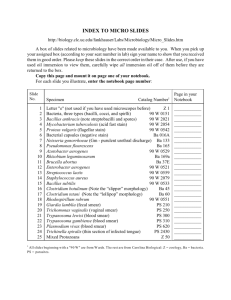
here.
advertisement

TB – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Jerrold J. Ellner MD Boston University Sept 2013 “If the number of victims that a disease claims is the measure of its significance, then all diseases, particularly the most dreaded infectious diseases such as bubonic plague, Asiatic cholera, etc., must rank far behind tuberculosis.” - Robert Koch, 1882 Short History of TB • 1882 – Koch discovers tubercle bacillus* • 1907 – von Pirquet adapts Koch’s tuberculin as diagnostic test • 1919 – Calmette & Guerin produce BCG vaccine • 1943 – Schatz and Waksman discover streptomycin* • 1948 – BMRC trial of streptomycin vs. bedrest • 1952 – development of INH • 1966 – development of rifampicin • 1978 – ‘short-course’ TB treatment (6 months) • 1990s- DOTS strategy Global TB 2010 • 8.8 million new cases – 1.1 HIV • 1.5 million deaths – 0.35 HIV • 0.65 MDR – 10% XDR = 3.4% new; 20% retreatment cases WHO Reports. 2011 TB Cases Natural History of TB 50% Reexpos 5% (40%) Reexpos 5% (2-10%/y) Lancet Inf Dis 2008;8:601-11 DIAGNOSIS OF ACTIVE TB TB diagnostics, 1882 TB diagnostics, 2010 AFB (acid fast bacilli) smear AFB (shown in red) are tubercle bacilli Proportion of Patients with Pulmonary TB with Positive AFB Smears 70 60 HIV uninf AFB positivity in TB patients Early HIV 50 40 Late HIV 30 20 10 0 Similar for “classic” RUL infiltrate MGIT LJ PCR FM ZN 1+ 101 102 103 104 2+ 3+ 105 4+ 106 107 E-MTD sensitivity >95% smear (+); 75-90% smear (-) Amplicor sensitivity >95% smear (+); 60-70% smear (-) 11 MMWR Jan 16, 2009 NEJM. – published on-line Sept Xpert – MTB-RIF • One sample – 98% smear pos, 73% smear neg • Three samples – 100% smear pos, 90% smear neg • Specificity - 99% • Sensitivity MDR-TB – 97% GeneXpert rolled out as first-line diagnostic for TB in South Africa - 31 March 2011 "If a minister can do it, it can’t be that hard," said South African Health Minister Aaron Moatsoaledi, Demonstrating GeneXpert test for TB GeneXpert Xpert MTB/RIF 5 16 20 80 Samples per shift 500-1000 IGRA v TST • Mtb specific antigens (ESAT-6, CFP10, TB 7-7) • Higher specificity, correlation with exposure, less cross-reactivity BCG, non tuberculosis mycobacteria • One visit dx • TST not quality controlled application, reading TST v IGRA • Variable cut-point, risk stratification • Strong epi basis • Standard definitions, TST conversion, boosting • ? Less variability near cutpoint • Preferable for annual screening • Less expensive Diagnosis LTBI • TST first: if negative IGRA: immunocompromised, high risk, ?active TB if positive IGRA: BCG vaccinated, ?NTM Nature Rev Micro. 2009 393 Trancripts TB v LTBI v HC Nature. 2010 Estimated HIV-TB Co-infection Prevalence, 2000 Rate per 100 000 <5 5 - 9.9 10 - 99 100 - 999 1000 - 4999 5000 or more No estimate From presentation made by: Paul Nunn, WHO, Geneva, Durban 2002 Accuracy of Determine TB-LAM, by CD4 96.6 98.3 63.9 % Sensitivity 69% for CD4 <50 Sensitivity 53% for CD4 50-100 Rapid Dx TB-HIV AFB Smear Neg PTB • Xpert sens 62% • LAM sens 45% • LAM plus/then Xpert sens 79% Optimal timing of antiretroviral therapy in adults with untreated HIV-infection and new TB ART started within 2 weeks of TB tx improves survival in PTB patients with Adv. immunosupression; increased risk of IRIS Why is TB treatment duration so long? Hypothetical Model of TB Chemotherapy D. Mitchison # bacilli anatomic/metabolic populns of bacilli cavitary TB A A: rapidly multiplying, INH>RIF>EMB B: slowly multiplying, PZA>RIF>INH C: sporadically multiplying, RIF>INH B C 1 2 3 4 # months of therapy 5 6 Drug-susceptible TB: strategies for shortening duration of treatment required for cure Optimize the use of the drugs in the regimen (RIF) •RIF at higher dose •RPT instead of RIF Replace EMB (low potency) with a more active drug (e.g. FQ) EMB PZA RIF RIF INH INH 1 2 3 Treatment month 4 5 6 Bedaquiline (‘Sirturo’, from Johnson & Johnson) Addition of bedaquiline (vs. placebo) to a 5-drug MDR-TB regimen resulted in: • Faster culture conversion • Higher sputum culture conversion rate at 24 weeks (78.8% vs. 57.6%) • Prevention of acquired resistance to other background drugs 108 From Johnson & Johnson #: number of subjects at risk (i.e., culture positive subjects ongoing in the trial at the corresponding time point) Note: The intersection of horizontal dotted line and each treatment arm represents the median time to sputum culture conversion. LINEZOLID in XDR-TB: Kaplan–Meier Curves for Culture Conversion According to Time since Randomization. NEJM. 2012 Lee M et al. N Engl J Med 2012;367:15081518. PRECLINICAL DEVELOPMENT TBA-354 Nitroimidazoles TB Alliance, U Auckland, U Illinois CPZEN-45 Caprazene nucleoside MCRF, Lily TBDDI, NIAID, IDRI Quinolone DC – 159a Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics JATA, Daiichi-Sankyo Pharmaceutical SQ609 Dipiperidines Sequella SQ641 Capuramycins Sequella BTZ043 Benzothiazinones New Medicines For Tuberculosis (NIM4TB) Q201 – Novel anti – TB agent Imidazopyridine Quro Science, Inc. PHASE I AZD587 Oxazolidinone Astrazeneca PHASE II PHASE III PA – 824 Nitroimidazoloxazine TB Alliance Gatifloxacin Fluoroquinolone WHO/TDR PNU – 100480 (Sutezolid) Oxazolidinone Pfizer Moxifloxacin Fluoroquinolone TB Alliance TMC207 (Bedaquiline) for MDR- TB Diarylquinoline Tibotec BVBA OPC-67683 (Delamanid) Nitrodihydroimidazooxazole Otsuka Pharmaceutical SQ109 Ethylenediamines Sequella, NIH TMC207 (Bedaquiline)for DS – TB Diarylquinoline TB Alliance, Janssen Rifapentine (TBTC study 29) Rifamycin CDC, Sanofi-aventis