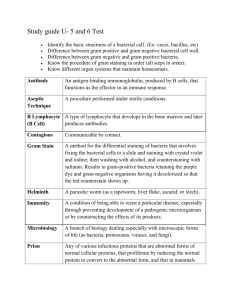
bacterial morphology, metabolism & physiology

BACTERIAL MORPHOLOGY,
METABOLISM & PHYSIOLOGY
By:
Maria Rosario L. Lacandula,MD,MPH
Department of Microbiology
College of Medicine
Our Lady of Fatima University
Objectives
The student should be able to:
describe the typical bacterial cell based on size, shape and groupings.
determine the medical importance of certain structural components in a bacterial cell.
to discuss the appropriate staining procedure to demonstrate bacterial morphology and special structures.
to perform the following staining techniques
Gram staining
Acid-Fast staining
Objectives
Discuss the growth requirements of bacteria
Differentiate bacteria as to:
source of carbon source of energy temperature requirement oxygen requirement
Discuss the bacterial growth curve
lag phase logarithmic phase stationary phase death phase
Beam of light
Microscope
Beam of electron
Bacterial Morphology
Bacterial Cell
Prokaryotes
No true nucleus
No organelles
Divide-binary fission
Parts of a Cell
Cell envelope
Cell wall- murein sacculus
Outer
Cell membrane-plasma membrane, cytoplasmic membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleiod
Ribosomes
Granules/inclusion bodies
Spores
plasmids
Appendages
Capsule
pili
flagella
Parts of a Cell
Cell wall
Peptidoglycan
N acetyl glucosamine & N acetyl Muramic acid
Protect the cell from osmotic changes
Rigidity
Multilayered in Gram positive
Teichoic acid
Mono to bi layered in Gram negative
.
Outer membrane- gram negative only
2 layers of lipids
Inner layer-phospholipids
Outer layer- Lipopolysaccharide
3 regions
Lipid A
Core polysaccharide
O antigen
Transmembrane proteins
Porins
Integral proteins
viability
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Lipid bi layer
Selective permeability
Site of ATP production
Viability
Cytoplasm
Nucleiod
Chromosomal DNA
Plasmids
Inclusion bodies
Storage of excess food and energy
Metachromatic granules/ Babes ernst granules
Much granule
Spores
Resist adverse condition
Ribosome- 70s- 50s & 30s
Capsule
Polysaccharide
Antiphagocytic
antigenic
Virulence
Pili
Common pili- fimbriae
Sex pili- conjugation
antigenic
Flagella
Locomotion
antigenic
Metabolism
Glucose catabolism
EMP pathway
HMP
Etner duodoroff
TCA
ETC
Fermentation
Homolactic fermentation
Heterolactic fermentation
Mixed acid fermentation
Peptidoglycan synthesis
Physiology
Nutritional requirement
Carbon
Lithotropic
Heterotrophic
Nitrogen
Inorganic ions
Growth factors
Physical Requirements
Oxygen
Superoxide dismutase
Catalase
Redox potential
Temperature
Ph
Osmotic condition
Bacterial growth cycle
No of viable cell
Lag log
Stationary death time