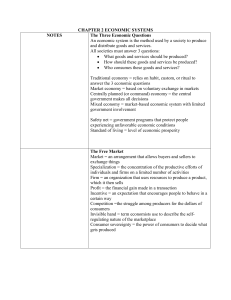
What are the three Economic Questions?
advertisement

The 7 Goals of an Economy 1. Economic efficiency- Making the most of your resources, an economy that can’t deliver goods isn’t efficient. 2. Economic freedom- Freedom from government intervention in the production and distribution of goods and services 3. Economic security and predictability- Assurance that goods and services will be available, payments will be made on time, and a safety net will protect individuals in times of economic disaster The 7 Goals of an Economy 4. Safety Net- government programs that protect people during bad economic times. Examples5. Economic equity- How much should you get paid for your services or lack of services. 6. Economic growth and innovation- Innovation leads to economic growth, and economic growth leads to a higher standard of living. 7. Value goals- Societies pursue additional goals, such as environmental protection, universal medical care, etc… Economic Goals of a Society • • Economic System- the method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services. Three Economics Systems 1. Capitalism 2. Command 3. Mixed Economy Market Economy (Capitalism) Definition- economy based on private ownership were individuals control the production, distribution and sale of goods. Key Person: Adam Smith- “Wealth of Nations” Why do markets exist? 1. Markets exist because none of us produces all the goods and services we require to satisfy our needs and wants. How is money and goods exchanged in a Free Market? 1. In a free market economy, households and business firms use markets to exchange money and products. Households own the factors of production and consume goods and services. The Forces in a Free Market Self-interest- In every transaction, the buyer and seller consider only their own personal gain. Selfinterest is the motivating force in the free market. Competition- Producers in a free market struggle for the dollars of consumers this is the regulating force of the free market. “Invisible hand”- The interaction of buyers and sellers, motivated by self-interest and regulated by competition, all happens without a central plan. The Principles of Free Enterprise 1. Profit Motive • The drive for the improvement of material well-being. 2. Open opportunity • The ability for anyone to compete in the marketplace. 3. Legal equality • Equal rights to all. 4. Private property rights • The right to control your possessions as you wish. 5. Free contract • The right to decide what agreements in which you want to take part. 6. Voluntary exchange • The right to decide what and when you want to buy and sell a product. 7. Competition • The rivalry among sellers to attract consumers. Market Economy- Strengths Economic Efficiency- as a self regulating system Capitalism is very efficient Economic Growth- Free market encourages innovation which leads to growth Economic Freedom- offers the most economic freedom Additional Goals- offers the largest variety of goods and services Market Economy- Weaknesses “Freedom” to starve, wealth is unevenly distributed NO equity or fairness NO motive to help the poor Greed for profit can result in dangerous goods being provided Poor Product safety Command Economy Definition- the government owns both land and capital. The government decides what to produce, how much to produce, and how much to charge. Key Person- Karl Marx: “Communist Manifesto” Two types of Command Economies1. Socialism- is a social and political philosophy based on the belief that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout a society. (Welfare Card) 2. Communism- is a political system characterized by a centrally planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the government. (Hammer and Sickle) Centrally Planned System Agriculture- the government created large state-owned farms and collectives for most of the country’s agricultural production. Industry- planners favored heavy-industry production (such as steel and machinery), over the production of consumer goods. Consumers- Consumer goods are scarce and usually of poor quality Centrally Planned Strength- Everyone knows what the plan is and is focused on completing that plan. Weaknesses- 1. Unable to pull this off in a modern country (countries are too big). 2. Inefficient and leads to shortages of needed items- but a surplus of non-essential items. (Underutilization) 3. Responds slowly to change 4. No worker incentives Mixed Economies Simple! An economy that combines two or more of the other economies listed. What type of economy does the United States have? • You guessed correct! A mixed economy • We have a mixture of market and command economies. • Most products are determined by supply/demand (market economy) but some products like milk have a set price determined by the government. Traditional Economy A traditional economy is where the price of goods and services stay the same over time. There are a few 3rd world countries still using this system. It usually involves bartering. Bartering: Trading goods and services for other goods and services. In a traditional economy, 1 goat may equal 10 bushels of wheat. 10 years from now what will 1 goat equal? Traditional Economies and the Inuit What are the three Economic Questions? The Three Basic Economic Questions 1. What goods and services should be produced? 2. How should these goods and services be produced? 3. Who consumes these goods and services? Difference between goods and services A good is a tangible object. Something you can see, touch, smell, taste, consume, or use. An iPad is an example of a good. A service is an intangible object. You can’t touch, taste, or feel it. Services are when you hire someone to do something for you. What goods and services should be produced? Basic Needs- food, clothing and shelter Problems in Modern Societies- How many resources do we devote to national defense, education, public health, welfare, consumer goods? - What consumer goods should we produce? How should these goods and services be produced? Although there are countless ways to create all the things we want and need, all require land, labor and capital The factors of production can be combined in different ways Should we produce electricity with oil, solar power, nuclear, water or coal? Should teachers have 20 or 50 students in a class? Who consumes these goods and services? How do we distribute abundance? • Who gets to eat a balanced diet and who doesn’t? • Who get to buy a luxury car and who can’t afford one? • Who lives in a mansion and who lives in the projects? • Factor payments- the income people receive for supplying factors of production- land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship. 1. Examples Who gets what, is the key difference between economic systems today. Every society answers these questions based on their social goals and values Four Factors of Production We can’t satisfy all of our wants and needs BECAUSE what is required to make the goods and services are SCARCE THE FOUR FACTORS OF PRODUCTION (resources) Land: Where your product will be made/created Labor: The people hired to create your product Capital: Physical, Financial, Human (see next slide) Entrepreneurs: The person/people who combine the other factors of production to create a business. What is the their main goal? 3 Types of Capital (All are needed) Human Capital: Your skills and abilities Physical Capital: All the products used to create the final product. • Cheese, sausage, dough, oven, etc. used to bake a pizza Financial Capital: Money needed to begin a business Become an inventor In your notebook, make a short list (at least 5) of goods or services you wish were possible or capable of being created. Examples (don’t use these for your own): • Clicker Remote that freezes time • Time machine • Don’t use money as the product you want to create (Example: Money Tree) Group of Inventors Create a small group of people in the class you can work with in and out of class. You will need at least 3 people in your group; no more than 5 people please. Group Project: Creating a New Product Share the ideas each person in your group came up with. Pick the best idea or combine a few ideas into a better idea. *Video Project*