbreak from an “on farm” act of agro-terrorism. Including food safety issues in the business risk assessment of a farm operation will identify all factors that can affect profit for a food producer.