Power Point - The world around us
advertisement

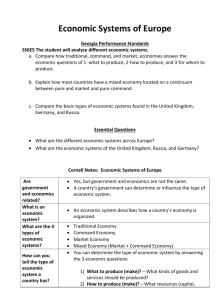
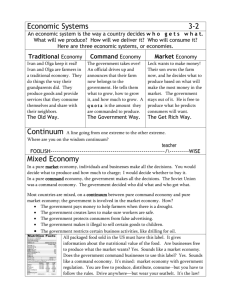
Economy Week of 10/5/2015 Journal Prompt • Examine your clothes and make a like of “Made In______” (country it was made in). • Answer the following questions: – How do you benefit from being able to buy clothes made in other countries? – Would you be in favor of a policy that will raise the price of tennis shoes but reduce the amount available? Why or why not. Standard • SS6E5 The student will describe different economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) and how they answer the basic economic questions (What to produce? For whom to produce?). Learning Targets • I can explain traditional, command, and market economies. • I can explain how traditional, command, and market economies decide what do produce, how to produce it, and for whom to produce. Create a statement… • Below are the terms will will cover in this unit. Define each term . Make and educated guess. • Economy • Command market • Mixed market • Trade • produce Economic Systems Because of the problem of scarcity (a limited supply of something) every country needs a system to determine how to use its resources. Countries develop economic systems to determine how to use the limited resources to answer the three economic questions. Three Questions We classify economic systems according to how they answer these 3 questions. What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce? Tariffs • Taxes placed on imported goods • Make imported products cost more • Increases the demand for a lower-priced item produced domestically • Example: America may charge a tariff on imported cheese to make it more expensive. This would make Americans buy the cheaper, American-made cheese. In the end, by enforcing a tariff, America helps support its farmers and makes more money Quotas • Put a legal limit on how much of a product can be imported • Can cause shortages • Causes prices to rise • Example: America may put a quota on how many BMW automobiles can be imported form Germany. This would make the price of BMW cars rise. It would also encourage Americans to buy cheaper, American-made cars. America benefits by selling more locally made cars and Germany benefits by selling more expensive BMWs. Embargoes • When trade is not allowed between two countries • No goods can be sold or bought between two countries • Like putting the countries in “Time Out” • Example: America as a trade embargo with Cuba. America cannot buy or sell anything from Cuba and Cuba cannot buy or sell anything from America. It is illegal to buy Cuban cigars in America, for example, because they are an import from Cuba Traditional Economy “That’s The Way We’ve Always Done It ” Traditional Economy • Who decides what to produce? – People follow their customs and make what their ancestors made. • Who decides how to produce goods & services? – People grow & make things the same way that their ancestors did. • Who are the goods & services • produced for? – People in the village who need them. Command Economy “We Do What We’re Told” Command Economy • Who decides what to produce? – Government makes all economic decisions • Who decides how to produce goods and services? – Gov’t decides how to make goods/services • Who are the goods and services produced for? – Whomever the government decides to give them to Market Economy “Make As Much As We Want and Do It Any Way We Want ” Market Economy • Who decides what to produce? – Businesses base decisions, like price, on supply and demand and free enterprise • Who decides how to produce goods and services? – Businesses decide how to produce goods • Who are the goods and services produced for? – consumers Mixed Economy No system in the world is 100% command, market, or traditional. It is a mixture of two systems. Mixed economy - economic system that incorporates elements of different systems (usually command and market) UK, Germany, and Russia are mixed: Market - malls, restaurants, entrepreneurship Command - minimum wage, labor laws Most countries have this system Economic Continuum • A group of financial experts set up a rating system to help us understand how much command and market each country has in it. • This Index of Economic Freedom gives each country a number that can be plotted on a economic continuum. Economic Systems Pure Command Pure Market United Kingdom 79% Germany Russia 71% 51% Pure Command Pure Market Canada 81% Cuba 28% Pure Command Brazil 57% Pure Market Australia 83% Pure Command Pure Market Economic Terms of Importance IRA • Choose from the following ways to explain 10 economic terms: • A) pictoword- draw a picture and include the definition of the word • B) acrostic poem - write an acrostic poem about the term (include a definition in the poem) • C) charades- create a symbol/gesture (without words/number) which explains the meaning of the term Summary Question What are the three types of economic systems? Traditional Command Market Summary Question Most countries are _____________ economies, because ___________________________. Most countries are mixed economies, because they have characteristics of 2 or more economic systems. They most often fall between command and market.