Types of Economic Systems Powerpoint Presentation
advertisement
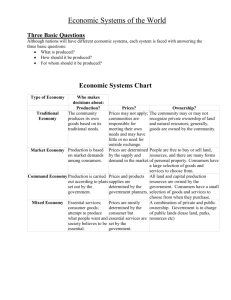
Unit 7: Foundations of Economics: Types of Economic Systems Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Introduction to Types of Economic Systems Notes: • The way a nation determines how to use its resources to satisfy its people’s needs and wants is called an economic system. • Economists have identified 4 types of economic systems. 1. 2. 3. 4. Traditional System Command System Market System Mixed System Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Traditional System Notes: • In a traditional economy, the 3 economic questions are answered according to tradition. • Economic decisions are based on customs and beliefs that have been handed down by generation. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Traditional System (cont’d.) Notes: • Parents teach children to perform the same tasks that they learned from their parents. • Examples: Inuit of North America, The Mbuti of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Aborigines of Australia. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Traditional System (cont’d.) Notes: • Advantages: (1) You know what is expected of you. (2) Family and community ties are usually very strong. • Disadvantages: (1) Change is discouraged, making production inefficient. (2) Choice among consumer goods is rare. (3) Accumulating wealth is not likely. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Command System Notes: • In a command economy government leaders control the factors of production and make all decisions about their use. • Through regulations about education the government guides people into certain jobs, which dictates what individuals earn. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Command System (cont’d.) Notes: • Examples: North Korea and parts of the People’s Republic of China. • Advantages: (1) Little uncertainty of employment. • Disadvantages: (1) Lack of incentives to work hard. (2) Lack of consumer choices. (3) Government sets workers salaries. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Market Economy Notes: • In a market economy, also called capitalism, individuals own the factors of production and make economic decisions through free interaction (free market) while looking out for their own and their families best interests. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Market Economy (cont’d.) Notes: • Prices in a market coordinate the interaction between buyers and sellers. • The freedom of prices to rise and fall results in a neutral, self-organizing, incentive-driven system. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Market Economy (cont’d.) Notes: • Economists use a model called a circular flow of income and output to illustrate how a market system works. • The factors of production flow from individuals to businesses, who use those factors to produce goods/services that flow back to individuals. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Market Economy (cont’d.) Notes: • Advantages: (1) People have freedom to choose a career, spend income, own property and take risks to earn profits. (2) Competition provides consumers with a wide variety of goods and services to choose from, as well as an efficient way of determining costs. • Disadvantages: (1) Because the pure market system is so driven by the individual looking out for their own interests, many fear that those too old, young, or sick to work will not survive unless churches, families or organizations step in to provide goods and services for them. Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Mixed Economy Notes: • A mixed economy combines basic elements of a market economy and a command economy. Most countries have a mixed economy where private ownership of property and individual decision making are combined with government intervention and regulations Types of Economic Systems Main Idea: Mixed Economy Notes: • Examples: United States • Advantages: (1) Wide range of choice on the part of the individual. (2) Regulations in place to protect environment, provide safety guidelines for workers, and laws to protect consumers. • Disadvantages: (1) Potential for profits might not be as great as in a pure market system.