Economic Systems 1
advertisement

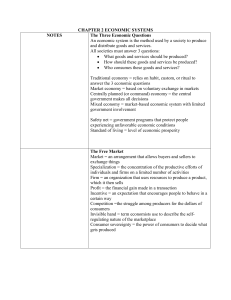
Economic Systems Comparing Economic Systems • • • • Warm Up- Economic Systems Free Market Voluntary exchange of goods between individuals and business in a market environment where goods are exchanged for money. Individuals and private businesses decide what to make and what to sell. Centrally planned economy There is no private property, the free market, consumer choice, and competition are not good determining factors for an economy. The central government decides what is produced and by whom and how it is consumed. Based on the definitions copy and answer the questions: 1. Which economic system do we have in the US and why do you think so? Activity-Economic Systems Gallery Exhibit • You are going to create a Gallery Exhibit that describes a type of economy. • You will be divided into six groups; each group will be assigned an economy. • In your group, you will be responsible for relaying the information to the rest of the class through your exhibit. • Each Exhibit will include: – – – – A definition of the Economic system. Three Advantages and Disadvantages of the system. Specific terms that describe the economy. A representative Icon for the economy. • Finally, on a separate sheet of paper, write three questions that the rest of the class should be able to answer after visiting your Exhibit Notes- Economic Systems Type of Economic System & Definition Advantages Disadvantages Description of Key terms Communist Manifesto - - -Karl Marx -Bourgeoisie -Proletariat -Goal of the Revolution Communist Manifesto vs. Wealth of Nations • Communist Manifesto – Written by Karl Marx – Argued that history is a struggle between the Bourgeoisie-owners, and the proletariat-workers. – He predicted that as capitalists (bourgeois) gained more wealth, the proletariat would become dissatisfied and rebel to form a classless society. Communist Manifesto vs. Wealth of Nations • Wealth of Nations – Written by Adam Smith – Argued that self interest of producers and consumers is the motivating force behind the economy. – Because of this self interest consumers get what they want at reasonable prices, and producers make what is dictated by the marketplace. This invisible hand guides the marketplace without any central planning by government. – The idea that government should not be involved in the economy is known as laissez faire. Keynesian Theory • Written by John Maynard Keynes • Argues that the economy is composed of three sectors: – – – – Individuals Business Government Proposes that by using fiscal policy, the use of government spending and revenue collection to influence the economy, that the government can, and should, help the economy. Working Economic Systems • Command/Centrally planned Economies- When a central authority is in command of the economy. • Socialism- a social and political system based on the principal that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout society. – In Socialist countries the government often owns many major industries. – Central planning is the key to economic equity. • Communism- characterized by a central planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the central government. – Usually communist governments come out of a revolution which places an authoritarian regime in power. Working Economic Systems • Market Economy- economic system in which decisions of production and consumption are made by individuals, it is a voluntary system of exchange in a marketplace, guided by self interest. – Market is based on the competition between producers for the dollars of consumers – Market economies are also referred to as free markets, or capitalism. Working Economic Systems • Mixed Economy- most modern economies are a combination of market and centrally planned. – The government purchases land, labor, and capital from households in the factor market, and – Purchases goods and services in the product market. United States has an economy based on this model. Circular Flow Diagram of a Mixed Economy Product market monetary flow physical flow Households expenditures Government expenditures physical flow monetary flow Factor market Firms Working Economic Systems • Traditional Economy- relies on habit, ritual or custom to decide questions of production and consumption of goods and services. – Revolves around the family – Work roles are divided by gender Agriculture and hunting are usually central in their lives. – Often these economies are slow to change and tend to be stagnant. – Bartering, or the direct exchange of goods or services for another, is often the means of trade in this kind of economy.